Abstract
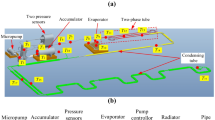
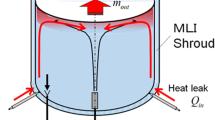
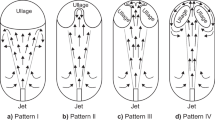
On-orbit filling is one of the important technologies for long-period space exploration. Filling without moving components and with low mass loss has obvious advantage for on-orbit fillings, especially for small volume filling. For such purpose, a no-pump no-vent filling system was proposed, and the working principle of the filling and the criterion to end the filling in microgravity were equivalently verified on ground. In such filling system, two distinct filling phases were witnessed: a fast and effective liquid transfer phase followed by a slow and ineffective vapor transfer phase. The vapor in this phase came from the evaporation of the remaining liquid in the capillary structure, which has to be evaporated by heating in microgravity. The heating power determines the period of the vapor transfer phase for a given system with certain capillary structure. It was found that the transition point of the system pressure from increase to decrease can be used as a criterion to end the filling. Experiment that simulated such vapor transfer phase on ground provides data supports for optimizing the filling control scenario.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cecere, A., Di Martino, G.D., Mungiguerra, S.: Experimental investigation of capillary-driven two-phase flow in water/Butanol under reduced gravity conditions. Microgravity Science and Technology. 31(4), 425–434 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09723-9
Chato, D.J.: Thermodynamic modeling of the no-vent fill methodology for transferring cryogens in low gravity. p. 13. NASA, (1988)
Chato, D.J.: Cryogenic transfer options for eexploration missions. p. 14. NASA, (1990)
Chato, D.J.: Ground testing of the nonvented fill method of orbital propellant transfer: Results of initial test series. Paper presented at the 27th Joint Propulsion Conference, California, USA, 24 June-27 June (1991)
Chato, D.J.: Technologies for refueling spacecraft on-orbit. (2000)
Chato, D.J., Moran, M.E., Nyland, T.W.: Initial experimentation on the nonvented fill of a 0.14 m3 (5 ft3) Dewar with nitrogen and hydrogen. p. 23. NASA, (1990)
Dominick, S.M., Tegart, J.R., Driscoll, S.L., Sledd, J.D., Hastings, L.J.: Fluid acquisition and resupply experiments on space shuttle flights STS-53 and STS-57. p. 60. NASA, (2011)
Eberhardt, R., Bailey, W., Symons, E., Kroeger, E.: Cryogenic fluid management facility. Paper presented at the 20th Joint Propulsion Conference, Ohio, USA, 11 June-13 June (1984)
Hartwig, J.W.: Propellant management devices for low-gravity fluid management: past, present, and future applications. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 54(4), 808–824 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A33750
Li, J.-C., Lin, H., Zhao, J.-F., Li, K., Hu, W.-R.: Dynamic behaviors of liquid in partially filled tank in short-term microgravity. Microgravity Science and Technology. 30(6), 849–856 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9642-5
Ma, Y., Li, Y., Wang, L., Zhu, K., Xu, M.J.: Review on on-orbit refueling techniques and schemes of cryogenic propellants. Journal of Astronautics 37(3), 245–252 (2016). http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2016.03.001
Ma, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, K., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Tan, H.: Investigation on no-vent filling process of liquid hydrogen tank under microgravity condition. Int J Hydrogen Energ. 42(12), 8264–8277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.02.198
Moran, M.E., Nyland, T.W., Papell, S.S.: Liquid transfer cryogenic test facility—initial hydrogen and nitrogen no-vent fill data. NASA, (1990)
Seo, M., Yoo, D., Jeong, S., Kim, Y.: Experimental investigation on No-Vent Fill (NVF) process using liquid Nitrogen. Progress in Superconductivity and Cryogenics 16(4), 71–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.9714/psac.2014.16.4.071
Taylor, W.J., Chato, D.J., Moran, M.M., Nyland, T.W.: On-orbit cryogenic fluid transfer research at NASA Lewis research center. Cryogenics. 32(2), 199–204 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-2275(92)90267-E
Wang, C., Li, Y., Wang, R.: Performance comparison between no-vent and vented fills in vertical thermal-insulated cryogenic cylinders. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 35(2), 311–318 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2010.09.013
Zhong, Z.: China successfully breaks through and masters key technologies for propellant on-orbit addition. Dual Use Technologies & Products 11, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.19385/j.cnki.1009-8119.2017.11.026
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by China Manned Space Engineering Application System, and the Center for Space Technology Program of Sun Yat-Sen University, Zhuhai Key Laboratory of Center for Space Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Multiphase Fluid Dynamics in Microgravity
Guest Editors: Tatyana P. Lyubimova, Jian-Fu Zhao
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Xu, J. & He, Z. Ground Experiment for On-Orbit Fluid Filling without Moving Component. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32, 265–273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09767-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09767-x