Abstract
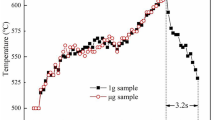
The solidification experiments of Al-2.8 wt.% Cu alloy were conducted under both microgravity and normal gravity conditions by using a 50-m-high drop tube. The solidification microstructure and element distribution were analyzed by using OM, EBSD and EPMA. Columnar dendrites were found growing epitaxially from the seeds during solidification under both microgravity and normal gravity conditions. Comparatively, the primary dendrite spacing and secondary dendrite spacing formed under microgravity condition were smaller, and the deviation angle between growth direction and the preferred crystal orientation < 001 > was smaller. Cu content in the center region of 1g sample is always higher than that of μg sample, and shows a characteristic of high in the middle and low at the edges along radial directions. While the Cu content in μg sample seems to display an opposite trend in the distribution along radial directions, and has a smaller wave amplitude. Microsegregation of Cu exists in both 1g sample and μg sample, and basically presents a gradually decreasing trend with the increase of solidification distance. Nevertheless, the degree of microsegregation in μg sample is always lower. The above results suggest that under normal gravity condition, Cu element had a trend to enrich to central area under the effect of convection, and therefore, might contribute to enlarge dendrite spacing and increase microsegregation in that area.






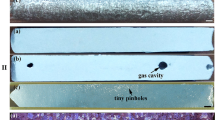
taken from the epitaxial growth area near the center of samples and next to the remelting interfaces. The Y0 direction of the inverse pole figure is parallel to the direction of epitaxial growth



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acer, E., Cadirli, E., Erol, H., Kaya, H., Gunduz, M.: Effects of growth rates and compositions on dendrite arm spacings in directionally solidified Al-Zn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4337-x
Asta, M., Beckermann, C., Karma, A., Kurz, W., Napolitano, R., Plapp, M., Purdy, G., Rappaz, M.: Solidification microstructures and solid-state parallels: Recent developments, future directions. Acta Mater. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2008.10.020
Cahoon, J.R., Chaturvedi, M.C., Tandon, K.N.: The unidirectional solidification of Al-4 Wt pct Cu ingots in microgravity. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-1019-8
Chen, L., Luo, X.: A new way to explore microgravity effect by drop tube experiment. Acta Metall. Sinica. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.03.021
Curreri, P.A., Lee, J.E., Stefanescu, D.M.: Dendritic solidification of alloys in low gravity. Metall. Trans. A. (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645800
Dupouy, M.D., Camel, D., Favier, J.J.: Natural convective effects in directional dendritic solidification of binary metallic alloys: Dendritic array primary spacing. Acta Metall. Mater. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(92)90122-U
Dupouy, M.D., Camel, D., Mazille, J.E., Hugon, I.: Columnar to equiaxed transition in a refined Al-Cu alloy under diffusive and convective transport conditions. Mater. Sci. Forum. (2000). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.329-330.25
Dupouy, M.D., Camel, D.: Effects of gravity on columnar dendritic growth of metallic alloys: flow pattern and mass transfer. J. Cryst. Growth. (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(97)00415-6
Favier, J.J., Garandet, J.P., Rouzaud, A., Camel, D.: Mass transport phenomena in microgravity: Preliminary results of the first MEPHISTO flight experiment. J. Cryst. Growth. (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0248(94)90517-7
Flemings, M.C., Mehrabian, R.: Macrosegregation in ternary alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811556
Hu, H.: Principle of metal solidification. Machine Industry Press, Beijing (2000)
Kurz, W., Fisher, D.J.: Fundamentals of solidification. Trans Tech Publications, Florida (1998)
Li, W., Jiang, H., Zhang, L., Li, S., He, J., Zhao, J., Ai, F.: Solidification of Al-Bi-Sn immiscible alloy under microgravity conditions of space. Scr Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.12.010
Liu, D.R., Mangelinck-Noel, N., Gandin, C.A., Zimmermann, G., Sturz, L., Thi, H.N., Billia, B.: Structures in directionally solidified Al-7 wt.% Si alloys: Benchmark experiments under microgravity. Acta Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.10.038
Luo, X., Feng, S., Li, Y.: Solidification of AlCuMgZn single crystal in space. Chin. J. Space Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.11728/cjss2016.04.445
Luo, X., Jin, D., Ren, Y.: Growth of single crystal alloy under microgravity condition. Mater. China. (2017). https://doi.org/10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2017.04.03
Luo, X., Wang, Y., Li, Y.: Role of hydrostatic pressure and wall effect in solidification of TC8 alloy. NPJ Microgravity. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41526-019-0083-2
Mehrabian, R., Keane, M., Flemings, M.C.: Interdendritic fluid flow and macrosegregation; influence of gravity. Metall. Mater. Trans. B (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02900233
Mullis, A.M.: The effects of fluid flow on secondary arm coarsening during dendritic solidification. J. Mater. Sci. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023977723475
Ratke, L., Genau, A., Steinbach, S.: Flow effects on the dendritic microstructure of AlSi-based alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-009-0050-9
Steinbach, I.: Pattern formation in constrained dendritic growth with solutal buoyancy. Acta Mater. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.02.004
Tan, L., Zabaras, N.: Modeling the growth and interaction of multiple dendrites in solidification using a level set method. J Comput Phys. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2007.03.023
Xie, F., Kraft, T., Zuo, Y., Moon, C.H., Chang, Y.: Microstructure and microsegregation in Al-rich Al–Cu–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00372-3
Yang, C., Liu, L., Zhao, X., Liu, G., Fu, H.: Dendrite arm spacings and microsegregation in and orientated single crystal superalloys DD407. Acta Metall. Sinica. (2011). https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1037.2011.00142
Yu, H., Tandon, K.N., Cahoon, J.R.: Solidification of hypereutectic Al-38 wt pct Cu alloy in microgravity and in unit gravity. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0290-4
Yuan, L., Lee, P.: Dendritic solidification under natural and forced convection in binary alloys: 2D versus 3D simulation. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0965-0393/18/5/055008
Zhang, N., Luo, X., Feng, S., Ren, Y.: Mechanism of gravity effect on solidification microstructure of eutectic alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.11.009
Zhao, Y., Zhang, B., Hou, H., Chen, W., Wang, M.: Phase-field simulation for the evolution of solid/liquid interface front in directional solidification process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.12.009
Zhou, Y., Hu, Z., Jie, W.: Solidification technology. Machine Industry Press, Beijing (1998)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the China manned space engineering (TGJZ800-2-RW024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Luo, X., Li, Y. et al. Gravity-induced Solidification Segregation and Its Effect On Dendrite Growth in Al-2.8 Wt.% Cu Alloy. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 33, 72 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-021-09913-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-021-09913-4