Abstract
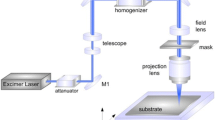
This paper describes the results of the application of laser direct imaging (LDI) lithography for dimensional tolerance improvement through surface treatment of cutting edge in the flexible fine dies (FFD). Laser direct imaging lithography was successfully performed on AISI W1-8 substrates by a specifically designed laser system using UV 355 nm light source. The characteristics of patterned line width according to conditions such as scan speed and multi pass were investigated by optical microscope. The average line width of LDIed patterns was observed to be about 1 mm. The experimental results show that the line width of patterned samples was reduced with increasing scan speed and decreasing repetition number (R/N) of scanning. This conclusion proves the feasibility in the selectively application for manufacturing flexible fine die.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. W. Kim, K. H. Kim, S. H. Cho, K. T. Ryu and M. C. Kang, Mechanical properties and cutting performance of Cr-Al-N hybrid coated micro-tool for micro high-speed machining of flexible fine die, Curr. Appl. Phys., 12 (2012) 14–18.
S. Iguchi, H. Kudo, T. Saito, M. Ogawa and H. Saito, A flexible and wearable biosensor for tear glucose measurement, Biomed. Microdevices, 9 (2007) 603–609.
Y. Wang, Z. Yang, Z. Hou, D. Xu, L. Wei, E. S. W. Kong and Y. Zhang, Flexible gas sensors with assemble carbon nanotube thin films for DMMMP vapor detection, SENSORS ACTUAT B-CHEM, 150 (2) (2010) 708–714.
Y. Liu, S. Gorgutsa, C. Santato and M. Skorobogatiy, Flexible, solid electrolyte-based lithium battery composed of LiFePO4 cathode and Li4Ti5O12 anode for applications in smart textiles, J. Electrochem. Soc., 159 (2012) 349–356.
S.-Y. Hwang, H.-H. Park, S.-M. Kang, H.-B. Shin and H. K. Kang, Fabrication of nanopatterned metal sheet using photolithography and electroplating, Thin solid films, 16 (2013) 132–135.
D. Xia, Z. Ku, D. Li and S. R. J. Brueck, Formation of hierarchical nanoparticle pattern arrays using colloidal lithography and two-step self-assembly: Microspheres atop nanospheres, Chem. Mater., 20 (5) (2008) 1847–1854.
S. J. Kwon, W. S. Chang and S. H. Jeong, Shape and size variations during nanopatterning of photoresist using nearfield scanning optical microscope, Ultramicroscopy, 105 (1–4) (2005) 316–323.
A. Tarun, M. Rosendo and H. Daza, Apertureless optical near-field fabrication using an atomic force microscope on photoresists, Appl. Phys. Lett., 80 (2002) 3400–3402.
J. Jersch, F. Demming and K. Dickmann, Nanostructuring with laser radiation in the nearfield of a tip from a scanning force microscope, APPL PHYS A-MATER, 64 (1997) 29–32.
S. Z. Shuja, B. S. Yilbas and O. Momin, Laser repetitive pulse heating and melt pool formation at the surface, The Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 25 (2011) 479–487.
S. Choi, C. S. Kim, K. Y. Jhang and W. S. Shin, Surface characteristics of aluminum 6061-T6 subjected to Nd:YAG pulsed laser irradiation, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 26 (2012) 2163–2166.
H. Sugimura, K. Hayashi, N. Saito, N. Nakagiri and O. Takai, Surface potential microscopy for organized molecular systems, Appl. Surf. Sci., 188 (3–4) (2002) 403–410.
Y. H Shen, S. Pal, J. Mandal, T. Sun, K. T. V. Grattan, S. A. Wade, S. F. Collins, G. W. Baxter, B. Dussardier and G. Monnom, Investigation of the photosensitivity, temperature sustainability and fluorescence characteristics of several Er-doped photosensitive fibers, Opt. Commun., 237 (4–6) (2004) 301–308.
W. P. King, T. W. Kenny, K. E. Goodson, G. L. W. Cross, M. Despont, U. T. Durig, H. Rothuizen, G. Binnig and P. Vettiger, Atomic force microscope cantilevers for combined thermomechanical data writing and reading, Appl. Phys. Lett., 78 (9) (2001) 1300–1302.
D. Su and Y. Zhu, Scanning moiré fringe imaging by scanning transmission electron microscopy, Ultramicroscopy, 110 (3) (2010) 229–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor In-Ha Sung
Ki-Taek Ryoo is a president of Finetech co., ltd. It mainly research and develop for flexible fine dies with high resolution. He has a bachelor’s degree from Pusan National University and a master’s course at Graduate School of Convergence Science in same University. Present research field is an optimizing of the flexible fine dies.
Myung-Chang Kang is a professor in the Graduate School of Convergence Science, Pusan National University. His research fields are a study on the fabrication of hybrid materials and the application of hybrid machining. He takes part in base project through the Global Frontier Hybrid Interface Materials (GFHIM) of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryoo, K., Kim, M., Sung, J. et al. Maskless laser direct imaging lithography using a 355-nm UV light source in manufacturing of flexible fine dies. J Mech Sci Technol 29, 365–370 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-1243-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-1243-7