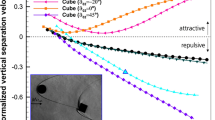
Abstract
The European participation in manned spaceflight had a strong impact on research in the natural sciences because weightlessness became available as experimental condition. Preparation for Spacelab required many decisions on organization, funding and allocation of resources. Lessons were learned from results obtained in precursors like Skylab or in unmanned programs such as TEXUS. ESA with scientists from the major disciplines instituted Working Groups that acted as consultant bodies. European experiment hardware has been realized by industry using specifications and not, traditionally, by evolution in a laboratory. The development of the Fluid Physics Module preceded many instruments for liquid research in space. The training of Payload Specialists for the operation of the FPM included theory of fluids and laboratory instruction. The dynamics of spacecraft with a partially filled tank can be studied in weightlessness only. Observation of the liquid behaviour inside the tank is a challenging problem but the momentum of the rigid part of the spacecraft can be tracked accurately. Analytical expressions for transient liquid flow in a moving tank should be identified, together with the tank motion. A validated model of liquid momentum transfer during spacecraft manoeuvres will make many missions more efficient and less costly. Sloshsat FLEVO was flown to provide reference data for this purpose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, H.N., ed.: The Dynamic Behavior of Liquids in Moving Containers. NASA SP-106, Washington DC (extensively revised and updated by F.T. Dodge, SwRI, 2001) (1966)
Ceronetti, G., Rovera, G.: The fluid physics module: a contribution to materials science and physics in space. In: Conf. Material Sciences in Space, Proceedings, ESA SP-142, pp. 137–147, June (1979)
CNES-ESA: Proceedings of the Conference on Attitude Control of Space Vehicles: Technological and Dynamical Problems Associated with the Presence of Liquids, Toulouse, France, Oct. 10–12. Proceedings, ESA SP-129 (1977)
Dodge, F.T., et al.: Fluid Physics, Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Experiments in Space. NASA CR-134742, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio TX, January (1975)
Hastings, G.A., Hill, D.W., Seebold, J.G., Satterlee, H.M.: The Literature of Low-G Propellant Behavior. Lockheed Missiles & Space Company Report, LMCS-A874730, May (1967)
Ibrahim, R.A.: Liquid Sloshing Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2005)
Kong, E.M., Saenz-Otero, A., Nolet, S., Berkovitz, D.S., Miller, D.W., Sell, S.W.: SPHERES as a formation flight algorithm development and validation testbed: current progress and beyond. In: 2nd Conf. Formation Flying Missions and Technologies, Washington D.C., Sep. 14–16, pp. 1–13 (2004)
Lamb, H.: Hydrodynamics, 6th edn. Dover, New York (1945)
Meyer, R.E.: Introduction to Mathematical Fluid Dynamics. Wiley, New York (1971)
Moses, J.L., Fogal, G.L., Scollon, T.R. Jr: Atmospheric cloud physics laboratory thermal control. J. Eng. Industr. 101, 191–196 (1979)
Prins, J.J.M.: Sloshsat FLEVO project, flight, and lessons learned, 56th international astronautical congress, Fukuoka, Japan, Oct. 2005. Proceedings [CD-ROM], Paper IAC-05-B5.5.05 (2005)
Staff of LAMF/Etsia and NLR: A preliminary Study of a Fluid Science Laboratory for Spacestation (Columbus), Parts 1–4, NLR, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, NLR TR-87023L, January (1987)
Veldman, A.E.P., Gerrits, J., Luppes, R., Helder, J.A., Vreeburg, J.P.B.: The numerical simulation of liquid sloshing on board spacecraft. J. Comput. Physics. 224, 82–99 (2007)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Summary Review of Microgravity Fluid Science Experiments. Extended Abstracts. ESA, Paris (1986a)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Observations on behaviour of liquid in weightlessness. In: Conf. Fluid Dynamics and Space. Rhode-St-Genèse, Belgium, June. Proceedings, ESA SP-265, pp.129–136 (1986b)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: The wet satellite model experiment. In: ESA SP-1132, 4 (1994)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Dynamics and control of a spacecraft with a moving, pulsating ball in a spherical cavity. Acta Astronautica. 40(512), 257–274 (1997)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Acceleration measurements on Sloshsat FLEVO for liquid force and location determination, In: 4th Conf. Spacecraft Guidance, Navigation and Control Systems, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, Oct. 18–21, 1999. Proceedings, ESA SP-425, pp. 579–585 (1999)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Diagnosis of water motion in the Sloshsat FLEVO tank. MSSU Journal. 2, 4 (2000)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Measured states of Sloshsat FLEVO, 56th International Astronautical Congress, Fukuoka, Japan, October. Proceedings [CD-ROM], Paper IAC-05-C1.2.09 (2005)
Vreeburg, J.P.B.: Sloshsat spacecraft calibration at stationary spin rates. J Spacecr. Rockets. 45(1), 65–75 (2008)
Vreeburg, J.P.B., Soo, D.N. (eds.) Proc. colloquium on sloshsat and Liquid dynamics in spacecraft. Estec, Noordwijk (NL),16–17 November, ESA WPP 158 (1998)
Vreeburg, J.P.B., Veldman, A.E.P.: Transient and sloshing motions in an unsupported container. In: Monti, R. (ed.) Fluid Physics in Microgravity, pp. 293–321. Taylor and Francis, New York (2001)
Vreeburg, J.P.B., Delil, A.A.M., Huijser, R.H., van den Assem, D.: Fluid Physics Instrumentation Study, Final Report (4 Volumes), ESA CR(P)-2133, Paris, France (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ELGRA-Medal Award in Physical Sciences 2007, presented at the ELGRA Biennial Symposium; September 2007, Florence, Italy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vreeburg, J.P.B. Liquid Dynamics from Spacelab to Sloshsat. Microgravity Sci. Technol 21, 11–20 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-008-9050-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-008-9050-3