Abstract
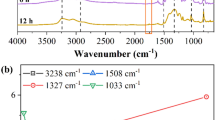
To study the variation of surface characteristics of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite insulation materials during the development of tracking, this paper established an experimental platform for tracking under the inclined plate method and prepared samples of glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin. In this paper, according to the experimental discharge phenomenon, discharge repetition rate phase diagram and corrosion degree of materials, the process of tracking was divided into four stages: initiation, stability, development and outbreak stages. Scanning electron microscope was used to observe the change of micromorphology of samples in different stages of tracking. The content of elements in different stages of tracking was determined by energy dispersive spectrometer. The surface characteristic functional groups in different stages of tracking were measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The results show that with the change of surface morphology and the formation of surface products during tracking, the content of C element in the spherical region of the material decreased first and then increased, and the content of O and Si increased first and then decreased. The epoxy group of the material was gradually decomposed. Carbonyl group was generated on the surface of the material, and then decomposed during the outbreak stages. In addition, the deterioration mechanism of thermal aging and tracking was quite different. Thermal aging provided convenient routes for the electron injection into the material during tracking, thus reducing the tracking and erosion resistance of the material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. X. Du, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 8, 897 (2001).
A. D. Lorenzi, L. Grando, A. Pesce, P. Bettini, and R. Specogna, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 16, 77 (2009).
E. Mboungou, C. Mavon, J. M. Friedt, C. Bergeon, and M. Fromm, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 15, 311 (2008).
S. T. Li, G. L. Yin, G. Chen, J. Y. Li, S. N. Ba, L. S. Zhong, and Y. X. Zhang, and Q. Q. Lei, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 17, 1523 (2010).
S. Kumagai and N. Yoshimura, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 8, 203 (2001).
J. H. Mason, B. X. Du, and S. Kobayashi, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 11, 911 (2004).
B. X. Du, J. W. Zhang, L. Gu, and H. J. Liu, “Application of Nonlinear Methods in Tracking Failure Test of Epoxy/SiO2 Nanocomposite”, IEEE Int’l. Conf. Solid Dielectrics, pp.1–4, 2010.
B. X. Du, J. W. Zhang, L. Gu, M. J. Tu, Z. Q. Wang, and D. M. Du, “Application of Nonlinear Methods in Tracking Failure Test of Silicone Rubber Nanocomposite”, 2010 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectic Phenomena, West Lafayette, IN, pp.1–4, 2010.
Z. Wang, Y. Cheng, and K. Wu, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 18, 561 (2011).
R. Boudissa, S. Djafri, A. Haddad, R. Belaicha, and R. Bearsch, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 12, 429 (2005).
Z. Zhang, X. Jiang, C. Sun, J. Hu, and H. Huang, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 17, 1787 (2010).
F. Zhang, X. Wang, L. M. Wang, Z. C. Guan, H. Wen, R. H. Li, and Y. Ma, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 15, 783 (2008).
W. Sima, Q. Yang, G. Ma, C. Jiang, L. Wu, and H. Cheng, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 17, 572 (2010).
X. Jiang, S. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Hu, and Q. Hu, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 17, 71 (2010).
J. H. Dymond, N. Stranges, K. Younsi, and J. E. Hayward, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 38, 577 (2002).
B. X. Du, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 12, 1162 (2005).
B. X. Du, X. H. Zhu, L. Gu, and H. J. Liu, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 18, 176 (2011).
M. Suchitra, N. M. Renukappa, C. Ranganathaiah, and J. S. Rajan, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 25, 2129 (2018).
J. Montesinos, R. S. Gorur, L. Zimmer, and N. F. Hubele, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 7, 408 (2000).
B. X. Du, Y. Liu, and H. J. Liu, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 15, 1379 (2008).
T. Okamoto, “Novel Partial Discharge Measurement Computer-aided Measurement Systems”, IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 21, 1015 (1986).
A. Ersoy, Y. Özcelep, and A. Kuntman, Turkish J. Elect. Eng. Comput. Sci., 16, 257 (2008).
A. Syakur, Hermawan, and H. Sutanto, “Study on Tracking Time of Epoxy Resin Insulating Material under Artificial Accelerated Aging”, 2017 International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Power Systems (ICHVEPS), Sanur, pp.503–507, 2017.
H. Khan, M. Amin, A. Ahmad, and M. Yasin, “Erosion/tracking Resistance Investigation of Micro/nano-SiO2 Filled RTV-SiR Composites for Outdoor High Voltage Insulations”, 2017 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, pp.15–19, 2017.
B. X. Du, High Voltage Eng., 31, 10 (2005).
Y. Q. Wang, H. Liu, W. Li, and R. J. Ding, Macromol. Res., 27, 310 (2019).
X. Liu, H. D. Lin, Y. M. Liang, C. Zhang, Q. Xie, and T. Shao, Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 30, 158 (2015).
C. Pan, W. Shen, K. Wu, Z. P. Lü, Y. Chang, and Y. H. Cheng, Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 26, 115 (2011).
J. V. Vas, B. Venkatesulu, and M. Joy Thomas, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 19, 91 (2012).
Y. X. Chen, X. D. Zhou, X. C. Yin, Q. F. Lin, and M. Q. Zhou, Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater., 63, 221 (2014).
V. Rajini, K. Kanchana, V. Gowrishree, and K. Udayakumar, “Comparison of Surface Tracking in Polymeric Insulating Materials”, International Conference on Power System Technology, IEEE, 2004.
Y. Zheng, Insulating Matericals, 45, 59 (2012).
S. Kumagal and N. Yoshimura, IEEE T. Dielect. El. In., 7, 424 (2000).
Z. H. Li, Y. Yin, J. Zhu, and D. M. Tu, Proceedings of the CSEE, 19, 70 (1999).
Y. Liang, Z. Jin, Y. P. Liu, and Y. X. Chen, Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 30, 189 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Feng, C., Luo, Y. et al. Study on Surface Characteristics of E-glass Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites in Different Stages of Tracking. Fibers Polym 21, 2556–2568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-1265-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-1265-y