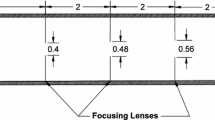
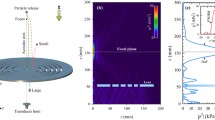
Abstract
Most studies on particle focusing using an aerodynamic lens concentrate on loss and focusing performance of the lens itself without accounting for the critical orifice that acts as the actual inlet. If the newly proposed design for an aerodynamic lens capable of focusing particles over a wide range of 30 nm — 10 μm is integrated into the critical orifice, this will result in a huge loss of super-micron particles (> 1 μm in diameter), and the downstream aerodynamic lens will no longer have an advantage. CFD simulations were performed to investigate the loss of particles in the critical orifice and a new converging-diverging critical orifice was proposed instead of the conventional flat critical orifice to reduce the particle loss. By optimizing the angle of the converging and diverging sections as well as the relaxation chamber design, we derived an optimal design for the final aerodynamic lens and integrated system. As a result, we can generate particle beams of less than 1 mm with more than 80% penetration efficiency for particles in the 50 nm -7 μm range, and a 60% penetration efficiency for particles of 30 nm and 10 μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Liu, P. Ziemann, D. Kittelson and P. McMurry, Generation of particle beams of controlled dimensions and divergence: I. Theory of particle motion in aerodynamic lenses and orifice expansions, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 22 (1995) 293–313.
P. Liu, P. Ziemann, D. Kittelson and P. McMurry, Generation of particle beams of controlled dimensions and divergence: II. Experimental evaluation of particle motion in aerodynamic lenses and orifice expansions, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 22 (1995) 314–324.
D. Lee, K. Park and M. Zachariah, Determination of size distribution of polydisperse nanoparticles with single particle mass spectrometry: The role of ion kinetic energy, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 39 (2005) 162–169.
D. Lee, A. Miller, D. Kittelson and M. Zachariah, Characterization of metal-bearing diesel nanoparticles using single particle mass spectrometry, J. Aerosol Sci., 37 (1) (2006) 88–110.
K. Lee, S. Cho and D. Lee, Development and experimental evaluation of aerodynamic lens as an aerosol inlet of single mass spectrometry, J. Aerosol Sci., 39 (2008) 287–304.
Y. Su, M. F. Sipin, H. Furutani and K. A. Prather, Development and characterization of an aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer with increased detection efficiency, Anal. Chem., 76 (2004) 712–719.
D. Y. Liu, D. Rutherford, M. Kinsey and K. A. Prather, Real-time monitoring of pyrotechnically derived aerosol particles in the troposphere, Anal. Chem., 69 (10) (1997) 1808–1814.
Y. Dong, A. Bapat, S. Hilchie, U. Kortshagen and S. Campbell, Generation of nano-sized free standing single crystal silicon particles, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B, 22 (4) (2004) 1923–1930.
F. Fonzo, A. Gidwani, M. Fan, D. Neumann, D. Iordanoglou, J. Heberlein, P. McMurry, S. Girshick, N. Tymiak, W. Gerberich and N. Rao, Focused nanoparticle-beam deposition of patterned microstructures, Appl. Phys. Lett., 77 (6) (2000) 910–912.
L. Qi, P. MuMurry, D. Norris and S. Girshick, Micropattern deposition of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals by aerodynamic focusing, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 44 (2010) 55–60.
W. Harris, P. Reilly and W. Whitten, Aerosol MALDI of peptides and proteins in an ion trap mass spectrometer: Trapping, resolution and signal-to-noise, Int. J. Mass. Spectrom, 258 (2006) 113–119.
W. Murphy and G. Sears, Production of particulate beams, J. Appl. Phys., 35 (1964) 1986–1987.
R. Das and D. Phares, Expansion of an ultrafine aerosol through a thin-plate orifice, J. Aerosol Sci., 35 (2004) 1091–1103.
R. Deng, X. Zhang, K. Smith, J. Wormhoudt, D. Lewis and A. Freedman, Focusing particle with diameters of 1 to 10 microns into beams at atmospheric pressure, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 42 (2008) 899–915.
D. Chen and Y. Pui, Numerical and experimental studies of particle deposition in a tube with a conical contractionlaminar flow regime, J. Aerosol Sci., 26 (4) (1995) 563–574.
X. Wang and P. McMurry, An experimental study of nanoparticle focusing with aerodynamic lenses, Int. J. Mass. Spectrom, 258 (2006) 30–36.
X. Wang and P. McMurry, A design tool for aerodynamic lens systems, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 40 (2006) 320–334.
X. Zhang, K. Smith, D. Worsnop, J. Jimenez, J. Jayne, C. Kolb, J. Morris and P. Davidovits, Numerical characterization of particle beam collimation: Part II Integrated aerodynamic-lens-orifice system, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 38 (2004) 19–638.
X. Wang, A. Gidwani, S. Girshick and P. McMury, Aerodynamic focusing of nanoparticles: II. Numerical simulation of particle motion through aerodynamic lenses, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 39 (2005) 624–636.
K. Lee, S. Kim and D. Lee, Aerodynamic focusing of 5–50 nm nanoparticles in air, J. Aerosol Sci., 40 (2009) 1010–1018.
K. Lee, T. Hwang and D. Lee, A numerical analysis of the aerodynamic focusing of particles with wide-range diameters of 30 nm-10 μm, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 47 (2013) 1001–1008.
P. Liu, R. Deng, K. Smith, L. Williams, J. Jayne, M. Canagaratna, K. Moore, T. Onasch, D. Worsnop and T. Deshler, Transmission efficiency of an aerodynamic focusing lens system: Comparison of model calculations and laboratory measurements for the aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 41 (2007) 721–733.
S. Chen, C. Tsai, C. Wu, D. Pui, A. Onischuk and V. Karasev, Particle loss in a critical orifice, J. Aerosol Sci., 38 (2007) 935–949.
J. F. Cahill, T. K. Darlington, X. Wang, J. Mayer, M. T. Spencer, J. C. Holecek, B. E. Reed and K. A. Prather, Development of a high-pressure aerodynamic lens for focusing large particles (4–10 μm) into the aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 48 (9) (2014) 948–956.
L. R. Williams et al., Characterization of an aerodynamic lens for transmitting particles greater than 1 micrometer in diameter into the aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer, Atmos Meas. Tech., 6 (2013) 3271–3280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Suk Goo Yoon
Donggeun Lee is a Professor at School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University and is now leading a basic research lab (BRL) and a Nanoparticle engineering lab. More information is available in http://home.pusan.ac.kr/~mnht.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, TH., Kim, SH., Kim, S.H. et al. Reducing particle loss in a critical orifice and an aerodynamic lens for focusing aerosol particles in a wide size range of 30 nm — 10 μm. J Mech Sci Technol 29, 317–323 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-1238-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-1238-4