Abstract
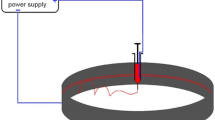
In this study, a syringe pump was designed and built to determine the effect of the physical properties of the spinning part of a machine and the physical properties of the wet spinning process. Through the wet spinning method and fuzzy separation process, solid fibers were produced under experiments designed by the response surface method and statistical model of composite center design to predict the exact tensile strength. Polymeric fibers produced by atomic absorption spectrometry were used as adsorbent. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of spinning velocity, length-to-diameter ratio of the spinner, spinner diameter, and weight percentage of the polymer on the mechanical properties and structure of the sample. Scanning electron microscopy tests were conducted on the samples to analyze their structural properties, and the output pictures showed that the samples had a desirable microstructure. Analysis of variance indicated that the physical parameters of spinning produced the most significant effect on improving fiber properties. Results of data analysis showed that the length-to-diameter ratio and spinner diameter were the most effective process conditions that could be used to examine the data on tensile strength and optimum ratio of fiber diameter to spinner diameter. Finally, optimization was performed using the utility function to maximize the amount of tensile strength, and the process experimental results were evaluated. The results showed that the response surface models could adequately predict the values of the response variable. The gage R&R method was used to determine the amount of error due to the measurement system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Lin, J. Shang and J. Zhao, Effect of the size of spinneret on the thermal stability of chemically liquefied wood, Wood Research, 59 (5) (2014) 59, 731-738.
R. Huisman and H. M. Heuvel, High-speed spinning of PET yarns: Effect of molecular weight, Indian J. of Fibre & Textile Research, 16 (1990) 7–11.
J. Prost and P. G. Gennes, The physics of liquid crystals, Clarendon press, Oxford, 18 (1993) 230–245.
H. Treptow, Polyester fibers, Man Made Fiber Year Book, Frankfurt (1986) 86–90.
K. Kim et al., Unique surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene yarns from aN,N-dimethylfor-mamide solution, Macromolecular Research, 13 (6) (2005) 533–537.
S. K. Mukhopadhyay, E. M. O. Babbington and P. W. Foster, Structural morphology of high speed spun polyester fibers, Textile Research Journal, England, 62 (7) (1992) 403–405.
S. Ramakrishna, K. Fujihara, W. Teo, T. Lim and Z. Ma, An introduction to electro spinning and nano fiber, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Singapore (2005) 211–223.
Y. P. Neo, S. Ray, A. J. Easteal, M. G. Nikolaidis and S. Y. Quek, Influence of solution and processing parameters towards the fabrication of electro spun zein fibers with sub-micron diameter, Journal of Food Engineering, Auckland, 109 (4) (2012) 645–651.
T. H. Young and L. W. Chen, Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process, Desalination, 103 (1995) 233–247.
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki and S. Ramakrishna, A review on polymer nan fibers by electro spinning and their applications in nano composites, Composites Science and Technology, China, 63 (15) (2003) 2223–2253.
B. Wijnen, E. J. Hunt, G. C. Anzalone and J. M. Pearce, Opensource syringe pump library, Plos One, United Kingdom (2014) 3–8.
T. Zehev and C. Gogos, Principles of polymer processing, John Wiley & Sons (2013).
E. Vennat, C. Bogicevic and J. M. Fleureau, Demineralized dentin 3D porosity and pore size distribution suing mercury porosimetry, Dental Materials, 25 (2009) 729–735.
J. P. Penning and A. Devries, The effect of yarn diameter on the drawing behavior of gel-spun ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene yarns, Polymer Bulletin, 31 (1993) 243–248.
A. T. Serkov, R. V. Egorova and G. D. Kovalev, The profile of spinneret holes, Chemistry and Technology of Natural Polymer Fibers, 6 (1) (1974) 65–68.
Y. Li, C. Cao and T. S. Chung, Fabrication of dual-layer Poly ether sulfone (PES) hollow yarn membranes with an ultrathin dense-selective layer for gas separation, Journal of Membrane Science, 24 (2004) 53–60.
T. S. Chung, J. J. Qin and J. Gu, Effect of shear rate within the spinneret on morphology, separation performance and mechanical properties of ultration poly ether sulfone hollow, Chemical Engineering Science, 55 (6) (2000) 1077–1091.
M. Raymond, D. C. Montgomery and C. M. Anderson-Cook, Response surface methodology: Process and product optimization using designed experiments, John Wiley & Sons (2016).
R. K. Burdick et al., Design and analysis of gauge R&R studies: Making decisions with confidence intervals in random and mixed ANOVA models, SIAM, 17 (2005).
D. C. Montgomery, Introduction to statistical quality control, John Wiley & Sons (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editor Chongdu Cho
Hossein Gheshlaghi Gadim received his M.S. (2015) from Khajeh Nasir Toosi University of Technology. His major research area is mechanical design and Metal Forming. He is currently a Ph.D. student at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Urmia University.
Ali Doniavi received his Ph.D. (1998) from Bath University, UK. He is currently a Professor at the Department of Industrial Engineering at Urmia University. His major research area is mechanical design and System engineering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gadim, H.G., Doniavi, A. Improving structural properties of polymer fibers to design and construct fiber spinneret and optimize process parameters using response surface method and gage R&R. J Mech Sci Technol 32, 1135–1142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0216-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0216-7