Abstract
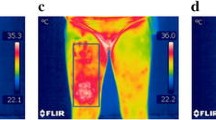
A thermograph is used to determine the real-time temperature distribution on the skin temperature wearing clothing treated by different ultra-violet (UV) energy. The thermogram images of body wearing clothing with the 4-channel PET knit fabric irradiated by UV, were compared visually with each other and analyzed quantitatively with image analysis. We analyzed the thermogram in a color image. For image analysis, the Inspector 4.0 (Matrox Electronic System, Ltd.) was used. The surface temperatures, calculated based on the percentage surface area of a given temperature range with an interval of 1 °C, were averaged of five subjects’ surface temperature. From the results of the microclimate temperature, there were not significant differences among the subjects’ surface temperatures wearing different time treated clothes. However, subjective evaluation shows that the clothing treated by UV for 90 min had the lowest thermal sensation and the highest comfort sensation. Based on the image analysis of the thermogram, the calculated thermal sensation of the clothes irradiated by UV for 0 min, 30 min and 90 min, were coincident with the subjective thermal sensation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. C. Min, S. C. Chung, E. J. Sung, H. J. Jeon, and C. J. Kim, Korean Journal of the Science of Emotion and Sensibility, 4, 23 (2001).
http://www.landinstruments.net/infrared, A Basic Guide to Thermography, Land Instrument International, 2004.
S. J. Park, J. M. Koo, and H. J. Lee, Evaluation of Massage Chair Effect on Human Body Using Infrared Imaging/Radiometric Camera, KSNT/SC0039, 279 (2004).
Y. C. Park, J. S. Chae, J. Y. Eom, S. S. Son, and I. S. Choe, The Journal of Korean Accpuncture & Moxibustion Society, 20, 134 (2003).
K. I. Shin and J. J. Kin, J. Korean Fiber Soc., 39, 714 (2002).
K. W. Oh, H. S. Kim, and S. H. Kim, J. Korean Fiber Soc., 39, 108 (2002).
Y. K. Choi, C. Choi, and J. C. Park, Korea Information Processing Society, 11B, 403 (2004).
B. J. Lee, Y. J. Lee, and K. H. Hong, “Proceedings of the Society of Living Environment System”, p.115, 2002.
H. Y. Choi and J. S. Lee, J. Korean Soc. Clothing Text., 29, 617 (2005).
H. Y. Choi and J. S. Lee, J. Korean Soc. Clothing Text., 29, 561 (2005).
H. Y. Choi and J. S. Lee, Fiber. Polym., 7, 442 (2006).
H. Y. Choi and J. S. Lee, Fiber. Polym., 7, 446 (2006).
M. Watanabe, “Hygiene of Clothing and Wear”, DobunShoin, Japan, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.Y., Lee, J.S. Quantitative thermographic analysis method for evaluating the thermal properties of PET irradiated by ultra-violet. Fibers Polym 9, 355–359 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-008-0057-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-008-0057-6