Abstract
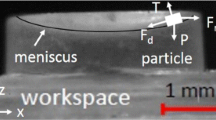
This work aims at increasing the velocity of micrometer scale particles controlled by non contact magnetic actuation systems. The particles are placed in an ambient environment (i.e. in air) to minimize the drag forces. However this approach raises two major issues: the repeatability and the precision of position are difficult to obtain in ambient environments due to the adhesion force between the substrate and the particle. This work proposes to use first a magnetic torque to provoke in-plane rotation of the particle to overcome adhesion between the particle and the substrate. Then a magnetic force is applied to induce the movement of the particle. To ensure that the static friction is broken and that the position of the particle can be controlled precisely a current pulse actuation mode is used. A dedicated closed loop control law which controls both the amplitude and the duration of the current simultaneously is proposed to ensure accurate positioning of the particle. Speed during pulse can reach 176 mm/s (more than 350 body lengths per second) in open loop on silicon substrates. Adhesion is overcome in 95% of the tests using the magnetic torque, compared to 66% using classical approaches. Precision of positioning of less than 20% of the size of the particle can be reached. The approach proposed in this paper is generic so that it can be easily transposed to other systems in the literature. The large number of experimental tests provides a deep understanding of the possibilities and challenges of magnetic actuation in ambient environments.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gauthier M, Régnier S (2011) Robotic micro-assembly. Wiley, Hoboken
Kharboutly M, Gauthier M (2013) High speed closed loop control of a dielectrophoresis-based system. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2013.6630761. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6630761&isnumber=6630547, pp 1446–1451
Chowdhury S, Jing W, Cappelleri D J (2015) Controlling multiple microrobots: recent progress and future challenges. J Micro-Bio Robot 10(1–4):1–11
Chaillet N, Régnier S (2013) Microrobotics for micromanipulation. Wiley, Hoboken
Bouchebout S, Bolopion A, Abrahamians J -O, Régnier S (2012) An overview of multiple dof magnetic actuated micro-robots. J Micro-Nano Mechatron 7(4):97–113
Diller E, Sitti M (2015) Untethered magnetic micromanipulation. Micro-and Nanomanipulation Tools
Feng L, Turan B, Ningga U, Arai F (2014) Three dimensional rotation of bovine oocyte by using magnetically driven on-chip robot. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, Chicago. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2014.6943225. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6943225&isnumber=6942370, pp 4668–4673
Khalil I S M, Ferreira P, Eleutério R, de Korte C L, Misra S (2014) Magnetic-based closed-loop control of paramagnetic microparticles using ultrasound feedback. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Hong Kong. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907411. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6907411&isnumber=6906581, pp 3807–3812
Mahoney AW, Nelson N D, Peyer K E, Nelson B J, Abbott J J (2014) Behavior of rotating magnetic microrobots above the step-out frequency with application to control of multi-microrobot systems. Appl Phys Lett 104(14):144101
Torres NA, Popa DO (2015) Cooperative control of multiple untethered magnetic microrobots using a single magnetic field source. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering (CASE), Gothenburg. https://doi.org/10.1109/CoASE.2015.7294330. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7294330&isnumber=7294025, pp 1608–1613
Tung H -W, Maffioli M, Frutiger D R, Sivaraman K M, Pane S, Nelson B J (2014) Polymer-based wireless resonant magnetic microrobots. IEEE Trans Robot 30(1):26–32
Floyd S, Pawashe C, Sitti M (2008) An untethered magnetically actuated micro-robot capable of motion on arbitrary surfaces. In: 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Pasadena. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2008.4543243. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4543243&isnumber=4543169, pp 419–424
Dkhil M, Kharboutly M, Bolopion A, Régnier S, Gauthier M (2017) Closed-loop control of a magnetic particle at the air - liquid interface. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 14(3):1387– 1399
Kummer M P, Abbott J J, Kratochvil B E, Borer R, Sengul A, Nelson B J (2010) OctoMag: an electromagnetic system for 5-DOF wireless micromanipulation. IEEE Trans Robot 26(6):1006– 1017
Diller E, Giltinan J, Jena P, Sitti M (2013) Three dimensional independent control of multiple magnetic microrobots. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Karlsruhe. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2013.6630929. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6630929&isnumber=6630547, pp 2576–2581
Ye Z, Diller E, Sitti M (2012) Micro-manipulation using rotational fluid flows induced by remote magnetic micro-manipulators. J. Appl. Phys. 112(6):064912
El-Gazzar AG, Al-Khouly LE, Klingner A, Misra S, Khalil ISM (2015) Non-contact manipulation of microbeads via pushing and pulling using magnetically controlled clusters of paramagnetic microparticles. In: 2015 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), Hamburg. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7353460. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7353460&isnumber=7353104, pp 778–783
Chung S E, Dong X, Sitti M (2015) Three-dimensional heterogeneous assembly of coded microgels using an untethered mobile microgripper. Lab Chip 15(7):1667–1676
Salmon H, Couraud L, Hwang G (2013) Swimming property characterizations of magnetic polarizable microrobots. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Karlsruhe. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2013.6631369. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6631369&isnumber=6630547, pp 5520–5526
Sitti M, Ceylan H, Hu W, Giltinan J, Turan M, Yim S, Diller E (2015) Biomedical applications of untethered mobile milli/microrobots. Proc IEEE 103(2):205–224
Ivan I, Hwang G, Agnus J, Chaillet N, Régnier S (2013) Nist and ieee challenge for magpier: the fastest mobile microrobots in the world. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 20(2):63–70
Bouchebout S, Bolopion A, Gauthier M, Régnier S (2014) Position control of a ferromagnetic micro-particle in a dry environment. In: IEEE/ASME International conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics, Besancon. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIM.2014.6878037. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6878037&isnumber=6878036, pp 1–6
Petruska A J, Edelmann J, Nelson B J (2017) Model-based calibration for magnetic manipulation. IEEE Trans Magn 53(7):1–6
Mulyokov K, Korznikov G, Abdulov R, Valiev R (1990) Magnetic hysteretic properties of submicron grained nickel and their variations upon annealing. J Magn Magn Mater 89(1–2):207– 213
Abbott J J, Peyer K E, Lagomarsino M C, Zhang L, Dong L X, Kaliakatsos I K, Nelson B J (2009) How should microrobots swim? Int J Robot Res 28(11–12):1434–1447
Abbott J J, Nagy Z, Beyeler F, Nelson B J (2007) Robotics in the small, part i: Microrobotics. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 14(2):92–103
Photron (2015) High speed camera products. www.photron.com
Jing W, Chen X, Lyttle S, Fu Z, Shi Y, Cappelleri DJ (2011) A magnetic thin film microrobot with two operating modes. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Shanghai. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2011.5980072. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5980072&isnumber=5979525, pp 96–101
Clarke D, Mohtadi C, Tuffs P (1987) Generalized predictive control part i. the basic algorithm. Automatica 23(2):137– 148
Frutiger D R, Vollmers K, Kratochvil B E, Nelson B J (2010) Small, fast, and under control: wireless resonant magnetic micro-agents. Int J Robot Res 29(5):613–636
Steager E B, Selman Sakar M, Magee C, Kennedy M, Cowley A, Kumar V (2013) Automated biomanipulation of single cells using magnetic microrobots. Int J Robot Res 32(3):346–359
Schürle S et al (2013) Three-dimensional, automated magnetic biomanipulation with subcellular resolution. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2013.6630762. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6630762&isnumber=6630547
Giltinan J, Diller E, Sitti M (2016) Programmable assembly of heterogeneous microparts by an untethered mobile capillary microgripper. Lab Chip 16(22):4445–4457
Shamma J S (2001) Gain scheduling. Wiley, Hoboken
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Labex ACTION project (contract “ANR-11-LABX-01-01”), by the “Région Franche Comté” and by the French RENATECH network and its FEMTO-ST technological facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolopion, A., Bouchebout, S. & Régnier, S. Fast, repeatable and precise magnetic actuation in ambient environments at the micrometer scale. J Micro-Bio Robot 13, 55–66 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-017-0101-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-017-0101-y