Abstract
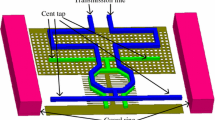
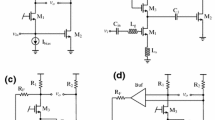
A 130 nm CMOS complementary-conducting-strip transmission line(CCS-TL)based multi-stage amplifier beyond 100 GHz was presented in this paper. Different structural parameters were investigated to achieve higher quality factor for the matching circuits. Moreover, CCS-TL based Marchand balun was implemented to achieve higher output power. The measured small signal gain was higher than 5 dB from 101 GHz to 110 GHz. DC power consumption was 67.2 mW with VD=1.2 V, and the chip size including contact PADs was 1.12 mm×0.81 mm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicolson S T, Tomkins A, Tang K W et al. A 1. 2 V, 140 GHz receiver with on-die antenna in 65 nm CMOS [C]. In: IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium. Atlanta, USA, 2008.
Khanpour M, Tang K W, Garcia P et al. A wideband Wband receiver front-end in 65 nm CMOS [J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(8): 1717–1730.
Xu Z, Gu Q J, Chang M C F. 200 GHz CMOS amplifier working close to device fT [J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(11): 639–641.
Momeni O. A 260 GHz amplifier with 9.2 dB gain and -3.9 dBm saturated power in 65 nm CMOS [C]. In: IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. San Francisco, USA, 2013.
Lu C, Mahmoudi R, von Roermund A H M et al. A 107 GHz LNA in 65 nm CMOS with inductive neutralization and slow-wave transmission lines [C]. In: IEEE Symposium on Communications and Vehicular Technology. Eindhoven, the Netherlands, 2012.
Yoshihara Y, Fujimoto R, Ono N et al. A 60-GHz CMOS power amplifier with Marchand balun-based parallel power combiner [C]. In: IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference. Fukuoka, Japan, 2008.
Chen C C, Tzuang C K C. Synthetic quasi-TEM meandered transmission lines for compacted microwave integrated circuits [J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2004, 52(6): 1637–1647.
Chiang M J, Wu H S, Tzuang C K C. Design of synthetic Quasi-TEM transmission line for CMOS compact integrated circuit [J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2007, 55(12): 2512–2520.
Wu Y H, Chiang M J, Wu H S et al. 24-GHz 0.18-µm CMOS four-stage transmission line-based amplifier with high gain-area efficiency [C]. In: IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference. Macau, China, 2008.
Hsieh K A, Wu H S, Tsai K H et al. A dual-band 10/24-GHz amplifier design incorporating dual-frequency complex load matching [J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(6): 1649–1657.
Yang S H, Tzuang C K C. 130-nm CMOS K-band twoelement differential power-combining oscillators [J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(3): 1174–1185.
Cheng Y, Hu C. MOSFET Modeling and BSIM3 User’s Guide [M]. Springer, USA, 1999.
Heydari B, Bohsali M, Adabi E et al. Low-power mmwave components up to 104 GHz in 90 nm CMOS [C]. In: IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. San Francisco, USA, 2007.
Nicolson S T, Voinigescu S P. Methodology for simultaneous noise and impedance matching in W-band LNAs [C]. In: IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium. San Antonio, USA, 2006.
Masud M A, Zirath H, Ferndahl M et al. 90 nm CMOS MMIC amplifier [C]. In: IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium. Atlanta, USA, 2008.
Fahimnia M, Mahmoud M T, Wan Y et al. A 59-66 GHz highly stable millimeter wave amplifier in 130 nm CMOS technology [J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2011, 21(6): 320–322.
Jin J D, Hsu S S H. A miniaturized 70-GHz broadband amplifier in 0.13-µm CMOS technology [J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(12): 3086–3092.
Kim Y, Kwon Y. A 60 GHz cascode variable-gain lownoise amplifier with phase compensation in a 0.13 µm CMOS technology [J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2012, 22(7): 372–374.
Wang T P, Wang H. A 71-80 GHz amplifier using 0.13-µm CMOS technology [J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2007, 17(9): 685–687.
Doan C H, Emami S, Niknejad A M et al. Millimeter-wave CMOS design [J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(1): 144–155.
Kuo H C, Yang C Y, Yeh J F et al. Design of a 0.13-µm Vband millimeter-wave CMOS low-noise amplifier and measurement methodology [C]. In: IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference. Macau, China, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (“863” Program, No. 2015AA01A703).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Wu, HS., Li, G. et al. 130 nm CMOS multi-stage synthetic transmission line based amplifier beyond 100 GHz. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 22, 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-016-2743-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-016-2743-6