Abstract
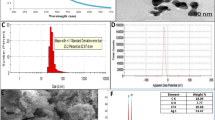
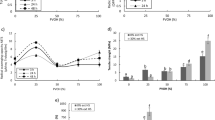
The essential oil liposomes, a kind of ecological friendly natural antibacterial agents, have good bactericidal effect. In the present study, tea tree oil liposomes (TTOLs) were prepared by the thin-membrane hydration method with sonication, and then were blended with chitosan (CS) to successfully fabricate novel TTOLs/CS composite sponges by freeze-dried method. Through the scanning electron microscope (SEM), fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and performance tests, it was found that the material had good water absorption, water retention and water vapor permeability due to the high porosity. Furthermore, the incorporation of TTOLs in the CS-based sponges significantly improved the microbicidel effect of the sponges against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Candida albicans (C. albicans). Killing log values of TTOLs/CS composite sponges against bacteria and fungi reached over 3. According to the microbial clearance test, propidium iodide (PI) fluorescence test and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation, the results indicated on one hand that TTOLs/CS composite sponges adsorbed and intercepted microbial cells through the internal pore and surface charge, and on the other hand that they could destroy bacterial intercellular substance, disperse cell colony and damage the integrity of cell membrane, finally leading to the death of microbial cells. In summary, TTOLs/CS composite sponges had great potential to be used as antimicrobial materials in the field of food, cosmetics, medicine, biomedical and biochemical engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ming, G. C. Xi, X. Ke, and H. J. Park, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 144, 51 (2010).
Y. C. Chung, H. L. Wang, Y. M. Chen, and S. L. Li, Bioresour. Technol., 88, 179 (2003).
P. Anaya, G. Cárdenas, V. Lavayen, A. García, and C. O'Dwyer, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 128, 3939 (2013).
S. Chen, Y. Hao, W. Cui, J. Chang, and Y. Zhou, J. Mater. Sci., 48, 6567 (2013).
S. Guang, Y. An, F. Ke, D. Zhao, Y. Shen, and H. Xu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 132, 42503 (2015).
T. Ikeda, K. Ikeda, K. Yamamoto, H. Ishizaki, Y. Yoshizawa, K. Yanagiguchi, S. Yamada, and Y. Hayashi, Biomed Res. Int., 2014, 786892 (2014).
P. Kanmani and J. W. Rhim, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 68, 258 (2014).
D. Wisser, F. M. Wisser, S. Raschke, N. Klein, M. Leistner, J. Grothe, E. Brunner, and S. Kaskel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 54, 12588 (2015).
Y. Omura, M. Shigemoto, T. Akiyama, H. Saimoto, Y. Shigemasa, I. Nakamura, and T. Tsuchido, Biocontrol Sci., 8, 25 (2003).
L. J. R. Foster and J. Butt, Biotechnol. Lett., 33, 417 (2011).
L. Y. Zheng and J. F. Zhu, Carbohydr. Polym., 54, 527 (2003).
C. Qin, H. Li, X. Qi, L. Yi, J. Zhu, and Y. Du, Carbohydr. Polym., 63, 367 (2006).
Y. J. Jeon, P. J. Park, and S. K. Kim, Carbohydr. Polym., 44, 71 (2001).
C. Juliano, C. Demurtas, and L. Piu, Flavour Frag. J., 23, 227 (2008).
A. Regiel, S. Irusta, A. Kyziol, M. Arruebo, and J. Santamaria, Nanotechnology, 24, 015101 (2013).
L. Hernandez-Ochoa, A. Gonzales-Gonzales, N. Gutierrez-Mendez, L. N. Munoz-Castellanos, and A. Quintero-Ramos, Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim., 10, 455 (2011).
S. Takenaka, E. Karg, C. Roth, H. Schulz, A. Ziesenis, U. Heinzmann, P. Schramel, and J. Heyder, Environ. Health Perspect., 109, 547 (2001).
A. A. Hazani, M. M. Ibrahim, A. I. Shehata, G. A. El-Gaaly, M. Daoud, D. Fouad, H. Rizwana, and N. M. S. Moubayed, Arch. Biol. Sci., 65, 1447 (2013).
Y. J. Lee, J. Kim, J. Oh, S. Bae, S. Lee, I. S. Hong, and S. H. Kim, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 31, 155 (2012).
K. A. Hammer, C. F. Carson, and T. V. Riley, J. Appl. Microbiol., 86, 985 (1999).
C. F. Carson and T. V. Hammer Kariley, Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 19, 50 (2006).
S. Cox, J. Gustafson, C. Mann, J. Markham, Y. Liew, R. Hartland, H. Bell, J. Warmington, and S. Wyllie, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 26, 355 (1998).
J. E. Gustafson, Y. C. Liew, S. Chew, J. Markham, H. C. Bell, S. G. Wyllie, and J. R. Warmington, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 26, 194 (1998).
S. D. Cox, C. M. Mann, J. L. Markham, H. C. Bell, J. E. Gustafson, J. R. Warmington, and S. G. Wyllie, J. Appl. Microbiol., 88, 170 (2000).
M. Chen, Y. Hu, J. Zhou, Y. Xie, H. Wu, T. Yuan, and Z. Yang, Rsc Adv., 6, 13032 (2016).
Y. Ge and M. Ge, Fiber. Polym., 16, 308 (2015).
M. Y. Bai, T. C. Chou, J. C. Tsai, and W. C. Yu, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 102, 2324 (2014).
S. F. van Vuuren, L. C. du Toit, A. Parry, V. Pillay, and Y. E. Choonara, Nat. Prod. Commun., 5, 1401 (2010).
M. Sherry, C. Charcosset, H. Fessi, and H. Greigegerges, J. Liposome Res., 23, 268 (2013).
Y. Ge and M. Q. Ge, J. Liposome Res., 25, 222 (2015).
F. L. Mi, S. S. Shyu, Y. B. Wu, S. T. Lee, J. Y. Shyong, and R. N. Huang, Biomaterials, 22, 165 (2001).
L. H. Ma, W. T. Yu, and X. J. Ma, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 106, 394 (2007).
J. F. Fundo, A. C. Galvis-Sanchez, I. Delgadillo, C. L. M. Silva, and M. A. C. Quintas, Food Biophys., 10, 324 (2015).
N. Sowasod, K. Nakagawa, W. Tanthapanichakoon, and T. Charinpanitkul, Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater., 32, 790 (2012).
G. R. Lang and G. Buchbauer, Flavour Frag. J., 27, 13 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yan Ge and Jiapeng Tang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Tang, J. Fabrication, Characterization and Antimicrobial property of natural TTOLs/CS composite sponges. Fibers Polym 17, 862–872 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6232-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6232-2