Abstract
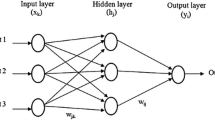
Stiffness is one of the most important utility properties of textile materials and plays a significant role in well-being due to its influence on physiological comfort [1]. On that point are a great deal of structural properties of textile materials also operating parameters (knitting+finishing) influencing stiffness and there are also statistically significant interactions between the principal factors determining the stiffness of textile materials. As part of our research, we proposed to facilitate the industry adjust the most relevant operating parameters before actual manufacturing to reach the desired stiffness and satisfy consumers. It warrants the application of artificial neural nets (ANNs) to predict the stiffness of finished knitted fabrics and the utilization of the Fuzzy Decision Tree in the selection procedure, to puzzle out the problem of insufficient data and boil down the complexity of predictive models. Moreover, a virtual leave one out approach dealing with overfitting phenomenon and allowing the selection of the optimal neural network architecture was applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Kan and C. Zhou, “High Performance Technical Textiles: Marine Textiles and Composites”, pp.385–406, 2019.
G. Grover, M. A. Sultan, and S. M. Spivak, J. Text. Inst., 84, 486 (1993).
R. H. Brand, Text. Res. J., 34, 791 (1964).
C. L. Hui, T. W. Lau, S. F. Ng, and K. C. C. Chan, Text. Res. J., 74, 375 (2004).
K. A. Brooks, J. Text. Inst., 82, 285 (1991).
P. L. Chen, R. L. Barker, G. W. Smith, and B. Scruggs, Text. Res. J., 64, 200 (1992).
Y. Li, J. H. Keighley, J. E. McIntyre, and I. F. G. Hampton, J. Text. Inst., 82, 277 (1991).
M. Matsudaira and M. Matsui, J. Text. Inst., 83, 133 (1992).
M. Matsudaira, J. Text. Inst., 83, 24 (1992).
Y. E. Macgahzy and R. M. Jr. Broughton, Text. Res. J., 62, 218 (1992).
R. S. Hallos, M. S. Bumip, and A. Weir, J. Text. Inst., 81, 15 (1990).
J. J. F. Knapton, Text. Res. J., 39, 889 (1968).
R. J. Hamilton and R. Postle, Text. Res. J., 44, 336 (1974).
J. A. Smirfitt, J. Text. Inst., 56, 298 (1965).
R. J. Hamilton and R. Postle, Text. Res. J., 44, 336 (1974).
W. S. Howorth and P. H. Oliver, J. Text. Inst., 49, 540 (1958).
T. W. Lau, P. C. L. Hui, F. S. F. Ng, and K. C. C. Chan, Comput. Ind., 57, 82 (2006).
G. V. Civille and C. A. Dus, J. Sens. Stud., 5, 19 (1990).
X. Zeng and L. Koehl, Int. J. Intell. Syst., 18, 355 (2003).
F. Fayala, H. Alibi, A. Jemni, and X. Zeng, Fiber. Polym., 15, 855 (2014).
H. Alibi, F. Fayala, N. Bhouri, A. Jemni, and X. Zeng, J. Tex. Inst., 104, 766 (2013).
A. Babay, M. Cheikhrouhou, B. Vermeulen, B. Rabenasolo, and J. M. Castelain, J. Text. Inst., 96, 185 (2005).
M. Tayefi, H. Esmaeili, M. S. Karimian, A. A. Zadeh, M. Ebrahimi, M. Safarian, M. Nematy, S. M. R. Parizadeh, G. A. Ferns, and M. Ghayour-Mobarhan, Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio., 139, 83 (2017).
W. Yang, X. Reziwanguli, J. Xu, P. Wang, J. Hu, and X. Liu, Proceedings 4th WARTIA, 173 (2018).
A. A. Gharehaghaji, M. Shanbeh, and M. Palhang, Text. Res. J., 77, 565 (2007).
Z. Khan, A. E. K. Lim, L. Wang, X. Wang, and R. Beltran, Text. Res. J., 79, 714 (2009).
J. A. Wehner, B. Miller, and L. Rebenfeld, Text. Res. J., 58, 581 (1988).
Y. Oussar, G. Monari, and G. Dreyfus, Neural Comput., 16, 419 (2004).
H. Alibi, F. Fayala, A. Jemni, and X. Zeng, Special Topics & Reviews in Porous Media, 3, 35 (2012).
C. Huang and C. Moraga, Int. J. Approx. Reason., 35, 137 (2004).
S. J. Raudys and A. K. Jain, IEEE T Pattern Anal., 13, 252 (1991).
J. L. Yuan and T. L. Fine, IEEE T Neural Networ, 9, 266 (1998).
P. Vroman, L. Koehl, X. Zeng, and T. Chen, Int. J. Comput. Int. Sys., 1, 329 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baghdadi, R., Alibi, H., Fayala, F. et al. Investigation on Stiffness of Finished Stretch Plain Knitted Fabrics Using Fuzzy Decision Trees and Artificial Neural Networks. Fibers Polym 22, 550–558 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-9314-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-9314-8