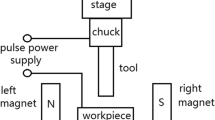
Abstract
Mechanical grinding techniques can cause residual stress, micro-cracks, and work hardening in workpieces. Processes employing magnetorheological (MR) fluid aim to reduce subsurface damage by avoiding the direct application of mechanical force. However, the material removal rate (MRR) achieved with processes such as MR fluid polishing is relatively low. In this study, operating conditions to improve MRR are analyzed using the design of experiments method. Through experiment, and using factorial analysis, it is concluded that MRR depends on magnetic field strength, depth of polishing, and polishing time. Based on these results, a re-designed electromagnet is proposed, analyzed, and tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Li, Z. Wang and Y. Wu, Relationship between subsurface damage and surface roughness of optical materials in grinding and lapping processes, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 205 (2008) 34–41, Doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.11.118.
S. Yin, H. Ohmori, Y. Dai, Y. Uehara, F. Chen and H. Tang, ELID grinding characteristics of glass-ceramic materials, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 49 (2009) 333–338, Doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.10.013.
H. Tang, Z. H. Deng, Y. S. Guo, J. Qian and D. Reynaerts, Depth-of-cut errors in ELID surface grinding of zirconiabased ceramics, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 88 (2015) 34–41, Doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2014.08.003.
J. Chen, Q. Fang and P. Li, Effect of grinding wheel spindle vibration on surface roughness and subsurface damage in brittle material grinding, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 91 (2015) 12–23, Doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.01.003.
S. D. Jacobs, S. A. Arrasmith, I. A. Kozhinova, L. L. Gregg, A. B. Shorey, H. J. Romanofsky, D. Golini, W. I. Kordonski, P. Dumas and S. Hogan, An overview of magnetorheological finishing (MRF) for precision optics manufacturing, Ceram. Trans., 102 (1999) 185–199.
D. Golini, W. I. Kordonski, P. Dumas and S. J. Hogan, Magnetorheological finishing (MRF) in commercial precision optics manufacturing, Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., 3782 BT-(1999) 80–91, Doi: 10.1117/12.360131.
A. Shorey, W. Kordonski and M. Tricard, Deterministic, precision finishing of domes and conformal optics, Wind. Dome Technol. Mater. IX (2005) 310–318, Doi: 10.1117/12.607456.
S. N. Shafrir, J. C. Lambropoulos and S. D. Jacobs, Subsurface damage and microstructure development in precision microground hard ceramics using magnetorheological finishing spots, Appl. Opt., 46 (2007) 5500–5515, Doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005500.
S. R. Arrasmith, S. D. Jacobs, J. C. Lambropoulos, A. Maltsev, D. Golini and W. I. Kordonski, Use of magnetorheological finishing (MRF) to relieve residual stress and subsurface damage on lapped semiconductor silicon wafers, Proc. of International Symposium on Optical Science and Technology (2001) 286–294, Doi.org/10.1117/12.453627.
M. Schinhaerl, C. Vogt, A. Geiss, R. Stamp, P. Sperber, L. Smith, G. Smith and R. Rascher, Forces acting between polishing tool and workpiece surface in magnetorheological finishing, Proc. of SPIE (2008) 706006–706012, http://dx.doi. org/10.1117/12.794196.
T. M. Gurubasavaraju, H. Kumar and M. Arun, Optimization of monotube magnetorheological damper under shear mode, Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 39 (6) (2017) 2225–2240.
A. B. Shorey, S. D. Jacobs, W. I. Kordonski and R. F. Gans, Experiments and observations regarding the mechanisms of glass removal in magnetorheological finishing, Appl. Opt., 40 (2001) 20–33, Doi: 10.1364/AO.40.000020.
S. D. Jacobs, S. R. Arrasmith, I. A. Kozhinova, S. R. Gorodkin, L. L. Gregg, H. J. Romanofsky, T. D. Bishop, A. B. Shorey and W. I. Kordonski, Effects of changes in fluid composition on magnetorheological finishing (MRF) of glasses and crystals, Initiat. Precis. Eng. Begin. A Millenn. (2001) Japan Soc Precis Engn; Amer Soc Precis Engn; Europ.
K. P. Hong, K. H. Song, M. W. Cho, S. H. Kwon and H. J. Choi, Magnetorheological properties and polishing characteristics of silica-coated carbonyl iron magnetorheological fluid, Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures (2017) 1045389X17730912.
Y. Wang, S. Yin and H. Huang, Polishing characteristics and mechanism in magnetorheological planarization using a permanent magnetic yoke with translational movement, Precis. Eng., 43 (2016) 93–104, Doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng. 2015.06.014.
Y. Q. Wang, S. H. Yin, H. Huang, F. J. Chen and G. J. Deng, Magnetorheological polishing using a permanent magnetic yoke with straight air gap for ultra-smooth surface planarization, Precis. Eng., 40 (2015) 309–317, Doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.11.001.
K. Saraswathamma, S. Jha and P. V. Rao, Design of Parallel plate magnetorheometer for evaluating properties of magnetorheological polishing fluid, Mater. Today Proc., 2 (2015) 3251–3259, Doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.134.
K. B. Kim, B. C. Kim, S. J. Ha and M. W. Cho, Effect of pre-treatment polishing on fabrication of anodic aluminum oxide using commercial aluminum alloy, Journal of Mechanical Science and Techonology, 31 (9) (2017) 4387–4393, Doi: 10.1007/s12206-017-0828-1.
J. W. Lee, S. J. Ha, Y. K. Cho, K. B. Kim and M. W. Cho, Investigation of the polishing characteristics of metal materials and development of micro MR fluid jet polishing system for the ultra precision polishing of micro mold pattern, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 29 (5) (2015) 2205–2211, Doi: 10.1007/s12206-015-0136-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor In-Ha Sung
Byung-Chan Kim received his M.S. in Mechanical Engineering from Inha University, Incheon, Korea, in 2016. He is currently in doctoral course at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Inha University. His research interest includes laser polishing and MR fluid polishing.
Seok-Jae Ha received his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Inha University, Incheon, Korea, in 2010 and 2015. He is currently a post-doctoral at the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH). His research interest includes cutting monitoring, MR fluid polishing, micro machining, and mask-less digital lithography.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.C., Chung, J.H., Cho, M.W. et al. Magnetorheological fluid polishing using an electromagnet with straight pole-piece for improving material removal rate. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 3345–3350 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0637-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0637-3