Abstract
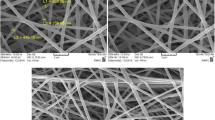
Tissue engineering provides new approaches to improve skin lesions. However, cell differentiation onto the engineered substrate with the skin-like pattern is the main challenge. Here we have tried to fabricate such the substrate via studying the change in polymers ratios and molecular weight, and grafting scaffold with silk fibroin (SF) biomaterial. To this end, chitosan and PEG were mixed at the volume ratios of 25:75, 50:50, and 65:35, and samples were lyophilized by the freeze-drying method. Based on the result, the ratio of 65:35 indicated better physicomechanical properties than two other scaffolds. Afterward, Chi/PEG scaffolds were prepared via mixing chitosan/PEG with (65:35) and PEG molecular weights of 2000, 4000, 6000, 10000 Da. It was found that the increase of PEG molecular weight (>4000) was led to the reduction in tensile strength and elongation of the scaffold network. Hence, PEG4000 was selected as the optimum molecular weight to design SF-grafted Chi/PEG scaffold. Therefore, Chi/PEG4000-SF scaffold was designed to evaluate the volume ratio of SF (1 %, 3 %, 5 %) and compare data with the decellularized dermis. The results showed Chi/PEG4000-SF(3%) scaffold not only was led to the same elongation as Chi/PEG-SF(5%) scaffold but also created the dermis-like modulus. Moreover, Chi/PEG-SF provided higher expression level of keratinocytes (bio-mimetic pattern) than decellularized dermis due to better physicomechanical properties. Hence, it seems that engineered scaffolds can be a more suitable option than native tissue (due to removal of limitations such as donor sites and immunogenicity, and their mechanical properties). This study can provide novel insight into the better design of skin-engineered scaffolds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Zarrintaj, S. Manouchehri, Z. Ahmadi, M. R. Saeb, A. M. Urbanska, D. L. Kaplan, and M. Mozafari, Carbohydr. Polym., 187, 66 (2018).
M. Horst, D. Eberli, R. Gobet, and S. Salemi, Front. Pediatr., 7, 91 (2019).
A. Izadyari Aghmiuni, S. Heidari Keshel, F. Sefat, and A. AkbarzadehKhiyavi, Mater. Sci. Eng. C., 120, 111752 (2021).
A. I. Aghmiuni, M. S. Baei, S. H. Keshel, and A. A. Khiyavi, Fiber. Polym., 21, 33 (2020).
B. S. Kim, Y. W. Kwon, J. S. Kong, G. T. Park, G. Gao, W. Han, M. B. Kim, H. Lee, J. H. Kim, and D. W. Cho, Biomaterials, 168, 38 (2018).
V. Andreu, G. Mendoza, M. Arruebo, and S. Irusta, Materials, 8, 5154 (2015).
Y. Xu, D. Xia, J. Han, S. Yuan, H. Lin, and C. Zhao, Carbohydr. Polym., 177, 210 (2017).
F. Khan, M. Tanaka, and S. R. Ahmad, J. Mater. Chem. B., 3, 8224 (2015).
F. Khan and M. Tanaka, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19, 17 (2017).
Ö. S. Somuncu, C. Karahan, S. Somuncu, and F. Şahin in “Stem Cells in Clinical Practice and Tissue Engineering” (R. Sharma Ed.), pp.315–333, IntechOpen, Rijeka, https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69905, 2018.
T. Du, Z. Chen, H. Li, X. Tang, Z. Li, J. Guan, C. Liu, Z. Du, and J. Wu, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 82, 580 (2016).
X. Liu, N. Dan, W. Dan, and J. Gong, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 82, 989 (2016).
J. M. Chalovich and E. Eisenberg, Sci. China Chem., 57, 490 (2014).
S.-H. Chen, C.-T. Tsao, C.-H. Chang, Y.-T. Lai, M.-F. Wu, C.-N. Chuang, H.-C. Chou, C.-K. Wang, and K.-H. Hsieh, Mater. Sci. Eng. C., 33, 2584 (2013).
B. Kundu, R. Rajkhowa, S. C. Kundu, and X. Wang, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 65, 457 (2013).
T. W. Chung and Y. L. Chang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 21, 1343 (2010).
A. Izadyari Aghmiuni, S. Heidari Keshel, F. Sefat, and A. Akbarzadeh Khiyavi, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 142, 668 (2020).
G. Guasch, “Biology and Engineering of Stem Cell Niches”, pp.127–143, Academic Press, 2017.
E. B. Lane and W. H. I. McLean, J. Pathol., 204, 355 (2004).
F. Wang, A. Zieman, and P. A. Coulombe, Methods Enzymol., 568, 303 (2016).
S. P. Huang, C. C. Hsu, S. C. Chang, C. H. Wang, S. C. Deng, N. T. Dai, T. M. Chen, J. Y. H. Chan, S. G. Chen, and S. M. Huang, Ann. Plast. Surg., 69, 656 (2012).
W. K. Ong and S. Sugii, Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 45, 1083 (2013).
L. Frese, P. E. Dijkman, and S. P. Hoerstrup, Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy, 43, 268 (2016).
A. Sterodimas, J. de Faria, B. Nicaretta, and I. Pitanguy, J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg., 63, 1886 (2010).
W. W. Thein-Han and R. D. K. Misra, Acta Biomater., 5, 1182 (2009).
J. Venkatesan, I. Bhatnagar, and S. K. Kim, Mar. Drugs., 12, 300 (2014).
D. Atila, D. Keskin, and A. Tezcaner, Carbohydr. Polym., 133, 251 (2015).
X. Zhao, X. Sun, L. Yildirimer, Q. Lang, Z. Y. (William) Lin, R. Zheng, Y. Zhang, W. Cui, N. Annabi, and A. Khademhosseini, Acta Biomater., 49, 66 (2017).
M. Rodríguez-Vázquez, B. Vega-Ruiz, R. Ramos-Zúñiga, D. A. Saldaña-Koppel, and L. F. Quiñones-Olvera, Biomed Res. Int., 2015, 821279 (2015).
X. Li, R. You, Z. Luo, G. Chen, and M. Li, J. Mater. Chem. B., 4, 2903 (2016).
A. K. Ekaputra, G. D. Prestwich, S. M. Cool, and D. W. Hutmacher, Biomacromolecules, 9, 2097 (2008).
A. Szentivanyi, T. Chakradeo, H. Zernetsch, and B. Glasmacher, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 63, 209 (2011).
H. I. Chang and Y. Wang, “Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering — Cells and Biomaterials”, pp.569–588, InTechOpen, 2011.
K. Vig, A. Chaudhari, S. Tripathi, S. Dixit, R. Sahu, S. Pillai, V. Dennis, and S. Singh, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18, 789 (2017).
Y. Liu, H. Luo, X. Wang, A. Takemura, Y. R. Fang, Y. Jin, and F. Suwa, Biomed Res. Int., 2013, 561410 (2013).
K. Boehnke, N. Mirancea, A. Pavesio, N. E. Fusenig, P. Boukamp, and H. J. Stark, Eur. J. Cell Biol., 86, 731 (2007).
Y. Wu, L. Chen, P. G. Scott, and E. E. Tredget, Stem Cells., 25, 2648 (2007).
H. Alam, L. Sehgal, S. T. Kundu, S. N. Dalal, and M. M. Vaidya, Mol. Biol. Cell., 22, 4068 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the help provided by the School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences to finalize this project with ethics code IR.SBMU.REC.1398.069.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghmiuni, A.I., Keshel, S.H., Rezaei-tavirani, M. et al. Effect of PEG Molecular Weight and Volume Ratio of Chitosan/PEG and Silk Fibroin on Physicomechanical Properties of Chitosan/PEG-SF Scaffold as a Bio-mimetic Substrate in Skin-tissue Engineering Applications. Fibers Polym 23, 3358–3368 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4579-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4579-0