Abstract
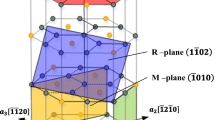
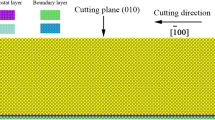
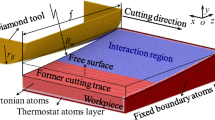
Sapphire is a promising material for various optical, electronic, and mechanical applications, but is very difficult to machine due to its high hardness and brittleness. In this study we attempt to study fundamental atomistic mechanisms of nano-scale cutting of sapphire using Molecular dynamics (MD). Atomistic models for diamond cutting of sapphire are developed using Vashishta and Lennard-Jones potentials and MD simulations address the effects of the tool edge radius and uncut chip thickness on the cutting process. Cutting and normal forces with different cutting parameters are calculated and compared with the experimental data in previous research. An analysis using a local measurement of atomistic strain also reveals detailed deformation mechanisms of the sapphire cutting process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Gu, C. W. Jeon, H. W. Choi, G. Rice, M. D. Dawson, E. K. Illy and M. R. H. Knowles, Micromachining and dicing of sapphire, gallium nitride and micro LED devices with UV copper vapour laser, Thin Solid Films, 453–454 (2004) 462–466.
Z. C. Li, Z. J. Pei and P. D. Funkenbusch, Machining processes for sapphire wafers: a literature review, Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 225 (2011) 975–989.
C. D. Jones, J. B. Rioux, J. W. Locher, H. E. Bates, S. A. Zanefla, V. Pluen and M. Mandelartz, Large-area sapphire for transparent armor, American Ceramic Society Bulletin, 85 (2006) 24–26.
B. Vogt, Scooping of sapphire domes on CNC machines, Industrial Diamond Review, 65 (2005) 24–26.
H. Park and H. M. Chan, A novel process for the generation of pristine sapphire surfaces, Thin Solid Films, 422 (2002) 135–140.
J. C. Huang and Y. J. Weng, The study on the nanomachining property and cutting model of single-crystal sapphire by atomic force microscopy, Scanning, 36 (2014) 599–607.
K. Liu, D. Zuo, X. P. Li and M. Rahman, Nanometric ductile cutting characteristics of silicon wafer using single crystal diamond tools, Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 27 (2009) 1361–1366.
G. Saurav, The current understanding on the diamond machining of silicon carbide, Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 47 (2014) 243001.
P. S. Pizani, R. Jasinevicius, J. G. Duduch and A. J. V. Porto, Ductile and brittle modes in single-point-diamond-turning of silicon probed by Raman scattering, Journal of Materials Science Letters, 18 (1999) 1185–1187.
Z. Kato, M. Sakairi and H. Takahashi, Nanopatterning on aluminum surfaces with AFM probe, Surface and Coatings Technology, 169–170 (2003) 195–198.
Y. Geng, Y. Yan, Y. Xing, X. Zhao and Z. Hu, Modelling and experimental study of machined depth in AFM-based milling of nanochannels, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 73 (2013) 87–96.
O. Takumi, N. Shinya and S. Jun-ichi, Scratch nanolithography on Si surface using scanning probe microscopy: Influence of scanning parameters on groove size, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 47 (2008) 712.
M. G. Mostofa, C. I. Park and S. S. Park, AFM probe based nano mechanical scribing of soda-lime glass, Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 15 (2013) 625–634.
K. Maekawa and A. Itoh, Friction and tool wear in nanoscale machining—a molecular dynamics approach, Wear, 188 (1995) 115–122.
C.-J. Kim, R. Mayor and J. Ni, Molecular dynamics simulations of plastic material deformation in machining with a round cutting edge, International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 13 (2012) 1303–1309.
S. Goel, X. Luo, A. Agrawal and R. L. Reuben, Diamond machining of silicon: A review of advances in molecular dynamics simulation, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 88 (2015) 131–164.
O. A. Olufayo and K. Abou-El-Hossein, Molecular dynamics modeling of nanoscale machining of silicon, Procedia CIRP, 8 (2013) 504–509.
C. Rambaut, K. H. Oh, H. Jaffrezic, J. Kohanoff and S. Fayeulle, Molecular dynamics simulation of electron trapping in sapphire, Journal of Applied Physics, 81 (1997) 3263–3267.
W. Wunderlich and H. Awaji, Molecular dynamics — simulations of the fracture toughness of sapphire, Materials & Design, 22 (2001) 53–59.
Y. G. Xu, K. Behdinan and Z. Fawaz, Molecular dynamics calculation of the J - integral fracture criterion for nano-sized crystals, International Journal of Fracture, 130 (2004) 571–583.
Z. C. Lin and Y. C. Hsu, Simulation analysis of nanocutting on the surface of sapphire, Advanced Materials Research, 579 (2012) 184–192.
Z.-C. Lin and Y.-C. Hsu, A calculating method for the fewest cutting passes on sapphire substrate at a certain depth using specific down force energy with an AFM probe, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 212 (2012) 2321–2331.
S. Nosé, A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods, The Journal of Chemical Physics, 81 (1984) 511.
W. G. Hoover, Molecular dynamics, Springer (1986).
T. Shardlow, Splitting for dissipative particle dynamics, Siam Journal on Scientific Computing, 24 (2003) 1267–1282.
P. Vashishta, R. K. Kalia, A. Nakano and J. P. Rino, Interaction potentials for alumina and molecular dynamics simulations of amorphous and liquid alumina, Journal of Applied Physics, 103 (2008) 083504.
V. R. Bhethanabotla and W. A. Steele, Moleculardynamics simulations of oxygen monolayers on graphite, Langmuir, 3 (1987) 581–587.
N. Silvestre, B. Faria and J. N. C. Lopes, Compressive behavior of CNT-reinforced aluminum composites using molecular dynamics, Composites Science and Technology, 90 (2014) 16–24.
S. Plimpton, Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular-dynamics, Journal of Computational Physics, 117 (1995) 1–19.
S. Alexander, Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the open visualization tool, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 18 (2010) 015012.
N. C. Admal and E. B. Tadmor, A unified interpretation of stress in molecular systems, Journal of Elasticity, 100 (2010) 63–143.
M. L. Falk and J. S. Langer, Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids, Physical Review E, 57 (1998) 7192–7205.
P. K. Wright and E. M. Trent, Metal cutting, Butterworth-Heinemann (2000).
M. B. Cai, X. P. Li, M. Rahman and A. A. O. Tay, Crack initiation in relation to the tool edge radius and cutting conditions in nanoscale cutting of silicon, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 47 (2007) 562–569.
G. Binnig, C. F. Quate and C. Gerber, Atomic force microscope, Physical Review Letters, 56 (1986) 930–933.
R. W. Carpick and M. Salmeron, Scratching the surface: Fundamental investigations of tribology with atomic force microscopy, Chemical Reviews, 97 (1997) 1163–1194.
A. A. Tseng, S. Jou, A. Notargiacomo and T. P. Chen, Recent developments in tip-based nanofabrication and its roadmap, Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 8 (2008) 2167–2186.
A. Aramcharoen and P. T. Mativenga, Size effect and tool geometry in micromilling of tool steel, Precision Engineering, 33 (2009) 402–407.
K. Liu and S. N. Melkote, Finite element analysis of the influence of tool edge radius on size effect in orthogonal micro-cutting process, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 49 (2007) 650–660.
M. C. Shaw, The size effect in metal cutting, Sadhana-Academy Proceedings in Engineering Sciences, 28 (2003) 875–896.
J. A. Patten and W. Gao, Extreme negative rake angle technique for single point diamond nano-cutting of silicon, Precision Engineering, 25 (2001) 165–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Haseung Chung
Woo Kyun Kim received his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from the University of Michigan, USA in 2009. He is currently Assistant Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering at the University of Cincinnati, USA. His research interests include atomic-scale friction and crystalline defects.
Bo Hyun Kim received his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from Seoul National University in 2005. He is currently Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Soongsil University, Seoul, South Korea. His research interests include micro machining and non-conventional machining processes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W.K., Kim, B.H. A molecular dynamics study on atomistic mechanisms of nano-scale cutting process of sapphire. J Mech Sci Technol 31, 4353–4362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0834-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0834-5