Abstract
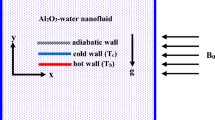
Natural convection in enclosures containing nanofluids is important in physical and environmental applications. Different models for conduction have been developed because of the importance of this phenomenon in natural convection in enclosures. In this study, effects of conduction models of Chon, Corcione, Khanafer, and Koo and Kleinstreuer on the natural convection inside a trapezoidal enclosure with hot and cold walls are evaluated numerically. The enclosure contains Al2O3-water nanofluid with variable properties. Effects of the conduction models on fluid flow, natural convection, variations in volume fraction, and diameter of nanoparticles in the models, as well as the variations in the Rayleigh number, are examined. Results show that at Rayleigh numbers of 105 and 106, the maximum and minimum values of the average Nusselt number are obtained using the models of Khanafer and Chon, respectively. In all models, the average Nusselt number presents upward and downward trends when the volume fraction of nanoparticles increases but decreases when the diameter of the nanoparticles increases. At Ra = 105 in all models, as the volume fraction of nanoparticles increases, the nanofluid provides a higher average Nusselt number compared with the base fluid. By contrast, at Ra = 106, at volume fractions larger than 0.01 and using the model of Chon, the average Nusselt number of the nanofluid is lower compared with that of the base fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, ASME Fluids Eng. Div., 231 (1995) 99–105.
N. Bachok, A. Ishak and I. Pop, Boundary layer flow over a moving surface in a nanofluid with suction or injection, Acta Mechanica Sinica, 28 (2012) 34–40.
J. C. D. Qi, A constrained particle dynamics for continuumparticle hybrid method in micro-and nano-fluidics, Acta Mechanica Sinica, 22 (2006) 503–508.
A Shahsavar, M. R. Salimpour, M. Saghafian and M. B. Shafii, Effect of magnetic field on thermal conductivity and viscosity of a magnetic nanofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 30 (2) (2016) 809–815.
Á. Lakatos, I. Csáky and F. Kalmár, Thermal conductivity measurements with different methods: A procedure for the estimation of the retardation time, Mater. Struct., 48 (2015) 1343–1353.
T. B. Chang and Y. K. Yang, Heat transfer performance of jet impingement flow boiling using Al2O3-water nanofluid, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 28 (4) (2014) 1559–1566.
S. Wang, Y. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Lin, Z. Li, W. Wang, Q. Wu, Y. Qian, H. Hong and C. Zhi, Enhancement of thermal conductivity in water-based nanofluids employing TiO2/reduced graphene oxide composites, J. Mater. Sci., 51 (2016) 10104–10115.
M. Yeganeh, N. Shahtahmasebi, A. Kompany, E. K. Goharshadi, A. Yousse and L. Šiller, Volume fraction and temperature variations of the effective thermal conductivity of nanodiamond fluids in deionized water, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 53 (2010) 3186–3192.
X. Zhang, H. Gu and M. Fujii, Effective thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of nanofluids containing spherical and cylindrical nanoparticles, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 31 (2007) 593–599.
R. Aghayari, H. Maddah, F. Ashori, A. Hakiminejad and M. Aghili, Effect of nanoparticles on heat transfer in mini double-pipe heat exchangers in turbulent flow, Heat Mass Transfer, 51 (2015) 301–306.
X. Zhang, H. Gu and M. Fujii, Effective thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of nanofluids containing spherical and cylindrical nanoparticles, J. Appl. Phys., 100 (2006) 044325.
H. Khorasanizadeh, G. A. Sheikhzadeh, A. A. Azemati and B. S. Hadavand, Numerical study of air flow and heat transfer in a two-dimensional enclosure with floor heating, Energy and Buildings, 78 (2014) 98–104.
H. Xie, M. Fujii and X. Zhang, Effect of interfacial nanolayer on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-?uid mixture, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 48 (2005) 2926–2932.
A. Shahsavar, M. R. Salimpour, M. Saghafian and M. B. Shafii, Effect of magnetic field on thermal conductivity and viscosity of a magnetic nanofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 30 (2016) 809–815.
A. Noghrehabadi and R. Pourraja, Experimental investigation of forced convective heat transfer enhancement of Al2O3/water nanofluid in a tube, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 30 (2) (2016) 943–952.
S. A. Putnam, D. G. Cahill, P. V. Braun, Z. Ge and R. G. Shimmin, Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle suspensions, J. Appl. Phys., 99 (2006) 084308.
M. Assael, C. F.Chen, I. Metaxa and W. Wakeham, Thermal conductivity of suspensions of carbon nanotubes in water, Int. J. Thermophys, 25 (2004) 971–985.
J. S. Jin, Thermal conduction of stable graphite suspensions considering structural characteristics of graphite aggregations, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 9 (2013) 2893–2898.
H. Xie, H. Lee, W. Youn and M. Choi, Nano?uids containing multi walled carbon nanotubes and their enhanced thermal properties, J. Appl. Phys., 94 (2003) 4967–4971.
R. Saidur, S. N. Kazi, M. S. Hossain, M. M. Rahman and H. A. Mohammed, A review on the performance of nanoparticles suspended with refrigerants and lubricating oils in refrigeration systems, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 15 (2011) 310–323.
R. Saidur, K. Y. Leong and H. A. Mohammad, A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 15 (2011) 1646–1668.
S. Lee and S. U. S. Choi, Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles, J. Heat Transfer, 121 (1999) 280–289.
M. Corcione, Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids, Energy Conversion and Management, 52 (2011) 789–793.
I. Tmartnhad, M. El Alami, M. Najam and A. Oubarra, Numerical investigation on mixed convection flow in a trapezoidal cavity heated from below, Energy Conversion and Management, 49 (2008) 3205–3210.
Y. Varol, Natural convection in divided trapezoidal cavities filled with fluid saturated porous media, J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 37 (2010) 1350–1358.
G. A. Sheikhzadeh, A. Arefmanesh, M. H. Kheirkhah and R. Abdollahi, Natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a cavity with partially active side walls, European J. Mechanics B/Fluids, 30 (2011) 166–176.
H. Saleh, R. Roslan and I. Hashim, Natural convection heat transfer in a Nano fluid filled trapezoidal enclosure, Int. J. Thermal Science, 54 (2011) 194–201.
R. Nasrin and P. Salma, Investigation of buoyancy-driven flow and heat transfer in a trapezoidal cavity filled with water-Cu Nano fluid, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 39 (2012) 270–284.
G. A. Sheikhzadeh, M. Ebrahim Qomi, N. Hajialigol and A. Fattahi, Numerical study of mixed convection flows in a liddriven enclosure filled with nano fluid using variable properties, Int. J. Results in Physics, 2 (2012) 5–13.
A. da Silva, É. Fontana, V. Mariani and F. Marcondes, Numerical investigation of several physical and geometric parameters in the natural convection into trapezoidal cavities, J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 55 (2012) 6808–6818.
J. Koo and C. Kleinstreuer, A new thermal conductivity model for nanofluids, J. Nanoparticle Res., 6 (2004) 577–588.
C. H. Chon, K. D. Kihm, S. P. Lee and S. U. S. Choi, Empirical correlation finding the role of temperature and particle size for nanofluid (Al2O3) thermal conductivity enhancement, Appl. Phys. Lett., 87 (2005) 153107.
K. Khanafer and K. Vafai, A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 54 (2011) 4410–4428.
A. Bijan, Convection heat transfer, Third Edition, Wily, New York(1984).
J. Koo and C. Kleinstreuer, Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks, J. Heat Mass Transfer, 48 (2005) 2652–2661.
Z. Alloui, P. Vasseur and M. Reggio, Natural convection of nanofluids in a shallow cavity heated from below, Int. J. Thermal Sciences, 50 (2010) 1–9.
S. M. Aminossadati and B. Ghasemi, Natural convection of water-CuO nanofluid in a cavity with two pairs of heat source-sink, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 38 (2011) 672–678.
K. Hoffman and S. T. Chiang, Computational fluid dynamics for engineers, Engineering Education System(1993).
J. D. Anderson, Computational Fluid Dynamics, The Basics with Applications, Springer(1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Jun Sang Lee
Ali Akbar Abbasian Arani received B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees from Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, in 1991 and 1994, respectively, and his Ph.D. degree from the University of Bordeaux 1, France, in 2006. He is currently Associate Professor in the Mechanical Engineering Department at the University of Kashan, Iran. His research interests include fluid mechanics and heat transfer, nanofluids and energy conversion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arani, A.A.A., Azemati, A.A., Rezaee, M. et al. Numerical study of different conduction models for Al2O3-water nanofluid with variable properties inside a trapezoidal enclosure. J Mech Sci Technol 31, 2433–2441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0441-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0441-5