Abstract
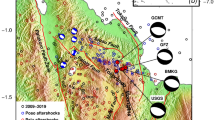
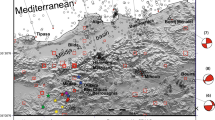
The present day tectonic deformation within Egypt is related to the regional tectonic forces of the surrounding plate boundaries including the African–Eurasian plate margin, the Red Sea plate margin and the Levant transform fault in addition to the local tectonics of Egypt. Based on the spatial distribution of earthquake epicenters in Egypt, the most seismically active areas are located in the Northern Red Sea, Gulf of Suez, Gulf of Aqaba and Mediterranean coastal zone. On 30 January 2012, a moderate earthquake of local magnitude ML 4.6 struck the northeast part of Egypt, at the entrance of Gulf of Suez. This event was felt in many areas surrounding the epicenter with low damage recorded. To understand the mechanism and the reflected irregularity of the evolved stress field concerning the Gulf of Suez area, calculation of source parameters and source mechanisms of this event are necessary. Moment tensor inversion is used to retrieve the fault plain solutions and the seismic moment by using waveforms recorded by the Egyptian National Seismic Network. The fit between observed and synthetic seismograms was computed for an elastic layered media and minimized using a least squares algorithm. The derived source mechanism indicates normal faulting along NNW–SSE trending faults, in agreement with the rifting of the northern Red Sea in its northern branches (Gulf of Suez and Gulf of Aqaba). The source parameters are estimated and the derived corner frequency f o for the P-wave spectra shows a value of 3.00 Hz. The seismic moment M o is 1.278 × 1023 Nm, the fault length r is 0.8 km, the average displacement D 0 is 0.023 m, and the value of the stress drop Δσ is 1.10 MPa. The source mechanism and source parameters imply the continuous activity of the Red Sea rift system at the Gulf of Suez opening.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Elenean KM (2004) Seismological aspects of recent earthquakes in the eastern mediterranean, article review. National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics, Helwan, p 100
Ambraseys NN, Melville CP, Adams RD (1994) The seismicity of Egypt. Cambridge Press, Arabia
Ben-Menahem A, Aboodi E (1971) Tectonic patterns in the northern Red Sea. J Geol Res 76(11):2674
Ben-Menahem A, Nur A, Vered M (1976) Tectonica, seismicity and structure of the Afro-Eurasian junction—the breaking of an incoherent plate. Phys Earth Planet Int 12:1–50
Bilham R (2006) Dangerous tectonics, fragile buildings, and tough decisions. Science 311:1873–1875
Bilham R, Gaur VK, Molnar P (2001) Himalayan seismic hazard. Science 293:1442–1444
Bosworth W, Taviani M (1996) Late Quaternary reorientation of stress field and extension direction in the southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt: evidence from uplifted coral terraces, mesoscopic fault arrays, and borehole breakouts. Tectonics 15:791–802
Bouchon M (2003) A review of the discrete wavenumber method. Pure Appl Geophys 160(3–4):445–465
Brune J (1970) Tectonic stress and the spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes. J Geophys Res 75:4997–5009
Brune J (1971) Correction. J Geophys Res 76:5002
Campus P, Faeh D (1997) Seismic monitoring of explosions: a method to extract information on the isotropic component of the seismic source. J Seismol 1:205–218
Cochran JR (1983) A model for development of Red Sea. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 67:41–67
Colletta B, Le Quellec P, Letouzey J, Moretti I (1988) Longitudinal evolution of the Suez rift structure (Egypt). Tectonophysics 153:221–233
Coutant O (1990) Program of numerical simulation AXITRA, Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique Report. University of Joseph Fourier (in French)
Daggett PH, Morgan P, Boulos FK, Hennin SF, El-Sherif AA, El-Sayed AA, Basta NZ, Melek YS (1986) Seismicity and active tectonics of the Egyptian Red Sea margin and the northern Red Sea. Tectonophysics 125:313–324
Dreger D, Woods B (2002) Regional distance seismic moment tensors of nuclear explosions. Tectonophysics 356(1–3):139–156
EGSMA (1981) Geologic map of Egypt 1: 2000000, Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority, Egypt
EL Hadidy S (1995) Crustal structure and its related causative tectonics in northern Egypt using geophysical data, Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Egypt
Fairhead JD, Girdler RW (1970) The seismicity of the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden and Afar triangle. Phil Trans R Soc A 267:49–74
Frohlich C (1994) Earthquakes with non-double-couple mechanisms. Science 264:804–809
Garfunkel Z, Bartov Y (1977) The tectonics of the Suez rift. Geol Surv Israel Bull 71:44
Gass IG (1977) The evolution of the Pan-African crystalline basement in NE Africa and south of Arabia. J Geol Soc Lond 134:129–138
Girdler RW, Styles P (1974) Two stages Red Sea floor spreading. Nature 247:7–11
Hanks TC, Ways M (1972) The use of body-wave spectra in the determination of seismic-source parameters. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62(1972):561–589
Hurukawa N. Murakami H, Seto N, Marzouk I, Megahed A, Ibrahim E (1997) Establishment of the seismological telemetric network at the southern part of the Gulf of Suez and the northern Red Sea. 10th International Seminar on Earthquake Prognostics, Cairo University, Extended Abstract, p 98
Julian BR, Miller AD, Foulger GR (1998) Non-double couple earthquake 1. Theory Rev Geophys 36:525–549
Keilis-Borok VI (1959) On the estimation of the displacement in an earthquake source and of source dimensions. Ann Geofis 12:205–214
Kikuchi M, Kanamori H (1991) Inversion of complex body waves-III. Bull Seis Soc Am 81:2335–2350
Le Pichon X, Francheteau J (1978) Plate-tectonic analysis of Red-Sea—Gulf of Aden Area. Tectonophysics 46:369–406
Lyberis N (1988) Tectonic evolution of the Gulf of Suez and the Gulf of Aqaba. Tectonophysics 153:209–220
Maamoun M, El-Khashab H (1978) Seismic studies of the Shedwan (Red Sea) Earthquake. Helwan Inst Astr Geophys Bull 171
Makris J, Rihm R (1991) Shear-controlled evolution of the Red sea: pull apart model. Tectonophysics 198:441–466
McKenzie D (1972) Active tectonics of the Mediterranean region. Geophys J Roy Ast Soc 30:109–185
McKenzie D, Davies D, Molnar P (1970) Plate tectonics of the Red Sea and East Africa. Nature 226:243–248
Megahed AS (1999) A seismological study of the southern part of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. MSc. thesis, Geology Department, Mansoura University, Egypt
Meshref WM (1990) Tectonic framework of Egypt. In: Rushdi S (ed) The geology of Egypt. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 113–155
Moustafa AM (1976) Block faulting in the Gulf of Suez. In: Fifth E (ed) G.P.C. Exploration Seminar, Cairo, pp 1–19
Piersanti A, Nostro C, Riguzzi F (2001) Active displacement field in the Suez–Sinai area: the role of postseismic deformation. EPSL 193:13–23
Reillinger R, Tocsoz N, McKlusky S, Barka A (2000) 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake was no surprise. GSA Today 10:1
Riguzzi F, Grazia P, Antonio P, Salah MM (2006) Current motion and short-term deformations in the Suez-Sinai area from GPS observations. J Geodyn 41:485–499
Roessler D, Krueger F, Ruempker G (2007) Inversion for seismic moment tensors in anisotropic media using standard techniques for isotropic media. Geophys J Int 169:136–148
Salamon A, Hofsetter A, Garfunkel Z, Ron H (1996) Seismicity of the eastern Mediterranean region; perspective from the Sinai subplate. Tectonophysics 262:239–305
Scherbaum F, Johnson J (1992) PITSA, programmable interactive toolbox for seismological analysis. In: Lee WHK (ed) IASPEI Software Library, vol 5. USA
Sileny J, Campus P, Panza GF (1996) Earthquake mechanism resolution by waveform inversion of a few local noisy records I. Synthetic tests. Geophys J Int 109:259–274
Sokos E, Zahradník J (2008) ISOLA: a Fortran code and a Matlab GUI to perform multiple-point source inversion of seismic data. Comput Geosci doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.005
Steckler MS (1985) Uplift and extension at the Gulf of Suez. Indications of induced mantle convection. Nature 317:135–139
Tapponnier P, Armijo R (1985) Seismotectonics of Northern Egypt. Terra Cognita 5:171 (Abstr.)
Thorne MS (2005) Broadband waveform modelling of deep mantle structure. Ph.D, Dissertation Thesis, Arizona State University, Arizona
Vavrycuk V (2007) On the retrieval of moment tensors from borehole data. Geoph Prospect 55(3):381–391
Yunga S, Lutikov A, Molchanov O (2005) Non-double-couple seismic sources, faults interaction and hypothesis of self-organized criticality. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 5:11–15
Zahradnik J, Plesinger A (2005) Long-period pulses in broadband records of near earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 95:1928–1939
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude and appreciation to their colleagues at the Seismology Department, Egyptian National Seismological Network ENSN who analyzed the waveform of the Gulf of Suez earthquake for use in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosny, A., Omar, K. & Ali, S.M. The Gulf of Suez earthquake, 30 January 2012, northeast of Egypt. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 24, 377–386 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-013-0244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-013-0244-2