Abstract
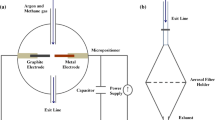
Carbon encapsulated iron nanoparticles (CEINPs) with very thin shells and good core-shell structures were prepared by DC arc discharge at argon intake temperature (AIT) of 800 °C. The results of high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscope, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) characterizations on the product B show that the thickness of the carbon shells of CEINPs in the product B is in the range of ca. 0.5–5.3 nm, i. e., which can be as thin as only two layers of graphite. The average diameter of the CEINPs is about 24.7 nm. The total content of Fe element in the product B is 77.0 wt%. The saturation magnetization (M s) and coercivity (H c) of the product B are 107.4 emu/g and 143 Oe, respectively. The formation of the CEINPs in the product B is discussed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi G M, Zhang Z D, Yang H C. Al2O3/Fe2O3 compositecoated polyhedral Fe nanoparticles prepared by arc discharge[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 384(1/2): 296–299.
Bystrzejewski M, Károly Z, Szépvölgyi J et al. Continuous synthesis of controlled size carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46(12): 2408–2417.
Wang Z H, Zhang Z D, Choi C J et al. Structure and magnetic properties of Fe(C) and Co(C) nanocapsules prepared by chemical vapor condensation [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2003, 361(1/2): 289–293.
Zhu G X, Wei X W, Jiang S. A-facile route to carboncoated nickel-based nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2007, 17(22): 2301–2306.
Scott J H J, Chowdary K, Turgut Z et al. Neutron powder diffraction of carbon-coated FeCo alloy nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 85(8): 4409–4411.
Wang B B, Kong Q S, Quan F Y et al. Preparation of nanostructured porous carbon composite fibers from ferrum alginate fibers [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2013, 128(3): 2216–2223.
Bystrzejewski M, Cudzilo S, Huczko A. Thermal stability of carbon-encapsulated Fe-Nd-B nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 423(1/2): 74–76.
Seo W S, Lee J H, Sun X et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents [J]. Nature Materials, 2006, 5(12): 971–975.
Qiu J S, Li Y F, Wang Y P et al. Preparation of carboncoated magnetic iron nanoparticles from composite rods made from coal and iron powders [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2004, 86(3): 267–274.
Yu C, Qiu J S. Preparation and magnetic behavior of carbon-encapsulated cobalt and nickel nanoparticles from starch [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2008, 86(8): 904–908.
Liu X G, Or S W, Sun Y P et al. Influence of a graphite shell on the thermal, magnetic and electromagnetic characteristics of Fe nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 548: 239–244.
Wang Z F, Xiao P F, He N Y et al. Synthesis and characteristics of carbon encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles produced by a hydrothermal reaction [J]. Carbon, 2006, 44(15): 3277–3284.
Zhang F, Cui L, Lin K et al. Preparation of carbonencapsulated iron nanoparticles in high yield by DC arc discharge and their characterization [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 553(4): 367–374.
Wu W Z, Zhu Z P, Liu Z Y et al. Preparation of carbonencapsulated iron carbide nanoparticles by an explosion method [J]. Carbon, 2003, 41(2): 317–321.
Ma C, Luo B, Song H H et al. Preparation of carbonencapsulated metal magnetic nanoparticles by an instant pyrolysis method [J]. New Carbon Materials, 2010, 25(3): 199–204.
Wang Z H, Han Z, Geng D Y et al. Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption of carbon-coated Sn nanorods [J]. Chemical Physics Letter, 2010, 489(4/5/6): 187–190.
Rechenberg H R, Coaquira J A H, Marquina C et al. Mössbauer and magnetic characterization of carbon-coated small iron particles [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2001, 226/227/228/229/230: 1930–1932.
Wu Z S, Ren W C, Gao L B et al. Synthesis of graphene sheets with high electrical conductivity and good thermal stability by hydrogen arc discharge exfoliation [J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(2): 411–417.
Zhang X F, Dong X L, Huang H et al. High permittivity from defective carbon-coated Cu nanocapsules [J]. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18(27): 275701.
Zhang Z D, Yu J L, Zheng J G et al. Structure and magnetic properties of boron-oxide-coated Fe(B) nanocapsules prepared by arc discharge in diborane [J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2001, 64(2): 024404.
Cui S, Scharff P, Siegmund C et al. Investigation on preparation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by DC arc discharge under N2 atmosphere [J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(5/6): 931–939.
Chung F C, Wu R J, Cheng F C. Fabrication of a Au@SnO2 core-shell structure for gaseous formal-dehyde sensing at room temperature [J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 190: 1–7.
Park E, Zhang J Q, Thomson S et al. Characterization of phases formed in the iron carbide process by X-Ray diffraction, Mössbauer, X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy analyses [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2001, 32B(5): 839–845.
Cao Q, Coulombe S. Organic layer-coated metal nanoparticles prepared by a combined arc evaporation/condensation and plasma polymerization process [J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2007, 16(2): 240–249.
Edwards E R, Antunes E F, Botelho E C et al. Evaluation of residual iron in carbon nanotubes purified by acid treatments [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 258(2): 641–648.
Zhou J S, Song H H, Chen X H et al. Oxidation conversion of carbon-encapsulated metal nanoparticles to hollow nanoparticles [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(15): 3730–3737.
Liu X G, Ou Z Q, Geng D Y et al. Influence of a graphite shell on the thermal and electromagnetic characteristics of FeNi nanoparticles [J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(3): 891–897.
Chaira D, Mishra B K, Sangal S et al. Efficient synthesis and characterization of iron carbide powder by reaction milling [J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 191(1/2): 149–154.
Pol V G, Wildermuth G, Felsche J et al. Sonochemical deposition of Au nanoparticles on titania and the significant decrease in the melting point of gold [J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2005, 5(6): 975–979.
Panchal V, Neergat M, Bhandarkar U. Synthesis and characterization of carbon coated nanoparticles produced by a continuous low-pressure plasma process [J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2011, 13(9): 3825–3833.
Kim S, Sergiienko R, Shibata E et al. Iron-included carbon nanocapsules coated with biocompatible poly(ethylene glycol) shells [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 122(1): 164–168.
Bystrzejewski M, Grabias A. Tailoring phase composition in carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles [J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(1): 152–156.
Sajitha E P, Prasad V, Subramanyam S V et al. Synthesis and characteristics of iron nanoparticles in a carbon matrix along with the catalytic graphitization of amorphous carbon [J]. Carbon, 2004, 42(14): 2815–2820.
Weissker U, Lofler M, Wolny F et al. Perpendicular magnetization of long iron carbide nanowires inside carbon nanotubes due to magnetocrystalline anisotropy [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106(5): 054909.
Jun Y W, Seo J W, Cheon J W. Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(2): 179–189.
Sun X C, Gutierrez A, Jose Yacaman M et al. Investigations on magnetic properties and structure for carbon encapsulated nanoparticles of Fe, Co, Ni [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 286(1): 157–160.
Sun G L, Li X J, Wang Q Q et al. Synthesis of carboncoated iron nanoparticles by detonation technique [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(5): 519–522.
Uo M, Tamura K, Sato Y et al. The cytotoxicity of metalencapsulating carbon nanocapsules[J]. Small, 2005, 1(8/9): 816–819.
Taylor A, Krupskaya Y, Costa S et al. Functionalization of carbon encapsulated iron nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2010, 12(2): 513–519.
Francüois M, Mélanie B, Souad A M et al. Electrode surface confinement of self-assembled enzyme aggregates using magnetic nanoparticles and its application in bioelectrocatalysis [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(1): 187–194.
Elliott B R, Host J J, Dravid V P. A descriptive model linking possible formation mechanisms for graphiteencapsulated nanocrystals to processing parameters [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1997, 12(12): 3328–3334.
Gamaly E G, Ebbesen T W. Mechanism of carbon nanotube formation in the arc discharge [J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1995, 52(3): 2083–2089.
Guan L, Cui L, Lin K et al. Preparation of few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets by DC arc discharge under nitrogen atmosphere of high temperature [J]. Applied Physics A: Materials Science and Processing, 2011, 102(2): 289–294.
Hatakeyama R, Jeong G H, Kato T et al. Effects of micro- and macro-plasma-sheath electric fields on carbon nanotube growth in a cross-field radio-frequency discharge [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 96(11): 6053–6060.
Ohno M, Yoh K. Micromagnetic simulation of magnetization reversal process and stray field behavior in Fe thin film wire [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(12):123908.
House J E. Inorganic Chemistry[M]. Elsevier, USA, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cui Shen, born in 1958, male, Dr, Prof.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, S., Zhang, L., Cui, L. et al. Preparation of carbon encapsulated iron nanoparticles with very thin shells by DC arc discharge. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 21, 11–18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-015-2375-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-015-2375-2