Abstract
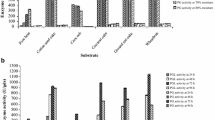
This study demonstrated that Bacillus licheniformis HDYM-03 and Bacillus megaterium HDYM-09, isolated from a liquid sample of flax retting pool, were able to produce pectinolytic enzymes using polysaccharides as substrates. Bacillus megaterium HDYM-09 produced pectin lyase that exhibited the highest activity of 2116.71 ± 11.55 U/mL. Bacillus licheniformis HDYM-03 produced pectate lyase that exhibited the highest activity of 611.21 ± 14.54 U/mL. Based on these findings, we constructed four retting systems to degrade the pectin substance. The results showed that the content of galacturonic acid in the mixed system was 529.21 μg/mL, the content of reducing sugar was 98.14 mg/mL, and the weight loss ratio of cells reached 19.49%, which were significantly higher than those in other systems. The mixed system has more advantages, and the utilization rate of degumming was higher, which further ensured that the degumming can be carried out efficiently and quickly. The mixed system exhibits feasible applications in the fiber and textile industry.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foulk JA, Rho D, Alcock MM et al (2011) Modifications caused by enzyme-retting and their effect on composite performance. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2011:179023
Akin DE (2013) Linen most useful: perspectives on structure, chemistry, and enzymes for retting flax. ISRN Biotech 2013:186534
Bai YK, Liu BY, He LF (2006) Pectinase and its applications in pulp and paper industry. Trans China Pulp Paper 21(2):88–91 (in Chinese)
Deng WK, Liu EP, Guo AP et al (2009) Study on characteristics of pectinase from a bacteria for degumming pineapple leaf fiber. Guangdong Agric Sci 9(6):190–193 (in Chinese)
Zheng K, Liu ZC, Duan SW et al (2012) Mechanism of the pectinases used for bast fibre bio-degumming. Curr Biotech 2(6):404–410 (in Chinese)
Huang H, Zhang X (2005) Effects of buffer system on laccase determination. Ind Microbiol 35(4):29–32 (in Chinese)
Wu CB, Cao YB, Wu HQ et al (2010) The application for Bacillus subtilis HW201 in flax retting-intermediate test. Plant Fiber Sci China 32(6):327–330 (in Chinese)
Ge JP, Ling HZ, Song G et al (2004) The study on isolation of pectinase-producing strains and its cultural conditions. China Biotechnol 24(8):93–95 (in Chinese)
Li ZM, Zhang HX, Bai ZH et al (2010) Advance in microbial pectinases research. Biotechnol Bull 3(1):42–49 (in Chinese)
Wang HL, Li XM, Ma YH et al (2014) Characterization and high-level expression of a metagenome-derived alkaline pectate lyase in recombinant Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 49(1):69–76
Zhuge B, Du GC, Zhuge J et al (2008) Properties of alkaline pectate lyase from recombinant strain E. coli JM109. Acta Microbiol Sin 48(1):121–125 (in Chinese)
Zhao D, Liu P, Pan C et al (2016) Flax retting by degumming composite enzyme produced by Bacillus licheniformis HDYM-04 and effect on fiber properties. J Text Inst 108(4):507–510
Ding J, Zhang X, Yao X et al (2010) Determination of sisal pectin content by carbazole colorimetric method. Food Res Dev 31(11):138–140 (in Chinese)
Wang J, Nie G, Li S et al (2010) Optimal wavelength for determining the content of reducing sugar by DNS method. Henan Agric Sci 4(1):115–118 (in Chinese)
Wang T, Qiu H, Chen H et al (2008) Exploration of the determination conditions of the content of d-galacturonic acid with the method of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS). J Anhui Agric Sci 36(16):6829–6832 (in Chinese)
Soriano M, Diaz P, Pastor F (2005) Pectinolytic systems of two aerobic sporogenous bacterial strains with high activity on pectin. Curr Microbiol 50(2):114–118
Doyle EA, Lambert KN (2002) Cloning and characterization of an esophageal-gland-specific pectate lyase from the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15(6):549–554
Wang Q, Chen A, Fang G et al (2017) Isolation of Bacillus cereus P05 and Pseudomonas sp. X12 and their application in the ramie retting. Ind Crops Prod 97(3):518–524
Sharma N, Rathore M, Sharma M (2012) Microbial pectinase: sources, characterization and applications. Rev Environ Sci Bio 12(1):45–60
Chiliveri SR, Koti S, Linga VR (2016) Retting and degumming of natural fibers by pectinolytic enzymes produced from Bacillus tequilensis SV11-UV37 using solid state fermentation. SpringerPlus 5:559
Biswapriya D, Kalyan C, Sagarmoy G et al (2012) Effect of efficient pectinolytic bacterial isolates on retting and fibre quality of jute. Ind Crops Prod 36(1):415–419
Zhao D, Liu PF, Pan C et al (2016) Bacterial succession and metabolite changes during flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) retting with Bacillus cereus HDYM-02. Sci Rep 6:31812
Di Candilo M, Bonatti PM, Guidetti C et al (2010) Effects of selected pectinolytic bacterial strains on water-retting of hemp and fibre properties. J Appl Microbiol 108(1):194–203
Mukhopadhyay A, Dutta N, Dhrubajyoti et al (2013) Degumming of ramie fiber and the production of reducing sugars from waste peels using nanoparticle supplemented pectate lyase. Bioresour Technol 137:202–208
Yu W, Wang G, Han J et al (2012) Application of functional degumming bacteria in hemp retting. Hubei Agric Sci 51(21):4772–4775 (in Chinese)
Brühlmann F, Kim KS, Zimmerman W et al (1994) Pectinolytic enzymes from Actinomycetes for the degumming of ramie bast fibers. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(6):7–12
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31270534, 31770538), the National Natural Science Youth Foundation of China (No. 31300355), and the Post-Doctorate Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. LBH-Z15214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, J., Yang, Z., Du, R. et al. Production of Pectinolytic Enzymes by Two Bacillus spp. Strains and Their Application in Flax Degumming. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 25, 413–419 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-018-0181-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-018-0181-3