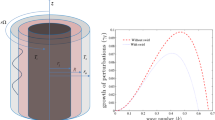
Abstract
The dynamics of a self-rewetting film falling along a vertical fiber under the influence of gravity are considered. The evolution equation of the interface of the self-rewetting film is established in the framework of a long-wave approximation theory. The effect of thermocapillarity (Marangoni effect) on the absolute/convective instability (AI/CI) is investigated for self-rewetting fluids of which the surface tension is a quadratic function of the temperature at the surface. The effect of thermocapillarity on the Rayleigh-Plateau instability is investigated by examining the dispersion relation. The characteristics of self-rewetting fluids are considered for different Marangoni numbers (Ma) in different regions of absolute/convective instability using a spatio-temporal stability analysis. Numerical simulations of the nonlinear evolution in various regions of absolute/convective instability are also performed. The results of numerical simulations are in excellent agreement with the spatio-temporal stability analysis. The effect of thermocapillarity on absolute and convective instability depends on the difference between the temperature at the interface \(\bar {\varTheta }_{i}\), and the temperature corresponding the minimum surface tension Θ0. The results indicate that the thermocapillarity suppresses the absolute instability and enhances the convective instability as Ma increases when \(\bar {\varTheta }_{i}-{\varTheta }_{0}> 0\), and enhances the absolute instability as Ma increases when \(\bar {\varTheta }_{i}-{\varTheta }_{0}< 0\).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, Y., Iwaski, A., Tanaka, K.: Thermal management with self-rewetting fluids. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 16(1-4), 148–152 (2005)
Abe, Y.: Self-rewetting fluids. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1077(1), 650–667 (2006)
Chen, X., Zhu, Z.Q., Liu, Q.S.: Thermodynamics behaviors of macroscopic liquid droplets evaporation from heated substrates. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 27(5), 353–360 (2015)
Chen, X., Wang, X., Chen, P.G., Liu, Q.S.: Thermal effects of substrate on Marangoni flow in droplet evaporation: response surface and sensitivity analysis. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 113, 354–365 (2017)
Dávalos-Orozco, LA, You, X.: Three-dimensional instability of a liquid layer flowing down a heated vertical cylinder. Phys. Fluids 12(9), 2198–2209 (2000)
Dávalos-Orozco, LA: Sideband thermocapillary instability of a thin film coating the outside of a thick walled cylinder with finite thermal. Interfacial Phenom. Heat Transfer 5(4), 287–298 (2017)
Dávalos-Orozco, LA: Sideband thermocapillary instability of a thin film falling down the inside of a thick-walled cylinder with finite thermal conductivity. Interfacial Phenom. Heat Transfer 6(3), 239–251 (2018)
Dávalos-Orozco, LA: Sideband thermocapillary instability of a thin film flowing down the outside of a thick walled cylinder with finite thermal conductivity. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 109, 15–23 (2019a)
Dávalos-Orozco, LA: Nonlinear sideband thermocapillary instability of a thin film coating the inside of a thick walled cylinder with finite thermal conductivity in the absence of gravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09751-5 (2019b)
Ding, Z., Wong, T.N.: Falling liquid films on a slippery substrate with Marangoni effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 90, 689–701 (2015)
Ding, Z., Wong, T.N.: Three-dimensional dynamics of thin liquid films on vertical cylinders with Marangoni effect. Phys. Fluids 29(1), 011701 (2017)
Ding, Z., Liu, R., Wong, T.N., Yang, C.: Absolute instability induced by Marangoni effect in thin liquid film flows on vertical cylindrical surfaces. Chem. Eng. Sci. 177, 261–269 (2018)
Ding, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, R., Yang, C.: Breakup of ultra-thin liquid films on vertical fiber enhanced by Marangoni effect. Chem. Eng. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2018.12.058 (2019)
Ding, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, R., Yang, C.: Thermocapillary effect on the dynamics of liquid films coating the interior surface of a tube. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 138, 524–533 (2019)
Duprat, C., Ruyer-Quil, C., Kalliadasis, S.: Absolute and convective instabilities of a viscous film flowing down a vertical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(24), 244502 (2007)
Frenkel, A.L.: Nonlinear theory of strongly undulating thin films flowing down vertical cylinders. Europhys Lett. 31(1), 347–384 (1999)
Gannon, M.G.L., Faber, T.E.: The surface tension of nematic liquid crystals. Phil. Mag. A. 37(1), 117–135 (1978)
Goren, S.L.: The instability of an annular thread of fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 12(02), 309–319 (1962)
Hu, Y., Lium, T., Li, X.: Heat transfer enhancement of micro oscillating heat pipes with self-rewetting Fluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 28(8), 1025–1033 (2014)
Huerre, P., Monkwitz, P.A.: Local and global instabilities inspatially developing flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech 37(1), 357–392 (2005)
Kliakhandler, I.L., Davis, S.H., Bankoff, S.G.: Viscous beads on vertical fibre. J. Fluid Mech. 429, 381–390 (2001)
Liu, R., Liu, Q.S.: Thermocapillarity effect on the dynamics of viscous beads on vertical fiber. Phys. Rev. E. 90(3), 033005 (2014)
Liu, R., Ding, Z., Zhu, Z.: Thermocapillarity Eeffect on the absolute and convective instabilities of film flows fown a fibre. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 112, 918–925 (2017)
Liu, R., Chen, X., Wang, X.: Effects of thermocapillarity on the dynamics of an exterior coating flow of a self-rewetting fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 136, 692–701 (2019)
Lin, S.P., Liu, W.C.: Instability of film coating of wires and tubes. AIChE J. 21(4), 775–782 (1975)
Ono, N., Kaneko, T., Nishigochi, S., Shoji, M.: Measurement of temperature dependence of surface tension of alcohol aqueous solutions by maximum bubble pressure method. J. Therm. Sci. Tech. Jpn. 4(2), 284–293 (2009)
Quéré, D.: Thin films flowing on vertical fibers. Europhys. Lett. 13(8), 347–384 (1990)
Rayleigh, L.: On the stablitily of liquid jets. P. Lond. Math. Soc. 10, 4–18 (1878)
Restolho, J., Mata, L.J., Saramago, B.: Peculiar surface behavior of some ionic liquids based on active pharmaceutical ingredients. J. Chem.Phys. 134(7), 2262 (2011)
Zhang, N.: Innovative heat pipe systems using a new working fluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 28(8), 1025–1033 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51766002, 11802066), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2018GXNSFBA138058), Guangxi’s Key Laboratory Foundation of Manufacturing Systems and Advanced Manufacturing Technology (Grant No. 17-259-05-002Z), and Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education (Grant No. 2019YCXS005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Multiphase Fluid Dynamics in Microgravity
Guest Editors: Tatyana P. Lyubimova, Jian-Fu Zhao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Li, X. & Liu, R. Effect of Thermocapillary on Absolute and Convective Instability of Film Flow of Self-Rewetting Fluid. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32, 415–422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09778-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09778-8