Abstract
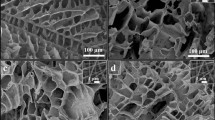
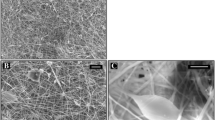
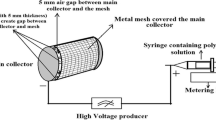
In this study, a three-dimensional (3D) poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microfibrous scaffold with high porosity (ca. 90 % porosity) was developed for evaluating its performance in tissue engineering application. A dope solution of PLGA/polyethylene oxide (PEO) blend was electrospun into a methanol coagulation bath for fabricating highly porous 3D PLGA scaffold and a salt leaching method was used for making interconnected pores of 100–200 µm size inside the scaffold. The morphological structure, pore size and porosity of the microfibrous scaffold were determined, and compared with twodimensional (2D) mat-type and 3D sponge-type of PLGA scaffold. Also, swelling ratio, water uptake and compressive strength were compared in order to elucidate the structure-property relationships of different types of the scaffolds, especially in a wet condition. As a result of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation, normal human dermal fibroblasts (nHDF) were migrated, attached, and proliferated well inside the 3D scaffold. MTT assay confirmed that the highly porous 3D PLGA microfibrous scaffold had superior cell adhesion and proliferation abilities due to fibrous structure of large specific surface area, and interconnected pore structure. Therefore, this high performance 3D PLGA scaffold can have a high potentiality for application in tissue engineering in comparison with conventional PLGA scaffolds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Hariraksapitak, O. Suwantong, P. Pavasant, and P. Supaphol, Polymer, 49, 2678 (2008).
J. M. Kanczler, J. Barry, P. Ginty, S. M. Howdle, K. M. Shakesheff, and R. O. Oreffo, Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co., 352, 135 (2007).
Y. C. Wang, M. C. Lin, D. M. Wang, and H. J. Hsieh, Biomaterials, 24, 1047 (2003).
J. Venugopal, S. Low, A. T. Choon, and S. Ramakrishna, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 84, 34 (2008).
C. S. Ki, S. Y. Park, H. J. Kim, H. M. Jung, K. M. Woo, J. W. Lee, and Y. H. Park, Biotechnol. Lett., 30, 405 (2008).
V. J. Moncy, T. Vinoy, T. J. Kalonda, R. D. Derrick, and N. Elijah, Acta Biomater., 5, 305 (2009).
R. W. Matthew, B. Richard, and K. Cay, Biomaterials, 27, 3608 (2006).
S. D. Wang, Y. Z. Zhang, G. B. Yin, H. W. Wang, and Z. H. Dong, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 113, 2675 (2009).
H. H. Sepideh, S. L. Katja, P. D. Andrew, R. Fady, S. Hunter, M. W. Benjamin, S. Richard, E. B. Ramin, and R. M. William, Biomaterials, 29, 2907 (2008).
J. Yuan, G. Kaustabh, Z. S. Xiao, L. Bingquan, C. S. Jonathan, D. P. Glenn, A. F. C. Richard, and H. R. Miriam, Biomaterials, 27, 3782 (2006).
C. S. Ki, J. W. Kim, J. H. Hyun, K. H. Lee, M. Hattori, D. K. Rah, and Y. H. Park, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 106, 3922 (2007).
C. S. Ki, D. H. Baek, K. D. Gang, K. H. Lee, I. C. Um, and Y. H. Park, Polymer, 46, 5094 (2005).
D. Bin, Y. Xiaoyan, Z. Yi, Z. Yuanyuan, L. Xiulan, Z. Yang, and Y. Kangde, Eur. Polym. J., 42, 2013 (2006).
N. Hemin and W. Chi-Hwa, J. Control. Release, 1210, 111 (2007).
T. Anna, S. Hanna, G. Paul, and W. Pernilla, Biomacromolecules, 9, 1044 (2008).
J. Venugopal, P. Vadgama, K. T. S. Sampath, and S. Ramakrishna, Nanotechnology, 18, 055101 (2007).
W. Patcharaporn, S. Neeracha, P. Prasit, and S. Pitt, Macromol. Biosci., 6, 70 (2006).
M. S. Khil, S. R. Bhattarai, H. Y. Kim, S. Z. Kim, and K. H. Lee, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 72B, 117 (2004).
I. K. Kwon, S. Kidoaki, and T. Matsuda, Biomaterials, 26, 3929 (2005).
M. Simonet, O. D. Scheider, P. Neuenschwander, and W. J. Stark, Polym. Eng. Sci., 47, 2020 (2007).
A. Thorvaldsson, H. Stenhamre, P. Gatenholm, and P. Walkenstrom, Biomacromolecules, 9, 1044 (2008).
Y. C. Fu, H. Nie, M. L. Ho, C. K. Wang, and C. H. Wang, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 99, 996 (2008).
M. V. Jose, V. Thomas, D. R. Dean, and E. Nyairo, Polymer, 50, 3778 (2009).
S. Sahoo, S. L. Toh, and J. C. H. Goh, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 95B, 19 (2010).
M. Li, M. J. Mondrinos, X. Chen, M. R. Gandhi, F. K. Ko, and P. I. Lelkes, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 79A, 963 (2006).
C. S. Ki, E. H. Gang, I. C. Um, and Y. H. Park, J. Membrane Sci., 302, 20 (2007).
S. Y. Park, C. S. Ki, Y. H. Park, H. M. Jung, K. M. Woo, and H. J. Kim, Tissue Eng. A, 16, 1271 (2010).
M. Koneracka, M. Muckova, V. Zavisova, N. Tomasovicova, P. Kopcansky, M. Timko, A. Jurikova, K. Csach, V. Kavecansky, and G. Lancz, J. Phys.-Condens. Matter., 20, 1 (2008).
W. J. Li, K. G. Danielson, P. G. Alexander, and R. S. Tuan, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 67A, 1105 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gang, E.H., Ki, C.S., Kim, J.W. et al. Highly porous three-dimensional poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microfibrous scaffold prepared by electrospinning method: A comparison study with other PLGA type scaffolds on its biological evaluation. Fibers Polym 13, 685–691 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0685-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0685-8