Abstract
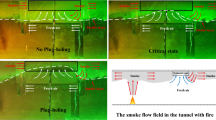
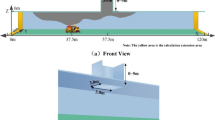
When the plug-holing phenomena occurs, the actual amount of smoke exhaust could not be able to satisfy the design criteria of the smoke ventilation. The plug-holing phenomenon is influenced by various factors, but has not yet suggested accurate criteria for the plugholing. Especially, the effect of tunnel geometry was not considered, despite the smoke movement is influenced by hydraulic diameter of tunnel. In this study, we performed the numerical simulation to analyze the effect of the hydraulic diameter of a tunnel on plug-holing.
According to the numerical result, it was identified that the total mass flux increased and the mass flux of smoke decreased as the hydraulic diameter of tunnel was increased. A new, modified Froude number is suggested for estimating the occurrence of plug-holing by including the effect of the hydraulic diameter for shallow tunnels. Additionally, the critical value of the modified Froude number is defined as 0.104 based on the results of the numerical simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. C. Park, Standard of smoke control systems in ultra highrise buildings, Magazine of ASREK, 38 (11) (2009) 10–25 (in Korean).
Y. Alarie, Toxicity of fire smoke, Crit. Rev. Toxicol, 2 (2002) 259–289.
S. R. Lee, A numerical study on smoke movement in longitudinal ventilation tunnel fires for different aspect ratio, Build. Environ., 41 (2006) 719–725.
G. Heskestad, Smoke distributions from fire plumes in uniform downdraft from a ceiling, Fire Saf. J., 39 (2004) 358–374.
P. L. Hinkley, The flow of hot gases along an enclosed shopping mall, Fire Res. (1970) note no.807.
D. Spratt, Efficient extraction of smoke from a thin layer under a ceiling, Fire Res.(1974) note no.1001.
J. Ji, Z. H. Gao, C. G. Fan, W. Zhong and J. H. Sun, A study of the effect of plug-holing and boundary layer separation on natural ventilation with vertical shaft in urban road tunnel fires, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 55 (2012) 6032–6041.
J. Ji, Z. H. Gao, C. G. Fan and J. H. Sun, A large Eddy simulation of stack effect on natural smoke exhausting effect in urban road tunnel fires, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 66 (2013) 531–542.
J. Ji, J. Y. Han, C. G. Fan, Z. H. Gao and J. H. Sun, Influence of cross-sectional area and aspect ratio of shaft on natural ventilation in urban road tunnel, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 67 (2013) 420–431.
Y. Wu and M. Z. Bakar, Control of smoke flow in tunnel fires using longitudinal ventilation systems -A study of the critical velocity, Fire Saf. J., 35 (2000) 363–390.
S. R. Lee, An experimental study of the effect of the aspect ratio on the critical velocity in longitudinal ventilation, Tunnel Fires. J. Fire Sci., 23 (2005) 119–138.
M. Weng, X. Lu, F. Liu, X. Shi and L. Yu, Prediction of backlayering length and critical velocity in metro tunnel fires, Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol., 47 (2015) 64–72.
R. A. Klein, SFPE handbook of fire protection engineering, Fire Saf. J.(1995).
L. Y. Cooper, M. Harkleroad, J. Quintiere and W. Rinkinen, An experimental study of upper hot layer stratification in full-scale multiroom fire scenarios, J. Heat Transfer, 104 (1982) 741–749.
M. Janssens and H. C. Tran, Data reduction of room tests for zone model validation, J. Fire Sci., 10 (1992) 528–555.
A. Hamins and K. Takashi, Characteristics of pool fire burning, Fire Resist. Ind. Fluids, 1284 (1995) 15–41.
J. G. Quintiere, Scaling applications in fire research, Fire Saf. J., 15 (1989) 3–29.
K. McGrattan, S. Hostikka, R. McDermott, J. Floyd, C. Weinschenk and K. Overholt, Fire dynamics simulator, technical reference guide, Volume 1: Mathematical model, NIST Spec., 1018(2013).
J. G. Quintiere, Principles of fire behavior, Cengage Learning(1998).
J. Morehart, E. Zukoski and T. Kubota, Characteristics of large diffusion flames burning in a vitiated atmosphere, Fire Saf. Sci., 3 (1991) 575–583.
B. Seo and J. Choi, Analysis of stack effect considering methods of smoke control in a high-rise building, 7th International Symposium of Asia Institute of Urban Enviroment (2010) 312–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Weon Gyu Shin
Dabin Baek obtained his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Mechanical Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea in 2013 and 2015, respectively. He is a Ph.D. candidate in School of Mechanical Engineering at Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
Sungryong Bae, Ph.D., is a Researcher in the Mechanical Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. He is the Assistant Professor in the Graduate School of Design and Architecture, Nagoya City University, Nagoya, Japan.
Hong Sun Ryou obtained his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Aeronautical Engineering from Seoul National University. He obtained Ph.D. degree in Aeronautics from Imperial College, London, UK. He is a Professor in School of Mechanical Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, D., Bae, S. & Ryou, H.S. A numerical study on the effect of the hydraulic diameter of tunnels on the plug-holing phenomena in shallow underground tunnels. J Mech Sci Technol 31, 2331–2338 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0429-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0429-1