Abstract
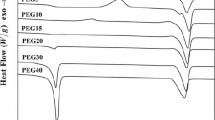
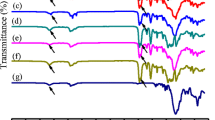
Linear shape memory polyurethane (SMPU) copolymers synthesized from 4,4′-methylene bis(phenylisocyanate) (MDI), poly(tetramethyleneglycol) (PTMG), and 1,4-butanediol (BD), and cross-linked SMPU by glycerol were being tested under the severe hydrolysis conditions for the tensile mechanical properties and the shape memory effect for 6 months. Tensile mechanical properties and shape memory effect were not substantially decreased after 6 months of storage, and SMPU structure was not affected during the long-term hydrolysis test as evidenced by IR, DSC, contact angle, and viscosity. Hydrolysis test was important in proving the durability of SMPU before application of SMPU in aqueous surrounding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Tobushi, H. Hara, E. Yamada, and S. Hayashi, Smart Mater. Struct., 5, 483 (1996).
T. Takahasi, N. Hayashi, and S. Hayashi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 60, 1061 (1996).
T. Kiyotsukuri, T. Masuda, N. Tsutsumi, W. Sakai, and M. Nagata, Polymer, 36, 2629 (1995).
J. H. Yang, B. C. Chun, Y. C. Chung, and J. W. Cho, Polymer, 44, 3251 (2003).
B. Singh and N. Sharma, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 93, 561 (2008).
X. Ramis, A. Cadenato, J. M. Salla, J. M. Morancho, A. Vallés, L. Contat, and A. Ribes, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 86, 483 (2004).
F. S. Chuang, H. Y. Tsi, J. D. Chow, W. C. Tsen, Y. C. Shu, and S. C. Jang, Degrad. Stabil., 93, 1753 (2008).
N. S. Allen, M. Edge, D. Mourelatou, A. Wilkinson, C. M. Liauw, M. D. Parellada, J. A. Barrio, and V. R. S. Quiteria, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 79, 297 (2003).
J. P. T. Jensen and J. Kops, J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem., 18, 2737 (2003).
A. M. Striegel, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods, 56, 117 (2003).
Y. H. Lin and H. Y. Yen, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 89, 101 (2006).
M. Urgun-Demirtas, D. Singh, and K. Pagilla, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 92, 1599 (2007).
S. S. Umare and A. S. Chandure, Chem. Eng. J., 142, 65 (2008).
C. Molero, A. de Lucas, and J. F. Rodríguez, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 93, 353 (2008).
J. H. Hong, H. J. Jeon, J. H. Yoo, W.-R. Yu, and J. H. Youk, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 92, 1186 (2007).
S. I. Lee, S. C. Yu, and Y. S. Lee, Polym. Deg. Stab., 72, 81 (2001).
R. Chandra and R. Rustgi, Prog. Polym. Sci., 23, 1273 (1998).
T. Pretsch, I. Jakob, and W. Müller, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., in press.
B. C. Chun, M. H. Chong, and Y.-C. Chung, J. Mater. Sci., 42, 6524 (2007).
B. S. Lee, B. C. Chun, Y.-C. Chung, K. I. Sul, and J. W. Cho, Macromolecules, 34, 6431 (2001).
M. K. Hur, J. M. Kwak, and T. Hur, Polymer (Korea), 20, 392 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, YC., Choi, J.W., Choi, N.E. et al. Endurance of linear and cross-linked shape memory polyurethane under rigorous hydrolysis conditions. Fibers Polym 10, 576–582 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-010-0576-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-010-0576-9