Abstract
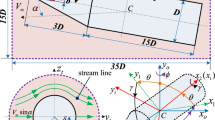
The aerodynamic characteristics of nine configurations of supersonic continuous deflectable nose guided missiles have been investigated. The optimized geometry was achieved based on the accuracy of confliction with constant target in ground to ground mission. The studied configurations consist of a spherical nose tip, a tangent ogive, one set of stabilizing tail fines and a cylindrical body whose midsection is flexible to form an arc of a circle. So the cylindrical body consists of a fixed part in the vicinity of the nose, middle flexible part and main body with stabilizers. The effects of fixed length (Fix = 0, 1.5, 3Cal) and flexible length (Flex = 1, 2.5, 5Cal) parameters on the aerodynamics and flight dynamics of guided missile have been studied. A code has been developed to solve full Navier-Stokes equations using finite volume and Runge-Kutta time stepping techniques and modified Baldwin-Lomax turbulence model. Multi-block technique was also used to solve the main body and fin parts flow fields. Further, a 3 degree of freedom code along with a pure pursuit guidance subroutine was developed to compare planar flight dynamics of missiles. It was found that although the missiles with bigger lengths for fixed and flex parts show more maneuverability, but this is not favorable for all missile missions as sometimes it decreases the confliction accuracy. Flight dynamic analysis shows that a change in initial launch angle may shift the favorite configuration. This means only the aerodynamic defined aim functions cannot completely supersede flight dynamic analysis in geometric optimization. Further, the thrust vector moment is an important portion of total control moment as it enhances the hitting accuracy and also decreases the importance of geometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Deng, F. Kong and H. D. Kim, Numerical simulation of fluidic thrust vectoring in an axisymmetric supersonic nozzle, J. of Mechanical Science and Technology, 28 (12) (2014) 4979–4987.
L. A. Darden, K. G. Peterson and N. M. Komerath, Vortex control using a moveable nose with pressure feedback, AIAA 95-3468, Atmospheric Flight Mechanics Conference (1995).
W. H. Hathaway, G. Winchenbach and J. Krieger, Freeflight tests of 10-degree cones with a one degree articulation angle, AIAA-1999-0434, 37th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit (1999).
M. E. Vaughn and L. M. Auman, A productivity-oriented application of computational fluid dynamics to the design of a hypervelocity missile, AIAA 2002-2937, 20th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference (2002).
M. E. Vaughn and L. M. Auman, Assessment of a productivity-oriented CFD methodology for designing a hypervelocity missile, AIAA 2003-3937, 21st AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference (2003).
M. E. Vaughn and L. M. Auman, An initial foray into the productive application of computational fluid dynamics, Aviation and Missile Research, Development, and Engineering Center, Technical Report AMR-SS-08-07 (2008).
M. E. Vaughn, An application of vorticity confinement to missile aerodynamic design, 24th Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA 2006-3866 (2006).
M. E. Vaughn, Relating vorticity confinement to the menter shear stress transport turbulence model, Aviation and Missile Research, Development, and Engineering Center, Technical Report AMR-SS-08-11 (2008).
W. B. Blake and E. D. Karni, A cambered body method for missile datcom, 23rd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA 2005-4971 (2005).
B. Shoesmith, T. Birch, M. Mifsud, M. Meunier and S. Shaw, CFD analysis of a supersonic projectile having a deflectable nose control, 3rd AIAA Flow Control Conference, AIAA 2006-3200 (2006).
Y. Yang, S. Jung, T. Cho and R. Myong, An aerodynamic shape optimization study to maximize the range of a guided missile, 28th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference (2010).
H. Nobahari, Y. Nabavi and H. Pourtakdoust, Aerodynamic shape optimization of unguided projectiles using ant colony optimization and genetic algorithm, 25th International Congress of the Aeronautical Sciences, Sharif University of Technology (2006).
M. Kwak, S. Yun, Y. Lee, H. Kwon, K. Kim and D. H. Lee, Optimum nose shape of a front-rear symmetric train for the reduction of the total aerodynamic drag, J. of Mechanical Science and Technology, 27 (12) (2013) 3733–3743.
M. Pasandideh-Fard and A. Khalghani, Aerodynamic shape optimization of supersonic projectile fins, Fluid Mechanics & Aerodynamics J., 1 (1) (2012) 73–87 (In Persian).
A. Jameson, W. Schmidth and E. Turkel, Numerical solution of the Euler equations by finite volume methods Using Runge Kutta time stepping schemes, AIAA paper 81-1259, 14th Fluid Dynamics and Plasma Dynamics Conference (1981).
M. Pasandideh-Fard and M. Malek-Jafarian, Full Navier Stokes computations of supersonic flows over a body at high angles of attack and investigation of cross flow separation, Scientia Iranica J., 11 (4) (2004) 339–350.
H. Montazeri, 3D numerical analysis & parametric study of supersonic projectiles with fins, using multi-block grid generations, M.Sc. Thesis, Eng. Faculty of Ferdowsi University, Iran (2005) (In Persian).
M. M. Alishahi, H. Emdad and O. Abouali, 3-D thin layer Navier-Stokes solution of supersonic turbulent flow, Scientia Iranica J., 10 (1) (2003) 74–83.
R. P. Raklis and W. B. Sturek, Surface pressure measurements on slender bodies at angle of attack at supersonic speeds, U.S. Army Ballistic Research Laboratory, Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland ARBRLMR-02876 (AD A064097) (1978).
A. Khalghani, M. H. Javareshkian and M. P. Fard, Continuous deflectable nose versus pivoted nose and canard control design for fin stabilized missiles at supersonic speeds, J. of Aeronautical Engineering, 15 (1) (2013) (In Persian).
R. C. Swanson and E. Turkel, On central difference and upwind scheme, J. Comp. Phys., 101 (1992) 297–306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Kyu Hong Kim
Abbas Khalghani received the B.S. from the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran, in 1988 and his M.S. in Mechanical Engineering from University of Tehran, Iran, in 2000. He is currently a Ph.D. student at Ferdowsi University of Mashhad. His research interests include experimental aerodynamics, CFD and flight dynamics.
Mahmoud Pasandideh Fard is an Associate Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Eng. at Ferdowsi University of Mashhad. He received his B.Sc. and M.Sc. in Mechanical engineering from Ferdowsi university of Mashhad, Iran, in 1985 and 1988. He received his Ph.D. in Aerospace Engineering in 1998 from Sydney University of Australia. He currently teaches and researches at the university. His research interests are include computational low and high speed aerodynamics, boundary layer flows, hydrodynamics, cavitation and super-cavitation, turbulence modeling and supersonic projectiles.
Mohammad Hassan DJavareshkian received his Ph.D. from Imperial College, University of London in 2006, in field of CFD. Since 2008 he has taught in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Research areas of interest are CFD, gas dynamics, oscillatory flows and aerodynamics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalghani, A., Pasandideh-Fard, M. & Djavareshkian, M.H. Aerodynamic shape study of supersonic surface to surface missiles with continuous flexible nose. J Mech Sci Technol 30, 3183–3192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0512-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0512-z