Abstract
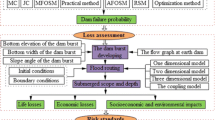
The loss of life risk evaluation model for dam break is built in this paper. By using an improved Monte Carlo method, the overtopping probability induced by concurrent flood and wind is calculated, and the Latin Hypercube Sampling is used to generate random numbers. The Graham method is used to calculate the loss of life resulting from dam failure. With Dongwushi reservoir located at Hebei Province taken as an example, the overtopping probability induced by concurrent flood and wind is calculated as 4.77×10−6. Loss of life is 24 220 when the warning time is 0.25–1 h and flood severity understanding is vague, which indicates that the risk is intolerable. The losses of life under three other conditions are tolerable: warning time 0.25–1 h, and precise flood severity understanding; warning time more than 1 h, and vague flood severity understanding; warning time more than 1 h, and precise flood severity understanding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Renzhong, Li Lei, Sheng Jinbao. On criterion of social and environmental risk of reservoir dams[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2006, 6(1): 8–11 (in Chinese).
Australian Committee on Large Dams (ANCOLD). Guidelines on Risk Assessment[S]. 2003.
Sheng Jinbao, Peng Xuehui. Study on risk criterion of China reservoir dams[C]. In: The First Youth Forum of Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society. China, 2003. 476–480 (in Chinese).
Peng Xuehui. Application of Risk Analysis in China Dam Safety[D]. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, Nanjing, 2003 (in Chinese).
Wang Renzhong, Li Lei, Sheng Jinbao. Study on risk judgment standard system for dangerous reservoirs[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2005, 25(5): 5–8 (in Chinese).
Li Lei, Zhou Kefa. Methods for evaluation of life loss induced by dam failure[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2006, 26(2): 76–80 (in Chinese).
Zhou Kefa. Study on the Analysis Method for Loss of Life due to Dam Breach[D]. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, Nanjing, 2006 (in Chinese).
Ma Rongyong. Risk Analysis Methods and Its Application for Dam[M]. Science Press, Beijing, 2004 (in Chinese).
Li Qingfu, Long Shaojiang. Risk assessment of dam overtopping[ J]. Water Power, 2006, 32(7): 20–22 (in Chinese).
SL274-2001. Design Code for Rolled Earth-Rock Fill Dams[S]. China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, Beijing, 2001 (in Chinese).
Yu P S, Yang T C, Chen S J. Comparison of uncertainty analysis methods for a distributed rainfall-runoff model[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2001, 244(1/2): 43–59.
Xie Renzhi. Dam Break Hydraulics[M]. Shandong Science and Technology Press, Jinan,1993 (in Chinese).
Li Lei, Wang Renzhong, Sheng Jinbao. Dam Risk Evaluation and Risk Management[M]. China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, Beijing, 2006 (in Chinese).
Graham W J. A Procedure for Estimating Loss of Life Caused by Dam Failure[R]. DSO-99-06. U. S. Bureau of Reclamation, Department of Interior, 1999.
Mo Chongxun, Dong Zengchuan. Application of interval analysis to evaluating overtopping risk[J]. Water Power, 2007, 33(6): 16–18 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Tianjin Natural Science Foundation*(No. 08JCZDJC25400, No. 09JCYBJC08700) and Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (“973” Program, No. 2007CB714101).
SUN Yuefeng, born in 1980, female, Dr.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Zhong, D., Li, M. et al. Theory and application of loss of life risk analysis for dam break. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 16, 383–387 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-010-1470-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-010-1470-7