Abstract
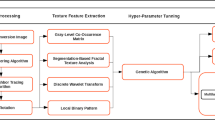
In today’s textile industry, the classification of woven fabrics is usually manual which requires considerable human efforts and a long time. With the rapid development of computer vision, the automatic and efficient methods for woven fabric classification are desperately needed. This paper proposes an automatic and real-time classification method to analyze three woven fabrics: plain, twill and satin weave. The methodology involves two approaches to extract texture features, that is, gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) and Gabor wavelet. Then, principal component analysis (PCA) is utilized to deal with the texture feature vectors to gain minimize redundancy and maximize principal component feature vectors. Finally, in the classification phase, probabilistic neural network (PNN) is applied to classify three basic woven fabrics. With strong realtime, fault-tolerance and non-linear classification capability, PNN can be a promising tool for classification of woven fabrics. The experimental results show that PNN classifier with faster training speed can classify woven fabrics accurately and efficiently. Besides, compared with GLCM method and Gabor wavelet method, the fusion of the two feature vectors obtains the best classification result (95 %).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. L. Hu, J. Text. Res., 25, 48 (2004).
C. Y. Shih and J. Y. Lee, Text. Res. J., 74, 107 (2004).
C. F. J. Kuo, C. Y. Shin, C. E. Ho, and K. C. Peng, Text. Res. J., 80, 2144 (2010).
X. Wang, N. D. Georganas, and E. M. Petriu, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 60, 44 (2011).
B. S. Jeon, J. H. Bae, and M. W. Suh, Text. Res. J., 73, 645 (2003).
C. F. J. Kuo and C. C. Tsai, Text. Res. J., 76, 375 (2006).
Y. B. Salem and S. Nasri, Signal, Image and Video Process, 4, 429 (2010).
M. Hanmandlu, D. Sujata, and D. K. Choudhury, Int. J. Comp. Sci. Appl., 2, 47 (2009).
J. F. Jing, J. Wang, P. F. Li, and Y. Li, Procedia Eng., 15, 5005 (2011).
R. M. Haralick, K. Shanmugam, and I. H. Dinstein, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyben., 3, 610 (1973).
G. M. Haley and B. S. Manjunath, Proc. IEEE. Int. Conf. Image Process, 1, 262 (1995).
J. Y. Yan, C. R. Wang, and Y. X. Wang, Netw. Comp. Security, 12, 46 (2010).
Z. Zhang, Y. P. Wang, and G. X. Xue, “Digital Image Processing and Machine Vision”, pp.388–404, Posts and Telecom Press, Bei Jing, 2012.
D. F. Specht, Neural Netw., 3, 109 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, J., Xu, M., Li, P. et al. Automatic classification of woven fabric structure based on texture feature and PNN. Fibers Polym 15, 1092–1098 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-1092-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-1092-0