Abstract
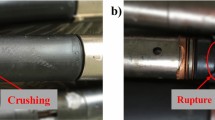
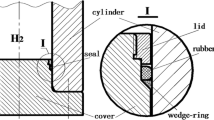
The ability of sealing suspension of solid expandable tubular (SET) is one of the important factors that determine whether pipe can expand normally and serve. To solve the problem that the SET deviates from the original position (causing for the failure to repair of leakage well) due to the insufficient suspension force after expansion, this paper establishes the two-dimensional coupling model of SET-rubber ring-expansion cone-casing based on laboratory experiment parameters, designs the parameters of the sealed suspension rubber ring and conducts simulation. The results show that when the compression amount of the rubber ring is designed to be 47 %-58 % of the rubber thickness, the SET has excellent sealing ability after expansion and can meet the requirements of suspension force; too much compression will affect the service life of the rubber ring. When the length of the rubber ring is 50 mm-110 mm, the driving force and contact pressure during expansion are suitable; the rubber ring spacing is designed to be 110 mm, which avoids interference after rubber compression and saves material. In addition, the vulcanizing bonding strength of the rubber ring should be greater than 120 kN to avoid peeling off due to the failure of the rubber ring and SET bonding. The research results of this paper provide a theoretical basis for the design of sealing suspension module of SET repair technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Pervez et al., Experimental and numerical simulation of in-situ tube expansion for deep gas wells, Materi and Manufa Processes, 27 (7) (2012) 727–732.
Z. M. Zhang et al., Expansion tube technology successfully applied in C LN8C well in ultra-deep side drilling in Tarim oilfield, J. Chem. Engineering & Equip, 6 (2008) 49–50.
L. L. Wang et al., Application of expandable tubular technology on highly deviated wells in Jidong oilfield, J. China Petro Machinery, 44 (11) (2016) 68–71+79.
C. Q. Shao, Introduction to expansion pipe technology, J. Petro Industry Technology, 22 (9) (2015) 152.
J. H. Fu et al., Dynamic analysis of solid expandable tubular and its applications in Tahe oilfield, Arab J. Sci. Eng., 40 (2015) 2437–2446.
Y. H. Ke, Discussion on application of deep well ultra-deep well drilling technology, J. Petro-Chemical Equipment, 21 (12) (2018) 100–102.
J. B. Zhang, T. H. Shi and Z. H. Lian, Drilling solid expansion tube technology, J. China Petro Machinery, S1 (2003) 128–131.
Q. Chen et al., Effect and thinking on the implementation of expansion tube technology standardization system, J. Techno Supervision in Petro Industry, 33 (12) (2017) 65–68.
Y. G. Liu et al., Design of expansion core cone angle in expansion tube technology, J. Southwest Petro Institute, 4 (2004) 70–72+93.
O. S. Al-Abri et al., On the performance analysis of AHSS with an application to SET technology-FEM simulations and experimental measurements, Thin-Walled Structures, 101 (2016b) 58–74.
H. L. Li et al., Development situation of OCTG and production localization of hi-grade OCTG (Part I), Steel Pipe, 6 (2007) 1–6.
Y. G. Liu et al., Application of simulation technology on the design of one special expandable tubular thread, Mach Design and Manufac Eng III (2014) 257–263.
A. Mazz et al., FEM Simulation of Swelling Elastomer Seals in Downhole Applications, San Diego, CA, United States (2013) 1–7.
T. Pervez et al., Use of SET in cased and open holes: Comparison between aluminum and steel, Mater Design, 29 (2008) 811–817.
O. S. Al-Abri et al., Optimum mandrel configuration for efficient down-hole tube expansion, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 6 (Dec) (2015) 061005.
X. S. Liao et al., Failure analysis and solution study of 203 mm solid expandable tubular, Engineering Failure Analysis, 106 (2019) 104135.
S. A. Al-Hiddabi et al., Analytical model of elastomer seal performance in oil wells, Applied Mathematical Modelling, 39 (2015) 2836–2848.
Y. P. Shi, ABAQUS Finite Element Analysis Example, Mechanical Industry Press (2016) 11.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51674214 and 51604234), Youth Scientific Research Innovation Team Project of Sichuan Province (2017TD0014), and the State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmissions open fund (Grant No. SKLMT-KFKT-201610).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editor Chongdu Cho
Xiaohua Zhu received his B.S., M.S., Ph.D. degrees in mechanical design and theory from Southwest Petroleum University of China, in 2000, 2002, and 2005, respectively. He is currently a Professor at the School of Mechatronic Engineering in the Southwest Petroleum University, as well as a member of the Chinese Mechanical Engineering Society. His main research interests include design downhole drilling tools, drill string dynamics analysis, new methods for improving drilling efficiency.
Feilong Cheng received his bachelor of engineering degree from Southwest Petroleum University in 2017, majoring in mechanical design, manufacturing and automation. Since September 2018, he has been studying for his master’s degree in Southwest Petroleum University. His main research direction is the new solid expandable tubular technology.
Changshuai Shi received his B.S. degree in process equipment and control from the Southwest University of Science and Technology in 2008, and M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in mechanical design and theory from Southwest Petroleum University of China, in 2011 and 2014, respectively. His main research interests include design of downhole drilling tools, fatigue of rubber component, and optimization of process craft of screw pump.
Jia’nan Li, a master’s student in mechanical engineering, graduated from Southwest Petroleum University majoring in mechanical manufacturing and automation. He once worked as a mechanical research and development engineer in Cnooc Service and Oilfield Technology Research Institute and other enterprises. He is committed to the development of new technology for drilling acceleration and efficiency improvement and downhole tool design.
Kailin Chen, male, graduate student, graduated from the Mechanical Engineering Department of Southwest Petroleum University with a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering in June 2017. He is currently engaged in research on solid expandable tubular and drilling speed-up tools.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Cheng, F., Shi, C. et al. Design and analysis of sealed suspension module based on solid expandable tubular repair technology. J Mech Sci Technol 34, 681–688 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-1215-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-1215-z