Abstract
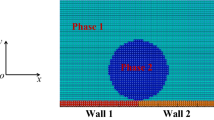
A droplet undergoes spreading, rebounding or splashing when it impacts solid boundary, which is a typical phenomenon of free surface flow that exists widely in modern industry. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method is applied to numerically study the dynamical behaviors of the droplet impacting solid boundary, and both the spreading and rebounding phenomena of the droplet are reproduced in the simulation. The droplet deformation, flow fields and pressure fields inside the droplet at different moments are analyzed. Two important factors, the initial velocity and diameter, are discussed in determining the maximum spreading factor, revealing that the maximum spreading factor increases with the increase of the impact velocity and droplet diameter respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi Mingheng. Behavior of a liquid droplet impinging on a solid surface[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 1985, 17(5): 419–425 (in Chinese).
Kim H Y, Chun J H. The recoiling of liquid droplets upon collision with solid surfaces[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2000, 13(3): 643–659.
He Zheng, Gao Ye, Gu Xuan et al. Investigating a dropletwall collision model[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2009, 30(3): 267–270 (in Chinese).
Zhang Xiaoguang, Basaran Osman A. Dynamic surface tension effects in impact of a drop with a solid surface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1997, 187(1): 166–178.
Pasandideh Fard M, Qiao Y M, Chandra S et al. Capillary effects during droplet impact on a solid surface[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1996, 8(3): 650–659.
Fujimoto Hitoshi, Shiotani Yu, Tong Albert Y et al. Threedimensional numerical analysis of the deformation behavior of droplets impinging onto a solid substrate[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2007, 33(3): 317–332.
Shen Shengqiang, Li Yan, Guo Yali. Numerical simulation of droplet impacting on isothermal flat solid surface[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2009, 30(12): 2116–2118 (in Chinese).
Castrejón-Pita J R, Betton E S, Kubiak K J et al. The dynamics of the impact and coalescence of droplets on a solid surface[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2011, 5(1): 014112.
Sehgal B R, Nourgaliev R R, Dinh T N. Numerical simulation of droplet deformation and break-up by lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 1999, 34(4): 471–488.
Quan Shenglin, Li Shuang, Li Weizhong et al. A simulation of impact of droplets on solid surfaces by using the Lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2009, 26(5): 627–631 (in Chinese).
Li Daming, Xu Yanan, Li Lingling et al. Tracking methods for free surface and simulation of a liquid droplet impacting on a solid surface based on SPH[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2011, 23(4): 447–456.
Tartakovsky Alexandre, Meakin Paul. Modeling of surface tension and contact angles with smoothed particle hydrodynamics[ J]. Physical Review E, 2005, 72(2): 026301.
Li Qiang, Cai Timin, He Guoqiang et al. Droplet collision and coalescence model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2006, 27(1): 67–73.
Ma Li, Tao Weiming, Guo Yimu et al. Elastic/plastic impact simulation of water jet using smoothed particle hydrodynamics and finite element method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2008, 42(2): 259–263 (in Chinese).
Fang H S, Bao K, Wei J A et al. Simulations of droplet spreading and solidification using an improved SPH model[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A, 2009, 55(2): 124–143.
Liu M B, Chang J Z, Liu H T et al. Modeling of contact angles and wetting effects with particle methods[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2011, 8(4): 637–651.
Qiang Hongfu, Liu Kai, Chen Fuzhen. Numerical implementation of deformation and motion of droplet at the interface between vapor and solid surface with smoothed particle hydrodynamics methodology[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(20): 204701 (in Chinese).
Su Tiexiong, Ma Liqiang, Liu Moubin et al. A numerical analysis of drop impact on solid surfaces by using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(6): 064702 (in Chinese).
Liu G R, Liu M B. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: A Meshfree Particle Method[M]. World Scientific, Singapore, 2003.
Li Daming, Li Xiaoyu, Lin Yi. Numerical simulation of droplet impacting liquid surface by SPH[J]. Science China: Technological Sciences, 2011, 54(7): 1873–1880.
Li Yan. Numerical Simulation on Dynamics of Droplet Impacting on Flat Hot Solid Surface[D]. Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2008. 35–39 (in Chinese).
Mao Ted, Kuhn David C S, Tran Honghi. Spread and rebound of liquid droplets upon impact on flat surfaces[J]. AIChE Journal, 1997, 43(9): 2169–2179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 51079095) and the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51021004).
Li Daming, born in 1957, male, Dr, Prof.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Bai, L., Li, L. et al. SPH modeling of droplet impact on solid boundary. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 20, 112–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-014-2179-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-014-2179-9