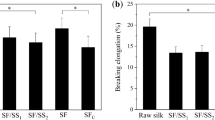
Abstract
Wet spun silk fibroin (SF) filaments have attracted considerable attention because of their potential in biotechnological applications including surgical sutures, tissue engineering and wound dressing. Although the molecular weight (MW) of polymers is one of key factors affecting the wet spinnability of dope along with the structural characteristics and properties of wet spun filament, no related study has been conducted. In this study, regenerated SFs with different MWs and concentrations were prepared by wet spinning. The effects of the SF concentration and MW on 1) wet spinnability and rheology of silk dope solution and 2) crystallinity index and post drawing performance of wet spun silk filament were examined. Their relationships were also investigated. The rheological measurements showed that an 80 mPa·s viscosity is needed to obtain a continuous wet spun SF filament. As the MW of SF increased, the peak position of the maximum draw ratio shifted to a lower SF concentration with a concomitant increase in the maximum draw ratio value at the peak. Interestingly, the crystallinity index obtained from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) revealed a similar trend to the maximum draw ratio suggesting that the post drawing ability is strongly affected by the quantity of short-ordered crystalline regions in wet spun SF filaments. On the other hand, X-ray diffraction did not detect any crystallinity change in the SF filament produced from the formic acid solvent system. It was concluded that MW strongly affected the dope solution viscosity and the crystallinity index from FTIR and these determined the fiber formation of dope and post drawing performance of fiber.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Sakabe, H. Ito, T. Miyamoto, Y. Noishiki, and W. S. Ha, Sen-I Gakkaishi, 45, 487 (1989).
N. Minoura, S. Aiba, Y. Gotoh, M. Tsukada, and Y. Imai, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 29, 1215 (1995).
J. W. Kim, C. S. Ki, Y. H. Park, H. J. Kim, and I. C. Um, Macromol. Res., 18, 442 (2010).
M. Santin, A. Motta, G. Freddi, and M. Cannas, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 46, 382 (1999).
L. Meinel, S. Hofmann, V. Karageorgiou, C. Kirker-Head, J. McCool, G. Gronowicz, L. Zichner, R. Langer, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 26, 147 (2005).
B. M. Min, G. Lee, S. H. Kim, Y. S. Nam, T. S. Lee, and W. H. Park, Biomaterials, 25, 1289 (2004).
U. Kim, J. Park, H. J. Kim, M. Wada, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 25, 2775 (2005).
C. S. Ki, S. Y. Park, H. J. Kim, H. M. Jung, K. M. Woo, J. W. Lee, and Y. H. Park, Biotechnol. Lett., 30, 405 (2008).
S. Y. Park, C. S. Ki, Y. H. Park, H. M. Jung, K. M. Woo, and H. J. Kim, Tissue Eng. Part A, 16, 1271 (2010).
J. Kim, C. Kim, C. Park, J. Seo, H. Kweon, S. Kang, and K. G. Lee, Wound Repair Regen., 18, 132 (2010).
A. Schneider, X. Y. Wang, D. L. Kaplan, J. A. Garlick, and C. J. Egles, Acta Biomater., 5, 2570 (2009).
I. C. Um, C. S. Ki, H. Kweon, K. G. Lee, D. W. Ihm, and Y. H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 34, 107 (2004).
K. Ohgo, C. H. Zhao, M. Kobayashi, and T. Asakura, Polymer, 44, 841 (2003).
S. H. Kim, Y. S. Nam, T. S. Lee, and W. H. Park, Polym. J., 35, 185 (2003).
B. D. Lawrence, J. K. Marchant, M. A. Pindrus, F. G. Omenetto, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 30, 1299 (2009).
A. B. Mathur, A. E. Tonelli, T. Rathke, and S. Hudson, Biopolymers, 42, 61 (1997).
I. C. Um and Y. H. Park, Fiber. Polym., 8, 579 (2007).
O. Etienne, A. Schneider, J. A. Kluge, C. Bellemin-Laponnaz, C. Polidori, G. G. Leisk, D. L. Kaplan, J. A. Garlick, and C. J. Egles, J. Periodont., 80, 1852 (2009).
H. J. Cho and I. C. Um, Int. J. Indust. Entomol., 23, 183 (2011).
I. C. Um, H. Kweon, K. G. Lee, D. W. Ihm, J. Lee, and Y. H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 34, 89 (2004).
S. W. Ha, A. E. Tonelli, and S. Hudson, Biomacromolecules, 6, 1722 (2005).
J. P. Yan, G. Q. Zhou, D. P. Knight, Z. Z. Shao, and X. Chen, Biomacromolecules, 11, 1 (2010).
O. Liivak, A. Blye, N. Shah, and L. W. Jelinski, Macromolecules, 31, 2947 (1998).
H. J. Cho, Y. J. Yoo, J. W. Kim, Y. H. Park, D. G. Bae, and I. C. Um, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 97, 1060 (2012).
J. S. Ko, K. H. Lee, D. G. Bae, and I. C. Um, Fiber. Polym., 11, 14 (2010).
G. Q. Zhou, Z. Z. Shao, D. P. Knight, J. P. Yan, and X. Chen, Adv. Mater., 21, 366 (2009).
C. S. Ki, K. H. Lee, D. H. Baek, M. Hattori, I. C. Um, D. W. Ihm, and Y. H. Park, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 105, 1605 (2007).
D. M. Phillips, L. F. Drummy, R. R. Naik, H. C. De Long, D. M. Fox, P. C. Trulove, and R. A. Mantz, J. Mater. Chem., 15, 4206 (2005).
H. J. Cho, C. S. Ki, H. Oh, K. H. Lee, and I. C. Um, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 51, 336 (2012).
N. W. Bhat and G. S. Nadiger, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 25, 921 (1980).
H. J. Cho and I. C. Um, Int. J. Indust. Entomol., 20, 99 (2010).
J. S. Ko and I. C. Um, Int. J. Indust. Entomol., 19, 181 (2009).
I. C. Um, H. Kweon, Y. H. Park, and S. Hudson, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 29, 91 (2001).
H. J. Kim, D. E. Chung, and I. C. Um, Int. J. Indust. Entomol., 26, 54 (2013).
I. C. Um, H. Y. Kweon, K. G. Lee, and Y. H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 33, 203 (2003).
J. L. Koenig in “Applied Infrared Spectroscopy” (D. N. Kendall Eds.), p.245, Reinhold Pub. Co., New York, 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, D.E., Um, I.C. Effect of molecular weight and concentration on crystallinity and post drawing of wet spun silk fibroin fiber. Fibers Polym 15, 153–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0153-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0153-8