Abstract
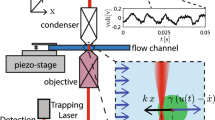
Laser-induced thermocapillary convection flows is a promising technique to manipulate micrometer size particles. Several parameters, such as the laser exposure time, the laser-particle distance, the particles’ diameter and the water layer thickness can be used to control the particles’ speed. This article deals with the study of the influence of the control parameters in the manipulation process using a systematic method: Design of Experiments (DoE). Additionally, a mathematical speed model of the manipulated particle as function of the mentioned parameters is proposed in order to enhance the manipulation accuracy and speed paving the way toward future works related to control strategies. Acid-washed glass beads ranging from 50 up to 150 microns were used for this purpose.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gauthier M, Andreff N, Dombre E (2014) Intracorporeal robotics. From milliscale towards nanoscale. Wiley edn
Xie H, Onal CD, Régnier S, Sitti M (2011) Atomic force microscopy based nanorobotics, springer tracts in advanced robotics, vol. 71, modelling, simulation setup building and experiments series edn
Bøggild P (2011) Micro and nano techniques for the handling of biological samples, p 141
Ongaro F, Scheggi S, Yoon C, van den Brink F, Oh SH, Gracias DH, Misra S (2016) J Micro-Bio Rob pp 1–8
Pieters RS, Tung HW, Nelson BJ (2017) Microrobots for active object manipulation. Springer International Publishing, pp 61– 72
Thakur A, Chowdhury S, Svec P, Wang C, Losert W, Gupta SK (2014) Int J Robot Res p 0278364914523690
Arai F, Maruyama H, Sakami T, Ichikawa A, Fukuda T (2003) IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 8 (1):3
Voldman J (2006) Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:425
Čemažar J, Miklavcic D, Kotnik T (2013) J Microelectron Electron Compon Mater 43:143
Kharboutly M, Gauthier M (2013). In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 1438–1443
Zemanek J, Drs J, Hurak Z (2014) In: IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics, pp 19–25
Jiang C, Mills JK (2015) IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 20(5):2350
Dkhil M, Kharboutly M, Bolopion A, Régnier S., Gauthier M (2015) IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering pp 1–13
Onda K, Arai F (2012)
Li X, Yang H, Wang J, Sun D (2015) Automatica 55:279
Chen H, Sun D (2012) IEEE Trans Robot 28(5):1069
Yang H, Gou X, Wang Y, Fahmy TM, Leung AYH, Lu J, Sun D (2015) Biophys J 108 (7):1645
Lin SCS, Mao X, Huang TJ (2012) Lab Chip 12(16):2766
Burns MA, Mastrangelo CH, Sammarco TS, Man FP, Webster JR, Johnsons BN, Foerster B, Jones D, Fields Y, Kaiser AR, Burke DT (1996)
Schatz MF, Neitzel GP (2001) Ann Rev Fluid Mech 33(1):93. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.33.1.93
Hu W, Ishii KS, Ohta AT (2011) Appl Phys Lett 99(9):094103. doi:10.1063/1.3631662
Hu W, Fan Q, Ohta AT (2013) Lab Chip 13(12):2285. doi:10.1039/C3LC50389E
Hu W, Fan Q, Ohta AT (2014) Robot Biomimetics 1(1):1. doi:10.1186/s40638-014-0014-3
Vela E (2010) Non-contact microscale manipulation using laser-induced convection flows. Ph.D. thesis, Universite Pierre et Marie Currie
Quispe J, Muñoz E, Vela E (2016) Appl Phys Lett 109(12):124102
Quispe JE, Inga JC, Muñoz E M, Régnier S, Vela E (2016) In: International Conference on manipulation automation and robotics at small scales (MARSS), (IEEE), pp. 1–6
Da Costa G (1993) Appl Opt 32(12):2143
Miniewicz A, Bartkiewicz S, Orlikowska H, Dradrach K (2016) Scientific Reports 6
Chraïbi H, Delville JP (2012) Phys Fluids 24(3):032102. 1994-present
Levich V, Krylov V (1969) Ann Rev Fluid Mech 1(1):293
Shin S, Jacobi I, Stone HA (2016). EPL Europhys Lett 113(2):24002
Montgomery DC (2012) Design and analysis of experiments, 8th edn
Shirley Dowdy DC, Stanley W (2004) Statistics for research, 3rd edn
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Programa Nacional de Innovación para la Competitividad y Productividad (FINCyT), Ministerio de la Producción, Perú, with grant #394-PNICP-PIBA-2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
E. Muñoz and J. Quispe have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, E., Quispe, J., Lambert, P. et al. Optimizing the speed of single infrared-laser-induced thermocapillary flows micromanipulation by using design of experiments. J Micro-Bio Robot 12, 65–72 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-017-0097-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-017-0097-3