Abstract
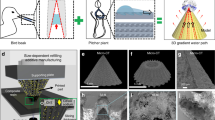
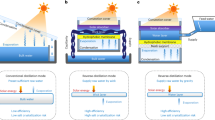
Solar desalination, harvesting solar energy to purify seawater, has received considerable attention due to water scarcity problems caused by climate change and human activity. In this study, we investigated a membrane desalination method that collects vaporized water from the surface of a sun-lit porous medium floating on salt water. To maximize the water evaporation rate at the membrane surface, several effective photothermal converting materials were coated on the membrane. In addition, to amplify the water transport to the sun-lit surface, the pore size of the porous medium also was controlled by filtering sugar particles by size. We found that the evaporation rate increased as the reflectivity of the coating materials decreased, and demonstrate the optimized pore size, leading to improved evaporation at the three-phase interface by controlling the size of the pores. The water transport is caused by the porous medium resulted from competition between capillary and viscous forces; thus, the optimal pore size for maximum water transport and evaporation rate is discussed. The finding of this study provide insight into optimizing the design of the membrane’s structure and coating materials to maximize the evaporation rate in solar desalination.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d :
-
Diameter of the pole [m]
- H :
-
Height [m]
- h :
-
Enthalpy [kJ/kg]
- K :
-
Permeability [m2]
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity [W/(m·K)]
- \({\dot m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate [kg/h]
- \({\bar M}\) :
-
Molar mass of fluid [kg/mol]
- P :
-
Pressure [Pa]
- \({\dot Q}\) :
-
Power [W]
- \({\dot q}\) :
-
Heat flux [W/m2]
- \({\bar R}\) :
-
Molar gas constant [J/(mol·K)]
- r :
-
Meniscus radius [m]
- T :
-
Temperature [K]
- u :
-
Velocity [m/s]
- evp :
-
Evaporation
- in :
-
Inlet
- l :
-
Liquid
- lv :
-
Liquid-vapor interface
- p :
-
Pore
- solar :
-
Solar
- s :
-
Solid
- v :
-
Vapor
- w :
-
Water
- α :
-
Turning angle of liquid-vapor interface [°]
- γ :
-
Reflectivity [-]
- η :
-
Evaporation efficiency [-]
- θ :
-
Contact angle [°]
- μ :
-
Viscosity [Pa·s]
- σ :
-
Surface tension [-]
- τ :
-
Accommodation coefficient [-]
References
K. Elsaid, M. Kamil, E. T. Sayed, M. A. Abdelkareem, T. Wilberfore and A. Olabi, Environmental impact of desalination technologies: A review, Science of the Total Environment, 748 (2020) 141528.
C. S. Bandi, R. Uppaluri and A. Kumar, Global optimization of MSF seawater desalination processes, Desalination, 394 (2016) 30–43.
B. Peñate and L. García-Rodríguez, Current trends and future prospects in the design of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology, Desalination, 284 (2012) 1–8.
S. J. Lee, T. S. Hann and S. H. Park, Seawater desalination using MOF-incorporated Cu-based alginate beads without energy consumption, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12 (2020) 16319–16326.
I. A. Said, N. Fuentes, Z. He, R. Xin, K. Zuo and Q. Li, Low-cost desalination of seawater and hybersaline brine using nanophotonics enhanced solar energy membrane distillation, Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 6 (2020) 2180–2196.
Z. Xu, L. Zhang, L. Zhao, B. Li, B. Bhatia, C. Wang, K. L. Wilke, Y. S. Song, O. Labban, J. H. Lienhard, R. Wang and E. N. Wang, Ultrahigh-efficiency desalination via a thermally-localized multistage solar still, Energy Environmental Science, 13 (2020) 830–839.
X. Zhou, F. Zhao, Y. Guo, B. Rosenberger and G. Yu, Architecting highly hydratable polymer networks to tune the water state for solar water purification, Science Advances, 6 (2019) 2375–2548.
X. Zhou, F. Zhao, P. Zhang and G. Yu, Solar water evaporation toward water purification and beyond, ACS Materials Letters, 3 (2021) 1112–1129.
X. Chen, Y. B. Zhu, H. Yu, J. Z. Liu, C. D. Easton, Z. Wang, Y. Hu, Z. Xie, H. A. Wu, X. Zhang, D. Li and H. Wang, Ultrafast water evaporation through graphene membranes with subnanometer pores for desalination, Journal of Membrane Science, 621 (2021) 118934.
Y. Li, T. Gao, Z. Yang, C. Chen, Y. Kuang, J. Song, C. Jia, E. M. Hitz, B. Yang and L. Hu, Graphene oxide-based evaporator with one-dimensional water transport enabling high-efficiency solar desalination, Nano Energy, 41 (2017) 201–209.
Q. Li, X. Zhao, L. Li, T. Hu, Y. Yang and J. Zhang, Facile preparation of polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotubes modified melamine solar evaporators for efficient steam generation and desalination, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 584 (2021) 602–609.
X. Dong, L. Cao, Y. Si, B. Ding and H. Deng, Cellular structured CNTs@SiO2 nanofibrous aerogels with vertically aligned vessels for salt-resistant solar desalination, Advanced Materials, 32 (2020) 1908269.
J. Y. Lee, K. Y. Kim, S. H. Park, G. Y. Yoon, J. J. Kim and S. J. Lee, Macroporous photo-thermal bilayer evaporator for highly efficient and self-cleaning solar desalination, Nano Energy, 77 (2020) 105130.
H. Bai, T. Zhao and M. Cao, Interfacial solar evaporation for water production: from structure design to reliable performance, Molecular Systems Design & Engineering, 5 (2020) 419–432.
C. Li, D. Jiang, B. Huo, M. Ding, C. Huang, D. Jia, H. Li, C. Y. Liu and J. Liu, Scalable and robust bilayer polymer foams for highly efficient and stable solar desalination, Nano Energy, 60 (2019) 841–849.
W. Xu, X. Hu, S. Zhuang, Y. Wang, X. Li, L. Zhou, S. Zhu and J. Zhu, Flexible and salt resistant janus absorbers by electrospinning for stable and efficient solar desalination, Advanced Energy Materials, 8 (2018) 1702884.
Y. Kuang, C. Chen, S. He, E. M. Hitz, Y. Wang, W. Gan, R. Mi and L. Hu, A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination, Advanced Materials, 31 (2019) 1900498.
X. Li, W. Xu, M. Tang, L. Zhou, B. Zhu, S. Zhu and J. Zhu, Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path, PNAS, 113 (2016) 13953–13958.
H. Ghasemi, G. Ni, A. M. Marconnet, J. Loomis, S. Yerci, N. Miljkovic and G. Chen, Solar steam generation by heat localization, Nature, 5 (2014) 4449.
J. Liu, Q. Liu, D. Ma, Y. Yuan, J. Yao, W. Zhang, H. Su, Y. Su, J. Gu and D. Zhang, Simultaneously achieving thermal insulation and rapid water transport in sugarcane stems for efficient solar steam generation, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 7 (2019) 9034–9039.
M. Gao, L. Zhu, C. K. Peh and G. W. Ho, Solar absorber material and system designs for photo-thermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production, Energy & Environmental Science, 12 (2019) 841–864.
S. Verma and R. Das, Concept of optimum basin thickness in heat exchanger-assisted solar still, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30 (2023) 310–321.
W. Ma, T. Lu, W. Cao, R. Xiong and C. Huang, Bioinspired nanofibrous aerogel with vertically aligned channels for efficient water purification and salt-rejecting solar desalination, Advanced Functional Materials, 33 (2023) 2214157.
S. Shoeibi, M. Saemian, S. M. Parsa, M. Khiadani, S. A. A. Mirjalily and H. Kargarsharifabad, A novel solar desalination system equipped with thermoelectric generator, reflectors and low-cost sensible energy-storage for coproduction of power and drinking water, Desalination, 567 (2023) 116955.
M. Sajedi, A. Safavinejad and M. Atashafrooz, Influences of radiative heat transfer on the entropy generation rates of forced convection fluid flow between two parallel isothermal plates filled with porous medium, Transport in Porous Media, 147 (2023) 703–724.
M. Sajedi, A. Safavinejad and M. Atashafrooz, Numerical analysis of entropy generation in a two-dimensional porous heat recovery system, Journal of Porous Media, 26 (2023) 51–68.
N. Farokhnia, P. Irajizad and S. Mohammad, Rational micro/nanostructuring for thin-film evaporation, The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 16 (2016) 8742–8750.
C. Xie, G. Liu and M. Wang, Evaporation flux distribution of drops on a hydrophilic or hydrophobic flat surface by molecular simulations, Langmuir, 32 (2016) 8255–8264.
H. K. Dhavaleswarapu, J. Y. Murthym and S. V. Garimella, Numerical investigation of an evaporating meniscus in a channel, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 55 (2012) 915–924.
F. M. Canbazoglu, B. Fan, A. Kargar, K. Vemuri and P. R. Bandaru, Enhanced solar evaporation of water from porous media, through capillary mediated forces and surface treatment, AIP Advances, 6 (2016) 8.
S. Ma, C. P. Chiu, Y. Zhu, C. Y. Tang, H. Long, W. Qarony, X. Zhao, X. Zhang, W. H. Lo and Y. H. Tsang, Recycled waste black polyurethane sponges for solar vapor generation and distillation, Applied Energy, 206 (2017) 63–69.
K. Wang, D. Y. Wang, M. Z. Wang, X. X. Dan, L. M. Che, H. H. Xu, H. Zhou, H. Liu, L. Singh and X. E. Wu, Functional photothermal sponges for efficient solar steam generation and accelerated cleaning of viscous crude-oil spill, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 204 (2020) 110203.
Y. Sun, J. Gao, Y. Liu, H. Kang, M. Xie, F. Wu and H. Qiu, Copper sulfide-macroporous polyacrylamide hydrogel for solar steam generation, Chemical Engineering Science, 207 (2019) 516–526.
X. Lin, J. Chen, Z. Yuan, M. Yang, G. Chen, D. Yu, M. Zhang, W. Hong and X. Chen, Integrative solar absorbers for highly efficient solar steam generation, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6 (2018) 4642–4648.
X. Hu, W. Xu, L. Zhou, Y. Tan, Y. Wang, S. Zhu and J. Zhu, Tailoring graphene oxide-based aerogels for efficient solar steam generation under one sun, Advanced Materials, 29 (2017) 1604031.
P. Zhang, J. Li, L. Lv, Y. Zhao and L. Qu, Vertically aligned graphene sheets membrane for highly efficient solar thermal generation of clean water, ACS Nano, 11 (2017) 5087–5093.
W. Zhang, W. Zhu, S. Shi, N. Hu, Y. Suo and J. Wang, Bioinspired foam with large 3D macropores for efficient solar steam generation, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6 (2018) 16220–16227.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT, MIST) (2022R1C1C1011232).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jinwook Choi was an undergraduate student at Kyungpook National University (South Korea), studying for a bachelor’s degree at the Department of Precision Mechanical Engineering, and now working in Kyungpook National University for his master’s degree.
Kim SeolHa graduated from POSTECH, Bachelor (Mechanical Engineering), and Doctor (Nuclear Engineering). He worked at the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Chinese Academy of Science as a researcher. Currently, he is working Kyungpook National University as a Professor.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Seo, Y., Paeng, C. et al. Controlling pore size and photothermal layer to improve solar-porous evaporation performance. J Mech Sci Technol 38, 2627–2635 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-024-0439-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-024-0439-8