Abstract
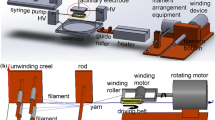
The development of a modified method to produce heat treated twisted nanofibrous yarns using two oppositely metallic spinnerets system is presented. This method allows the production of more uniform, stronger twisted poly acrylonitrile (PAN) yarns. The novelty of this system permits for in-situ heat treating of the nanofiber yarns. The average diameter of twisted nanofiber yarns is 340.65 µm with 5.8 CV%. The values of the initial modulus and stress of heat treated yarns increase from 1.90 GPa and 61.30 MPa in untreated one to 4.51 GPa and 116.56 MPa, respectively. In order to quantify the alignment of the nanofibers Fourier power spectrum (FPS) and image analysis were used. So the treated yarn shows more degree of nanofiber alignments than the untreated one.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. L. Yarin, S. Koombhongse, and D. H. Reneker, J. Appl. Phys., 89, 3018 (2001).
P. P. Tsaia, S. H. Gibson, and P. Gibson, J. Electrostatics, 54, 333 (2002).
H. J. Jin, S. Fridrikh, G. C. Rutledge, and D. Kaplan, Biomacromolecules, 3, 1233 (2002).
J. S. Kim and D. H. Reneker, Polym. Compos., 20, 124 (1999).
J. Lannutti, D. Reneker, T. Ma, D. Tomasko, and D. Farson, Mater. Sci. Eng.:C, 27, 504 (2007).
S. Lee and S. Kay Obendorf, Text. Res. J., 77, 696 (2007).
I. D. Norris, M. M. Shaker, F. K. Ko, and A. G. MacDiarmid, Synth. Met., 114, 109 (2000).
A. G. MacDiarmid, W. E. Jones, I. D. Norns, J. Gao, A. T. Johnson, N. J. Pinto, J. Hone, B. Han, F. K. Ko, H. Okuzaki, and M. Llaguno, Synth. Met., 119, 27 (2001).
S. H. Lee, B. C. Ku, and X. Wang, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Pro., 708, 403 (2002).
X. Y. Wang, L. A. Samuelson, and J. Kumar, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Pro., 708, 397 (2002).
C. J. Buchko, L. C. Chen, Y. Shen, and D. C. Martin, Polymer, 40, 7397 (1999).
E. Kenawy, K. Mansfield, G. L. Bowlin, D. G. Simpson, and G. E. Wnek, J. Contr. Release, 81, 57 (2002).
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, and S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol., 6, 2223 (2003).
J. Doshi and D. H. Reneker, J. Electrostatics, 35, 151 (1995).
D. H. Reneker, A. L. Yarin, H. Fong, and S. Koombhongse, J. Appl. Phys., 87, 4531 (2000).
W. E. Teo and S. Ramakrishna, Nanotechnology, 17, R89 (2006).
J. Doshi and D. H. Reneker, J. Electrostatics, 35, 151 (1995).
J. A. Matthews, G. E. Wnek, D. G. Simpson, and G. L. Bowlin, Biomacromolecules, 3, 232 (2002).
K. J. Shields, M. J. Beckman, G. L. Bowlin, and J. S. Wayne, Tissue Eng., 10, 1510 (2004).
S. F. Fennessey and R. J. Farris, Polymer, 45, 4217 (2004).
W. E. Teo, M. Kotaki, X. M. Mo, and S. Ramakrishna, Nanotechnology, 16, 918 (2005).
W. A. Yee, M. Kotaki, Y. Liu, and X. Lu, Polymer, 48, 512 (2007).
A. Theron, E. Zussman, and A. L. Yarin, Nanotechnology, 12, 384 (2001).
D. Li, Y. L. Wang, and Y. N. Xia, Nano Lett., 3, 1167 (2003).
D. Li, Y. L. Wang, and Y. N. Xia, Adv. Mater., 16, 361 (2004).
P. D. Dalton, D. Klee, and M. Moller, Polymer, 46, 611 (2005).
J. Kameoka, R. Orth, Y. N. Yang, D. Czaplewski, and R. H. G. Mathers, Nanotechnology, 14, 1124 (2003).
P. Katta, M. Alessandro, R. D. Ramsier, and G. G. Chase, Nano Lett., 4, 2215 (2004).
E. P. S. Tan, S. Y. Ng, and C. T. Lim, Biomaterials, 26, 1453 (2005).
Y. Q. Wu, L. A. Carnell, and R. L. Clark, Polymer, 48, 5653 (2007).
F. Dabirian, S. Sarkeshik, and A. Kianiha, Current Nanoscience, 5, 318 (2009).
S. Sarkar, S. Deevi, and G. Tepper, Macromol Rapid Commun, 28, 1034 (2007).
C. X. Xu, X. W. Sun, B. J. Chen, P. Shum, S. Li, and X. Hu, J. Appl. Phys., 95, 661 (2004).
Z. Ma, M. Kotaki, R. Inai, and S. Ramakrishna, Tissue Engineering, 11, 101 (2005).
J. M. Deitzel, J. D. Kleinmeyer, J. K. Hirvonen, and N. C. Beck Tan, Polymer, 42, 8163 (2001).
H. Fong, L. Weidong, C. S. Wang, and R. A. Vaia, Polymer, 43, 775 (2002).
E. Smit, U. Büttner, and R. D. Sanderson, Polymer, 46, 2419 (2005).
H. Pan, L. Li, L. Hu, and X. Cui, Polymer, 47, 4901 (2006).
W. E. Teo, R. Gopal, R. Ramaseshan, K. Fujihara, and S. Ranakrishna, Polymer, 48, 3400 (2007).
B. K. Gu, M. K. Shin, K. W. Sohn, S. I. Kim, S. J. Kim, S. K. Kim, H. Lee, and J. S. Park, Appl. Phys. Lett., 90, 263902 (2007).
F. Dabirian, Y. Hosseini, and S. A. Hosseini Ravandi, JTI, 98, 237 (2007).
M. B. Bazbouz and G. K. Stylios, Eur. Polym. J., 44, 1 (2008).
X. Wang, K. Zhang, M. Zhu, H. Yu, Z. Zhou, Y. Chen, and B. S. Hsiao, Polymer, 49, 2755 (2008).
C. K. Liu, R. J. Sun, K. Lai, C. Q. Sun, and Y. W. Wang, Mater. Lett., 62, 4467 (2008).
F. Dabirian and S. A. Hosseini, Fibres & Textiles in Eastern Europe, 17, 45 (2009).
U. Ali, Y. Q. Zhou, X. G. Wang, and T. Lin, The Journal of the Textile Institute, DOI: 10.1080/00405000.2011.552254.
M. Yousefzadeh, M. Latifi, W. E. Teo, M. Amani-Tehran, and S. Ramakrishna, Polym. Eng. Sci., 51, 323 (2011).
C. Pirlot, I. Willems, A. Fonseca, J. B. Nagy, and J. Delhalle, Adv. Eng. Mater., 4, 109 (2002).
A. Aivaskhani and S. A. Hosseini, 6th National Conference on Textile Engineering, Iran, 2007.
A. Ziabicki, “Fundamentals of Fiber Formation”, John Wiley & Sons, USA, 1976.
V. B. Gupta and V. K. Kothari, “Manufactured Fiber Technology”, Chapman & Hall, London, 1997.
J. Zhang, L. Q. Huang, and S. Y. Wang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 101, 787 (2006).
S. F. Fennessey, “Polymer Science and Engineering”, University of Massachusetts Amherst, 2006.
C. M. James, “Acrylic Fiber Technology and Applications”, M. Dekker, 1995.
R. Jalili, M. Morshed, and S. A. Hosseini Ravandi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 101, 4350 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabirian, F., Ravandi, S.A.H., Sanatgar, R.H. et al. Manufacturing of twisted continuous PAN nanofiber yarn by electrospinning process. Fibers Polym 12, 610–615 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-011-0610-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-011-0610-6