Abstract
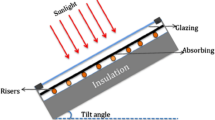
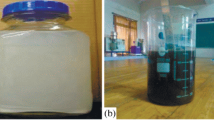
The thermal performance of a solar flat plate collector incorporating CuO nanofluid as a working medium was examined in the present study. The solar collector with two riser tubes was studied experimentally and the results compared with the numerical outcomes predicted using commercially available Ansys 19.0 software. The solar water heater was examined for water and CuO nanofluid with 0.2 wt% and 0.4 wt% for two different volume flow rates of 0.5 and 1 lit/min. The present study claims that the instantaneous thermal efficiency for 0.2 wt% and 0.4 wt% increased by 12.01 % and 7.56 %, respectively, compared to water as a working medium. The effect of CuO/distilled water nanofluid on the collector's efficiency was also numerically studied using a two-phase CFD model. It is observed that the CFD and experimental results show good agreement with each other, with a maximum error of 5.84 % and 4.29 % for the nanofluid and water as working fluids, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Q :
-
Useful heat gain
- ṁ w :
-
Mass flow rate of working fluid
- T o :
-
Outlet temperature
- T i :
-
Inlet temperature
- A :
-
Area of collector
- F R :
-
Heat removal factor
- G T :
-
Global radiation
- U L :
-
Overall heat loss coefficient
- T amb :
-
Ambient air temperature
- η i :
-
Instantaneous efficiency
- τα :
-
Product of absorptivity and transmissivity
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- u :
-
Uncertainty parameter
- o :
-
Outlet
- i :
-
Inlet
- amb :
-
Ambient
- w :
-
Working fluid
- W :
-
Wind
- η O :
-
Overall efficiency
References
W. Yu, D. M. France, J. L. Routbort and S. U. S. Choi, Review and comparison of nanofluid thermal conductivity and heat transfer enhancements, Heat Transf. Eng., 29 (2008) 432–460.
D. Zhu et al., Dispersion behavior and thermal conductivity characteristics of Al2O3-H2O nanofluids, Curr. Appl. Phys., 9 (2009) 131–139.
H. J. Kim, S. H. Lee, J. H. Lee and S. P. Jang, Effect of particle shape on suspension stability and thermal conductivities of water-based bohemite alumina nanofluids, Energy, 90 (2015) 1290–1297.
J. Hong and D. Kim, Effects of aggregation on the thermal conductivity of alumina/water nanofluids, Thermochim. Acta, 542 (2012) 28–32.
E. Natarajan and R. Sathish, Role of nanofluids in solar water heater, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., (2009) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1876-8.
S. K. Verma, A. K. Tiwari and D. S. Chauhan, Experimental evaluation of flat plate solar collector using nanofluids, Energy Convers. Manag., 13 (2017) 103–115.
H. K. Gupta, G. D. Agrawal and J. Mathur, Investigations for effect of Al2O3−H2O nanofluid flow rate on the efficiency of direct absorption solar collector, Case Stud. Therm. Eng., 5 (2015) 70–78.
T. P. Otanicar and J. S. Golden, Comparative environmental and economic analysis of conventional and nanofluid solar hot water technologies, Environ. Sci. Technol., 43 (2009) 6082–6087.
S. Salavati Meibodi, A. Kianifar, H. Niazmand, O. Mahian and S. Wongwises, Experimental investigation on the thermal efficiency and performance characteristics of a flat plate solar collector using SiO2/EG-water nanofluids, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 65 (2015) 71–75.
Z. Said, M. H. Sajid, M. A. Alim, R. Saidur and N. A. Rahim, Experimental investigation of the thermophysical properties of AL2O3-nanofluid and its effect on a flat plate solar collector, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 48 (2013) 99–107.
M. Mercan and A. Yurddaş, Numerical analysis of evacuated tube solar collectors using nanofluids, Sol. Energy, 191 (2019) 167–179.
O. Mahian, A. Kianifar, S. A. Kalogirou, I. Pop and S. Wongwises, A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 57 (2013) 582–594.
Q. He, S. Zeng and S. Wang, Experimental investigation on the efficiency of flat-plate solar collectors with nanofluids, Appl. Therm. Eng., 88 (2014) 165–171.
D. G. Gunjo, P. Mahanta and P. S. Robi, CFD and experimental investigation of flat plate solar water heating system under steady state condition, Renew. Energy, 106 (2017) 24–36.
T. Yousefi, F. Veysi, E. Shojaeizadeh and S. Zinadini, An experimental investigation on the effect of Al2O3−H2O nanofluid on the efficiency of flat-plate solar collectors, Renew. Energy, 39 (2012) 293–298.
A. A. Hawwash, A. K. Abdel Rahman, S. A. Nada and S. Ookawara, Numerical investigation and experimental verification of performance enhancement of flat plate solar collector using nanofluids, Appl. Therm. Eng., 130 (2018) 363–374.
A. A. Abdelfattah et al., Thermal performance augmentation of a semi-circular cylinder in crossflow using longitudinal fins, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 125 (2021) 105159.
M. L. Elsayed, M. A. Abdelatief, S. A. Ahmed, M. S. Emeara and W. M. Elwan, Thermal design evaluation of ribbed/grooved tubes: an entropy and exergy approach, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 120 (2021) 105048.
ASHRAE, Methods of Testing To Determine The Thermal Performance of Solar Collectors, ASHRAE Standard 93–1986, ASHRAE, Atlanta, USA (1985).
D. R. Clary and G. Mills, Preparation and thermal properties of CuO particles, J. Phys. Chem. C, 115 (2011) 1767–1775.
M. A. Abdelatief, A. A. Zamel and S. A. Ahmed, Elliptic tube free convection augmentation: an experimental and ANN numerical approach, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 108 (2019) 104296.
M. A. Abdelatief and M. A. Omara, Free convection experimental study inside square tube with inner roughened surface at various inclination angles, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 144 (2019) 11–20.
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful for the Department of Mechanical Engineering, NIT Jamshedpur for helping make this research work completed successfully.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Helal Ahmad Farhan is research scholar at NIT Jamshedpur India who completed Master’s from NIT Jamshedpur. His research area is nanofluid application for solar thermal applications.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farhan, H.A., Nayak, S., Sanjay et al. Numerical analysis with experimental validation for thermal performance of flat plate solar water heater using CuO/distilled water nanofluid in closed loop. J Mech Sci Technol 37, 2649–2656 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-023-0438-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-023-0438-1