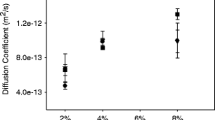
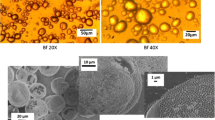
Abstract
Effects of water-soluble co-solvents(WSCs)on the properties of water/oil Pickering emulsions were investigated. Pickering emulsions were prepared in the system of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene(TMB)/ hydrophobic silica/ water with varied concentrations of WSCs(ethanol, acetic acid and glycerin). Mean droplet diameter distributions of the obtained emulsions were studied to investigate the effects of WSCs types and concentrations. The results demonstrated that mean droplet diameter distributions decreased at first and then increased with the increase of WSC concentration. Moreover, the effect of WSC concentration on the phase inversion locus was further investigated. At the same time, infrared radiation(IR)spectrometer was used to investigate the mechanism. The results showed that the WSC attaching on hydrophobic silica changed the wettability of the particles, which facilitated the formation and phase inversion of the emulsion. The hydrogen bonds between the co-solvent groups attaching on the solid particles made a great effect on the droplet size of the emulsion and strengthened the interaction among emulsifiers. Overall, proper WSC was in favor of the stability of Pickering emulsion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aveyard R, Binks B P, Clint J H. Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles [J]. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2003, 100: 503–546.
Binks B P. Particles as surfactants—Similarities and differences [J]. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci, 2002, 7(1): 21–41.
Binks B P, Horozov T S. Colloidal Particles at Liquid Interfaces[M]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2006.
Finkle P, Draper H D, Hildebrand J H. The theory of emulsification [J]. J Am Chem Soc, 1923, 45(12): 2780–2788.
Giermanska-Kahn J, Schmitt V, Binks B P et al. A new method to prepare monodisperse Pickering emulsions [J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18: 2515–2518.
Binks B P, Whitby C P. Nanoparticle silica-stabilized oilin-water emulsions: Improving emulsion stability [J]. Colloids Surf A, 2005, 253: 105–115.
Binks B P, Lumsdon S O. Pickering emulsions stabilized by monodisperse latex particles: Effects of particle size [J]. Langmuir, 2001, 17: 4540–4547.
Frijters S, Günther F, Harting J. Domain and droplet sizes in emulsions stabilized by colloidal particles [J]. Phys Rev E, 2014, 90: 042307.
Destribats M, Gineste S, Laurichesse E et al. Pickering emulsions: What are the main parameters determining the emulsion type and interfacial properties? [J] Langmuir, 2014, 30: 9313–9326.
Williams M, Warren N J, Fielding L A et al. Preparation of double emulsions using hybrid polymer/silica particles: New Pickering emulsifiers with adjustable surface wettability [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2014, 6: 20919–20927.
Melle S, Lask M, Fuller G G. Pickering emulsions with controllable stability [J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21: 2158–2162.
Binks B P, Rodrigues J A. Influence of surfactant structure on the double inversion of emulsions in the presence of nanoparticles[J]. Colloids Surf A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2009, 345: 195–201.
Binks B P, Philip J, Rodrigues J A. Inversion of silicastabilized emulsions induced by particle concentration [J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21: 3296–3302.
Binks B P, Lumsdon S O. Influence of particle wettability on the type and stability of surfactant-free emulsions [J]. Langmuir, 2000, 16: 8622–8631.
Yang X, Liang Y, Cheng Y et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin over carbon nanotube-supported Ru catalysts assembled at the interfaces of emulsion droplets [J]. Catal Commun, 2014, 47: 28–31.
Moller K, Wienhofer G, Westerhaus F et al. Oxidation of 1, 2,4-trimethylbenzene(TMB),2,3,6-trimethylphenol(TMP) and 2-methylnaphthalene to 2,3,5-trimethylbenzoquinone (TMBQ)and menadione(vitamin K3)[J]. Catal Today, 2011, 173: 68–75.
Binks B P, Lumsdon S O. Catastrophic phase inversion of water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by hydrophobic silica [J]. Langmuir, 2000, 16: 2539–2547.
Zhang R, Yang L, Tu R et al. Emulsion phase inversion from oil-in-water(1)to water-in-oil to oil-in-water(2)induced by in situ surface activation of CaCO3 nanoparticles via adsorption of sodium stearate [J]. Colloids Surf A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 477: 55–62.
Ling N N A, Haber A, May E F et al. NMR studies of emulsion microstructure approaching the phase inversion point [J]. Colloids Surf A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 462: 244–251.
Lv G, Wang F, Cai W et al. Influences of addition of hydrophilic surfactants on the W/O emulsions stabilized by lipophilic surfactants [J]. Colloids Surf A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 457: 441–448.
Bus J, Groeneweg F, Vader F. Effect of hydrogen bonding on water in oil emulsion properties [J]. Prog Colloid Polym Sci, 1990, 82: 122–130.
Ghosh S, Tran T, Rousseau D. Comparison of Pickering and network stabilization in water-in-oil emulsions [J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27: 6589–6597.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China(“973” Program, No.2012CB720302).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Xie, S., Cai, W. et al. Effects of water-soluble co-solvent on properties of W/O pickering emulsions. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 22, 218–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-016-2807-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-016-2807-7