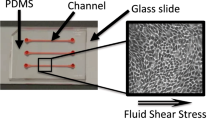
Abstract
Drug-induced acute kidney injury causes massive morbidity and mortality at exorbitant cost, yet there is currently no effective method for preclinical in vitro testing for nephrotoxicity. Proximal tubule cells are a key target for nephrotoxins, but heretofore, it has been a challenge to maintain their differentiation in vitro. One promising approach is to culture them in suspension, under physiological levels of shear, so as to induce and maintain structural and functional differentiation. Advances in materials, additive manufacturing, and injection molding have reduced the complexity and cost of suspension cultures hardware by orders of magnitude, making it a viable alternative for high throughput screening. This study defines the global transcriptome responses of human renal proximal tubular cells to suspension culture. GSEA/Cytoscape/ClueGO analysis showed near perfect concurrence with GPS-SIGORA analysis in the areas of mineral absorption and ribosome assembly, and defined the nucleic acid and protein mechanisms underlying the transcriptome response to suspension culture. Proximal tubular cells in suspension culture showed increased growth and viability assayed as reducing potential compared to cells cultured under static conditions. Suspension culture of human renal proximal tubular cells now allows investigations in basic cell biology, toxicology, drug screening, and tissue engineering, free of artificial matrices, feeder layers, fetal gene expression, or the need for complex engineering technologies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
ATP-binding cassette
- FDR:
-
False Discovery Rate
- FWER:
-
Family Wise Error Rate
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- GPS:
-
Gene-Pair Signatures
- GSEA:
-
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
- NES:
-
Normalized Enrichment Scores
- OAT:
-
Organic anion transporter
- OCT:
-
Organic cation transporter
- RFU:
-
Relative fluorescence units
- SIGORA:
-
Signature Over-Representation Analysis
- SLC:
-
Solute carrier
References
Astashkina, A.I., Mann, B.K., Prestwich, G.D., Grainger, D.W.: A 3-D organoid kidney culture model engineered for high-throughput nephrotoxicity assays. Biomaterials. 33(18), 4700–4711 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.02.063
Bach, P.H.: Detection of chemically induced renal injury: the cascade of degenerative morphological and functional changes that follow the primary nephrotoxic insult and evaluation of these changes by in-vitro methods. Toxicol. Lett. 46(1–3), 237–249 (1989)
Baer, P.C., Nockher, W.A., Haase, W., Scherberich, J.E.: Isolation of proximal and distal tubule cells from human kidney by immunomagnetic separation. Technical note. Kidney Int. 52(5), 1321–1331 (1997)
Benjamini, Y., Hochberg, Y.: Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B. 57, 289–300 (1995)
Bindea, G., Mlecnik, B., Hackl, H., Charoentong, P., Tosolini, M., Kirilovsky, A., Fridman, W.H., Pages, F., Trajanoski, Z., Galon, J.: ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics. 25(8), 1091–1093 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101
Braam, B., Allen, P., Benes, E., Koomans, H.A., Navar, L.G., Hammond, T.: Human proximal tubular cell responses to angiotensin II analyzed using DNA microarray. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 464(2–3), 87–94 (2003)
Brinley, A.A., Theriot, C.A., Nelman-Gonzalez, M., Crucian, B., Stowe, R.P., Barrett, A.D., Pierson, D.L.: Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in a modeled spaceflight system. J. Cell. Biochem. 114(3), 616–624 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24403
Christensen, E.I., Verroust, P.J., Nielsen, R.: Receptor-mediated endocytosis in renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 458(6), 1039–1048 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0685-8
Cialdai, F., Vignali, L., Morbidelli, L., Colciago, A., Celotti, F., Santi, A., Caselli, A., Cirri, P., Monici, M.: Modeled microgravity affects fibroblast functions related to wound healing. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29(1–2), 121–132 (2017)
Cowger, N.L., Benes, E., Allen, P.L., Hammond, T.G.: Expression of renal cell protein markers is dependent on initial mechanical culture conditions. J. Appl. Physiol. 92(2), 691–700 (2002)
Crean, D., Bellwon, P., Aschauer, L., Limonciel, A., Moenks, K., Hewitt, P., Schmidt, T., Herrgen, K., Dekant, W., Lukas, A., Bois, F., Wilmes, A., Jennings, P., Leonard, M.O.: Development of an in vitro renal epithelial disease state model for xenobiotic toxicity testing. Toxicol. in Vitro. 30(1 Pt A), 128–137 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2014.11.015
Dolbeare, F.A., Smith, R.E.: Flow cytometric measurement of peptidases with use of 5-nitrosalicylaldehyde and 4-methoxy-beta-naphthylamine derivatives. Clin. Chem. 23(8), 1485–1491 (1977)
Du, Z., Duan, Y., Yan, Q., Weinstein, A.M., Weinbaum, S., Wang, T.: Mechanosensory function of microvilli of the kidney proximal tubule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(35), 13068–13073 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405179101
Duan, Y., Gotoh, N., Yan, Q., Du, Z., Weinstein, A.M., Wang, T., Weinbaum, S.: Shear-induced reorganization of renal proximal tubule cell actin cytoskeleton and apical junctional complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105(32), 11418–11423 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804954105
Essig, M., Friedlander, G.: Tubular shear stress and phenotype of renal proximal tubular cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14(Suppl 1), S33–S35 (2003)
Foroushani, A.B., Brinkman, F.S., Lynn, D.J.: Pathway-GPS and SIGORA: identifying relevant pathways based on the over-representation of their gene-pair signatures. PeerJ. 1, e229 (2013). https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.229
Gautier, L., Cope, L., Bolstad, B.M., Irizarry, R.A.: affy--analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics. 20(3), 307–315 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405
Gentleman, R.C., Carey, V.J., Bates, D.M., Bolstad, B., Dettling, M., Dudoit, S., Ellis, B., Gautier, L., Ge, Y., Gentry, J., Hornik, K., Hothorn, T., Huber, W., Iacus, S., Irizarry, R., Leisch, F., Li, C., Maechler, M., Rossini, A.J., Sawitzki, G., Smith, C., Smyth, G., Tierney, L., Yang, J.Y., Zhang, J.: Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 5(10), R80 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80
Guo, P., Weinstein, A.M., Weinbaum, S.: A hydrodynamic mechanosensory hypothesis for brush border microvilli. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 279(4), F698–F712 (2000)
Hammond, T.G.: Analysis and isolation of renal tubular cells by flow cytometry. Kidney Int. 42(4), 997–1005 (1992)
Hammond, T.G., Allen, P.L.: The Bonn criteria: minimal experimental parameter reporting for clinostat and random positioning machine experiments. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 23(2), 271–275 (2011)
Hammond, T.G., Birdsall, H.H.: Hepatocyte CYP2B6 can be expressed in cell culture systems by exerting physiological levels of shear: implications for ADME testing. A review. J Toxicol. 2017, 1–5 (2017a). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1907952
Hammond, T.G., Birdsall, H.H.: Suspension culture device fabricated from breathable materials and methods of making and using same (DUS5312PROV). USA Patent. (2017b)
Hammond, T.G., Hammond, J.S.: Optimized suspension culture: the rotating-wall vessel. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 281(1), F12–F25 (2001)
Hammond, T.G., Benes, E., O'Reilly, K.C., Wolf, D.A., Linnehan, R.M., Taher, A., Kaysen, J.H., Allen, P.L., Goodwin, T.J.: Mechanical culture conditions effect gene expression: gravity-induced changes on the space shuttle. Physiol. Genomics. 3(3), 163–173 (2000)
Hammond, T., Allen, P., Birdsall, H.: Is there a space-based technology solution to problems with preclinical drug toxicity testing? Pharm. Res. 33(7), 1545–1551 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1942-0
Homan, K.A., Kolesky, D.B., Skylar-Scott, M.A., Herrmann, J., Obuobi, H., Moisan, A., Lewis, J.A.: Bioprinting of 3D convoluted renal proximal tubules on perfusable chips. Sci. Rep. 6, 34845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34845
Institute of Medicine: Accelerating the development of biomarkers for drug safety: Workshop summary. Institute of Medicine (US) Forum on Drug Discovery, Development, and Translation. National Academies Press (US), Washington (2009)
Kaysen, J.H., Campbell, W.C., Majewski, R.R., Goda, F.O., Navar, G.L., Lewis, F.C., Goodwin, T.J., Hammond, T.G.: Select de novo gene and protein expression during renal epithelial cell culture in rotating wall vessels is shear stress dependent. J. Membr. Biol. 168(1), 77–89 (1999)
Kim, S.M., Kim, H., Yang, D., Park, J., Park, R., Namkoong, S., Lee, J.I., Choi, I., Kim, H.S., Kim, H., Park, J.: An experimental and theoretical approach to optimize a three-dimensional clinostat for life science experiments. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 29(1–2), 97–106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-016-9529-2
King, S.M., Higgins, J.W., Nino, C.R., Smith, T.R., Paffenroth, E.H., Fairbairn, C.E., Docuyanan, A., Shah, V.D., Chen, A.E., Presnell, S.C., Nguyen, D.G.: 3D proximal tubule tissues recapitulate key aspects of renal physiology to enable nephrotoxicity testing. Front. Physiol. 8, 123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00123
Long, J.P., Hughes, J.H.: Epstein-Barr virus latently infected cells are selectively deleted in simulated-microgravity cultures. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 37(4), 223–230 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02577533
Maggiorani, D., Dissard, R., Belloy, M., Saulnier-Blache, J.S., Casemayou, A., Ducasse, L., Gres, S., Belliere, J., Caubet, C., Bascands, J.L., Schanstra, J.P., Buffin-Meyer, B.: Shear stress-induced alteration of epithelial Organization in Human Renal Tubular Cells. PLoS One. 10(7), e0131416 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131416
Moestrup, S.K., Kozyraki, R., Kristiansen, M., Kaysen, J.H., Rasmussen, H.H., Brault, D., Pontillon, F., Goda, F.O., Christensen, E.I., Hammond, T.G., Verroust, P.J.: The intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor and target of teratogenic antibodies is a megalin-binding peripheral membrane protein with homology to developmental proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 273(9), 5235–5242 (1998)
Nielsen, R., Christensen, E.I., Birn, H.: Megalin and cubilin in proximal tubule protein reabsorption: from experimental models to human disease. Kidney Int. 89(1), 58–67 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2015.11.007
Nigam, S.K., Wu, W., Bush, K.T., Hoenig, M.P., Blantz, R.C., Bhatnagar, V.: Handling of drugs, metabolites, and uremic toxins by kidney proximal tubule drug transporters. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10(11), 2039–2049 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.02440314
Nislow, C., Lee, A.Y., Allen, P.L., Giaever, G., Smith, A., Gebbia, M., Stodieck, L.S., Hammond, J.S., Birdsall, H.H., Hammond, T.G.: Genes required for survival in microgravity revealed by genome-wide yeast deletion collections cultured during spaceflight. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 976458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/976458
Oo, Z.Y., Kandasamy, K., Tasnim, F., Zink, D.: A novel design of bioartificial kidneys with improved cell performance and haemocompatibility. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 17(4), 497–507 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12029
Park, J., Shrestha, R., Qiu, C., Kondo, A., Huang, S., Werth, M., Li, M., Barasch, J., Susztak, K.: Single-cell transcriptomics of the mouse kidney reveals potential cellular targets of kidney disease. Science. 360(6390), 758–763 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar2131
Pfaller, W., Gstraunthaler, G.: Nephrotoxicity testing in vitro--what we know and what we need to know. Environ. Health Perspect. 106(Suppl 2), 559–569 (1998)
Ritchie, M.E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C.W., Shi, W., Smyth, G.K.: Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(7), e47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Schophuizen, C.M., De Napoli, I.E., Jansen, J., Teixeira, S., Wilmer, M.J., Hoenderop, J.G., Van den Heuvel, L.P., Masereeuw, R., Stamatialis, D.: Development of a living membrane comprising a functional human renal proximal tubule cell monolayer on polyethersulfone polymeric membrane. Acta Biomater. 14, 22–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2014.12.002
Seitz, C., Frensing, T., Hoper, D., Kochs, G., Reichl, U.: High yields of influenza a virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells are promoted by an insufficient interferon-induced antiviral state. J. Gen. Virol. 91(Pt 7), 1754–1763 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.020370-0
Shaffer, J.P.: Multiple hypothesis testing. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 46, 561–584 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ps.46.020195.003021
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N.S., Wang, J.T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., Ideker, T.: Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13(11), 2498–2504 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Soldatow, V.Y., Lecluyse, E.L., Griffith, L.G., Rusyn, I.: Models for liver toxicity testing. Toxicol. Res. (Camb). 2(1), 23–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TX20051A
Sonnaert M., Papantoniou I., Luyten F.P., Schrooten J.I.: Quantitative validation of the Presto Blue metabolic assay for online monitoring of cell proliferation in a 3D perfusion bioreactor system. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 21(6), 519–529. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEC.2014.0255
Subramanian, A., Tamayo, P., Mootha, V.K., Mukherjee, S., Ebert, B.L., Gillette, M.A., Paulovich, A., Pomeroy, S.L., Golub, T.R., Lander, E.S., Mesirov, J.P.: Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102(43), 15545–15550 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Verroust, P.J., Christensen, E.I., Hammond, T.G.: Vesicular flow in epithelial cells: physiopathologic importance of two multiligand receptors. Bull Acad Natl Med. 180(6), 1187–1197; discussion 1197–8 (1996)
Warnke, E., Kopp, S., Wehland, M., Hemmersbach, R., Bauer, J., Pietsch, J., Infanger, M., Grimm, D.: Thyroid cells exposed to simulated microgravity conditions – comparison of the fast rotating clinostat and the random positioning machine. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28(3), 247–260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-015-9456-7
Wieser, M., Stadler, G., Jennings, P., Streubel, B., Pfaller, W., Ambros, P., Riedl, C., Katinger, H., Grillari, J., Grillari-Voglauer, R.: hTERT alone immortalizes epithelial cells of renal proximal tubules without changing their functional characteristics. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 295(5), F1365–F1375 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.90405.2008
Wilmer, M.J., Ng, C.P., Lanz, H.L., Vulto, P., Suter-Dick, L., Masereeuw, R.: Kidney-on-a-Chip Technology for drug-induced nephrotoxicity screening. Trends Biotechnol. 34(2), 156–170 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.11.001
Acknowledgements
NASA Grants NNX13AN32G, NNX12AM93G, and NNX10AP01G supported these studies. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center and the Veterans Health Administration Office of Research and Development in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Contents do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States of America. We thank the Medical College of Georgia for performing gene arrays. We thank David Corcoran Ph.D. and the Duke Genomic Analysis and Bioinformatics Shared Resource for performing Gene Array analysis. We thank Erica Acton and Corey Nislow of the University of British Columbia for performing analysis both by Cytoscape using ClueGO and SIGORA. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammond, T.G., Allen, P.L. & Birdsall, H.H. Gene Pathways Analysis of the Effects of Suspension Culture on Primary Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30, 951–963 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9658-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-018-9658-x