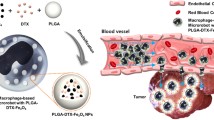
Abstract
In the present work, we prepare and evaluate a cell-based microrobot for active drug delivery to tumors. The microrobots are fabricated using the engulfment activity of immune macrophages with drug-loaded magnetic liposomes (MNP-DLs) via phagocytosis. The synthesized MNP-DLs and the microrobots have high energy absorbance to NIR light with increased drug release rate after laser irradiation. The tumor killing ability of the prepared microrobots is validated on a colorectal cancer cell line. In addition, the active tumor targeting function by an external electromagnetic actuating (EMA) system and chemotaxis is verified. Experiment results show that a single microrobot can be manipulated by the EMA system to obtain the average velocity of approximately 11 μm/s, and the robots can cross the membranes mimicking the blood barrier to tumor chemo-attractants with the infiltration rate up to 74%. Consequently, this study proposes and analyzes an innovative aspect of the developed therapeutic cellular micro-platform for active tumor targeting and externally triggered drug delivery.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behkam B, Sitti M (2007) Bacterial flagella-based propulsion and on/off motion control of microscale objects. Appl Phys Lett 90:023902
Zhang L, Abbott JJ, Dong L, Kratochvil BE, Bell D, Nelson BJ (2009) Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl Phys Lett 94:064107
Felfoul O, Mohammadi M, Taherkhani S, de Lanauze D, Zhong Xu Y, Loghin D et al (2016) Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions. Nat Nanotechnol 11:941–947
Sitti M (2009) Miniature devices: voyage of the microrobots. Nature 458:1121–1122
Taherkhani S, Mohammadi M, Daoud J, Martel S, Tabrizian M (2014) Covalent binding of Nanoliposomes to the surface of Magnetotactic Bacteria for the synthesis of self-propelled therapeutic agents. ACS Nano 8:5049–5060
Martel S, Mohammadi M, Felfoul O, Lu Z, Pouponneau P (2009) Flagellated Magnetotactic Bacteria as controlled MRI-trackable propulsion and steering Systems for Medical Nanorobots Operating in the human microvasculature. Int J Robot Res 28:571–582
Kojima M, Zhang Z, Nakajima M, Ooe K, Fukuda T (2013) Construction and evaluation of bacteria-driven liposome. Sensors Actuators B Chem 183:395–400
Park SJ, Park SH, Cho S, Kim DM, Lee Y, Ko SY et al (2013) New paradigm for tumor theranostic methodology using bacteria-based microrobot. Sci Rep 3:3394
Uthaman S, Zheng S, Han J, Choi YJ, Cho S, Nguyen VD et al (2016) Preparation of engineered Salmonella Typhimurium-driven hyaluronic-acid-based microbeads with both chemotactic and biological targeting towards breast Cancer cells for enhanced anticancer therapy. Adv Healthc Mater 5:288–295
Kojima M, Zhang Z, Nakajima M, Fukuda T (2012) High efficiency motility of bacteria-driven liposome with raft domain binding method. Biomed Microdevices 14:1027–1032
Park SJ, Bae H, Ko SY, Min J-J, Park J-O, Park S (2013) Selective bacterial patterning using the submerged properties of microbeads on agarose gel. Biomed Microdevices 15:793–799
Zhang Z, Li Z, Yu W, Li K, Xie Z, Shi Z (2013) Propulsion of liposomes using bacterial motors. Nanotechnology 24:185103
Carlsen RW, Edwards MR, Zhuang J, Pacoret C, Sitti M (2014) Magnetic steering control of multi-cellular bio-hybrid microswimmers. Lab Chip 14:3850–3859
Zhuang J, Wright Carlsen R, Sitti M (2015) pH-taxis of biohybrid microsystems. Sci Rep 5:11403
Choi M-R, Stanton-Maxey KJ, Stanley JK, Levin CS, Bardhan R, Akin D et al (2007) A cellular Trojan horse for delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles into tumors. Nano Lett 7:3759–3765
Nguyen VD, Han J, Go G, Zhen J, Zheng S, Le VH et al (2017) Feasibility study of dual-targeting paclitaxel-loaded magnetic liposomes using electromagnetic actuation and macrophages. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:1226–1236
Choi J, Kim HY, Ju EJ, Jung J, Park J, Chung HK et al (2012) Use of macrophages to deliver therapeutic and imaging contrast agents to tumors. Biomaterials 33:4195–4203
Fu J, Wang D, Mei D, Zhang H, Wang Z, He B et al (2015) Macrophage mediated biomimetic delivery system for the treatment of lung metastasis of breast cancer. J Control Release 204:11–19
Li D, Choi H, Cho S, Jeong S, Jin Z, Lee C et al (2015) A hybrid actuated microrobot using an electromagnetic field and flagellated bacteria for tumor-targeting therapy. Biotechnol Bioeng 112:1623–1631
Han J, Zhen J, Nguyen VD, Go G, Choi Y, Ko SY et al (2016) Hybrid-actuating macrophage-based microrobots for active Cancer therapy. Sci Rep 6:28717
Mura S, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2013) Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat Mater 12:991–1003
Racuciu M, Creanga DE, Airinei A (2006) Citric-acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biological applications. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter 21:117–121
Muthu MS, Kulkarni SA, Raju A, Feng SS (2012) Theranostic liposomes of TPGS coating for targeted co-delivery of docetaxel and quantum dots. Biomaterials 33:3494–3501
Liu Y, Yang M, Zhang J, Zhi X, Li C, Zhang C et al (2016) Human induced pluripotent stem cells for tumor targeted delivery of gold Nanorods and enhanced Photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 10:2375–2385
Muthu MS, Kulkarni SA, Xiong J, Feng SS (2011) Vitamin E TPGS coated liposomes enhanced cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of docetaxel in brain cancer cells. Int J Pharm 421:332–340
Min JH, Kim ST, Lee JS, Kim K, Wu JH, Jeong J et al (2011) Labeling of macrophage cell using biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 109:07B309
Patel B, Gupta N, Ahsan F (2015) Particle engineering to enhance or lessen particle uptake by alveolar macrophages and to influence the therapeutic outcome. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 89:163–174
Huang W-C, Chiang W-H, Cheng Y-H, Lin W-C, Yu C-F, Yen C-Y et al (2015) Tumortropic monocyte-mediated delivery of echogenic polymer bubbles and therapeutic vesicles for chemotherapy of tumor hypoxia. Biomaterials 71:71–83
Li Z, Huang H, Tang S, Li Y, Yu X-F, Wang H et al (2016) Small gold nanorods laden macrophages for enhanced tumor coverage in photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 74:144–154
Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S (2014) Cell-mediated delivery of nanoparticles: taking advantage of circulatory cells to target nanoparticles. J Control Release 190:531–541
Pang L, Qin J, Han L, Zhao W, Liang J, Xie Z et al (2016) Exploiting macrophages as targeted carrier to guide nanoparticles into glioma. Oncotarget 14:37081–37091
DeNardo DG, Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E, Ruffell B, Shiao SL, Madden SF et al (2011) Leukocyte complexity predicts breast Cancer survival and functionally regulates response to chemotherapy. Cancer Discov 1:54–67
Nguyen VD, Zheng S, Le VH, Han J, Park JO Manipulation of tumor targeting cell-based microrobots carrying NIR light sensitive therapeutics using EMA system and chemotaxis, 2017 International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS)2017, pp. 1–6
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Industrial Technology Innovation Program [10060059, Externally Actuatable Nanorobot System for Precise Targeting and Controlled Releasing of Drugs] funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT) 2016M3A9E9941514.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 653 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du Nguyen, V., Le, V.H., Zheng, S. et al. Preparation of tumor targeting cell-based microrobots carrying NIR light sensitive therapeutics manipulated by electromagnetic actuating system and Chemotaxis. J Micro-Bio Robot 14, 69–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-018-0110-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-018-0110-5