Abstract
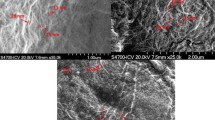
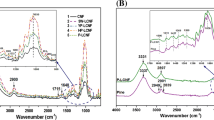
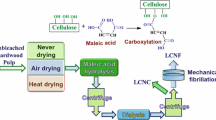
Nano-size fibers from lignocellulosic biomass were successfully obtained by akali-treatment and electrospinning using ionic liquid. The effects of the lignin and the hemicelluloses content on the spinnability, the web morphology, the micro-structure and the thermal stability of the electrospun fibers were investigated. The lower lignin content resulted in better spinnability, fine and uniform fiber diameter, higher crystallinity and decrease of thermal stability. This study reveals the possibility of the utilization for the lignocellulosic biomass other than pulp or cotton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Schiffman and C. L. Schauer, Polym. Rev., 48, 317 (2008).
H. Fong, I. Chun, and D. H. Reneker, Polymer, 40, 4585 (1999).
D. Li and Y. Xia, Adv. Mater., 16, 1151 (2004).
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, and S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol., 63, 2223 (2003).
M. Li, M. J. Mondrinos, M. R. Gandhi, F. K. Ko, A. S. Weiss, and P. I. Lelkes, Biomaterials, 26, 5999 (2005).
Y. Zhang, H. Ouyang, C. T. Lim, S. Ramakrishna, and Z. M. Huang, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B, 72B, 156 (2005).
T. J. Sill and H. A. von Recum, Biomaterials, 29, 1989 (2008).
T. T. Nge and J. J. Sugiyama, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 81A, 124 (2007).
Y. Nishio, Adv. Polym. Sci., 205, 91 (2006).
N. Gathergood, M. T. Garcia, and P. J. Scammells, Green Chem., 6, 166 (2004).
B. Jastorff, R. Störmann, J. Ranke, K. Mölter, F. Stock, B. Oberheitmann, W. Hoffmann, J. Hoffmann, M. Nüchter, and B. Ondruschka, J. Filser, Green Chem., 5, 136 (2003).
P. Wasserscheid, R. van Hal, and A. Bösmann, Green Chem., 4, 400 (2002).
R. C. Remsing, R. P. Swatloski, R. D. Rogers, and G. Moyna, Chem. Commun., 12, 1271 (2006).
M. B. Turner, S. K. Spear, J. D. Holbrey, and R. D. Rogers, Biomacromolecules, 5, 1379 (2004).
M. B. Turner, S. K. Spear, J. G. Huddleston, J. D. Holbrey, and R. D. Rogers, Green Chem., 5, 443 (2004).
G. Viswanathan, S. Murugesan, V. Pushparaj, O. Nalamasu, P. M. Ajayan, and R. J. Linhardt, Biomacromolecules, 7, 415 (2006).
S. Xu, J. Zhang, A. He, J. Li, H. Zhang, and C. C. Han, Polymer, 49, 2911 (2008).
M.-L. Beatriz, R.-F. Francisco, T.-C. Ratricia, R.-W. Benjamin, L.-C. Jaime, and S.-M. Dalia, J. Agric. Food. Chem., 59, 870 (2011).
C.-W. Kim, D.-S. Kim, S.-Y. Kang, M. Marquez, and Y. L. Joo, Polymer, 47, 5097 (2006).
S.-L. Quan, S.-G. Kang, and I.-J. Chin, Cellulose, 17, 223 (2010).
G. Buschle Diller, C. Fanter, and F. Loth, Text. Res. J., 69, 244 (1999).
H. Wang, R. Postle, R. Kessler, and W. Kessler, Text. Res. J., 73, 664 (2003).
S. H. Lee, T. V. Doherty, R. J. Linhardt, and J. S. Dordick, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 102, 1368 (2009).
M. L. Nelson and R. T. O’Connor,, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 8, 1325 (1964b).
S. Y. Oh, D. I. Yoo, Y. Shin, and G. Seo, Carbohyd. Res., 340, 417 (2005).
Y. Ahn, S. H. Lee, H. J. Kim, Y. -H. Yang, J. H. Hong, Y.-H. Kim, and H. Kim, Carbohyd. Polym., 88, 395 (2012).
T. J. Simmons, S. H. Lee, J. Miao, M. Miyauchi, T.-J. Park, S. S. Bale, R. Pangule, J. Bult, J. G. Martin, J. S. Dordick, and R. J. Linhardt, Wood Sci. Technol., 45, 719 (2011).
M. Wada and R. Hori, Cellulose, 13, 281 (2006).
E. Abraham, B. Deepa, L. A. Pothan, M. Jacob, S. Thomas, U. Cvelbar, and R. Anandjiwala, Carbohyd. Polym., 86, 1468 (2011).
B. C. Mitra, R. K. Basak, and M. J. Sarkar, Appl. Polym. Sci., 67, 1093 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y., Ahn, Y., Lee, S.H. et al. Lignocellulosic nanofiber prepared by alkali treatment and electrospinning using ionic liquid. Fibers Polym 14, 530–536 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-0530-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-0530-8