Abstract
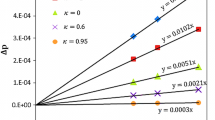
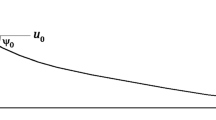
We numerically investigated the behavior of the water meniscus formed between a flat surface and a tip surface, which is flat or circular in shape, using the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The shape of the water meniscus formed between the flat bottom surface and the tip surface depends on the tip shape and the interaction between the water meniscus and the bottom or tip surface. The interaction is determined by the contact angles of the bottom and tip surfaces, resulting in different contact lengths between the water meniscus and the bottom or tip surface. The difference in these contact lengths depends on the effects of both the tip curvature and the interaction between the water meniscus and the bottom or tip surface. We classified the shapes of the water meniscus into seven different patterns as a function of the contact angles of the flat bottom and tip surfaces: concave, semi-concave, inverse semi-concave, column, convex, semi-convex, and inverse semi-convex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Salaita, Y. Wang and C. A. Mirkin, Applications of dippen nanolithography, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2 (2007) 145–155.
A. Mirkin, The power of the pen: development of massively parallel dip-pen nanolithography, ACS Nano, 1 (2007) 79–83.
D. S. Ginger, H. Zhang and C. A. Mirkin, The evolution of dip-pen nanolithography, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 43 (2004) 30–45.
R. D. Piner, J. Zhu, F. Xu, S. Hong and C. A. Mirkin, Dip-pen nanolithography, Science, 283 (1999) 661–663.
J. Jang, G. C. Schatz and M. A. Ratner, Liquid meniscus condensation in dip-pen nanolithography, J. Chem. Phys, 116 (2002) 3875–3886.
P. Manandhar, J. Jang, G. C. Schatz, M. A. Rantner and S. Hong, Anomalous surface diffusion in nanoscale direct deposition processes, Phys. Rev. Lett., 90 (2002) 115505.
N. Cho, S. Ryu, B. Kim, G. C. Schatz and S. Hong, Phase of molecular ink in nanoscale direct deposition processes, J. Chem. Phys., 124 (2006) 024717.
B. L. Weeks, A. Noy, A. E. Miller and J. J. De Yoreo, Effect of dissolution kinetics on feature size in dip-pen nanolithography, Phys. Rev. Lett., 88 (2002) 255505.
J. R. Hamptom, A. A. Dameron and P. S. Weiss, Transport rates vary with deposition time in dip-pen nanolithography, J. Phys. Chem. B, 109 (2005) 23118.
D. L. Malotky and M. K. Chaudhury, Investigation of capillary forces using atomic force microscopy, Langmuir, 17 (2001) 7823–7829.
W. C. Carter, The forces and behavior of fluids constrained by solids, Acta metal., 36 (1988) 2283–2292.
E. J. D. Souza, M. Brinkmann, C. Mohrdieck, A. Crosby and E. Arzt, Capillary forces between chemically different substrates, Langmuir, 24 (2008) 10161–10168.
E. J. D. Souza, M. Brinkmann, C. Mohrdieck and E. Arzt, Enhancement of capillary forces by multiple liquid bridges, Langmuir, 24 (2008) 8813–8820.
T. Stifer, O. Marti and B. Bhushan, Theoretical investigation of the distance dependence of capillary and van der Waals forces in scanning force microscopy, Phys. Rev. B, 62 (2000) 13 667–13 673.
M. Farshchi-Tabrizi, M. Kapple, Y. Cheng, J. Gutmann and H. J. Butt, On the adhesion between fine particles and nanocontacts: an atomic force microscope study, Langmuir, 22 (2006) 2171–2184.
A. K. Gunstensen and D. H. Rothman, Lattice Boltzmann model of immiscible fluids, Phy. Rev. A, 43 (1991) 4320–4327.
X. Shan and H. Chen, Lattice Boltzmann model of simulating flows with multiple phases and components, Phy. Rev. E, 47 (1993) 1815–1819.
M. R. Swift, W. R. Osborn and J. M. Yeomans, Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of nonideal fluids, Phy. Rev. Lett., 75 (1995) 830–833.
T. Inamuro, T. Ogata, S. Tajima and N. Konishi, A lattice Boltzmann method for incompressible two-phase flows with large density differences, J. Comput. Phys., 198 (2004) 628–644.
Y. Y. Yan and Y. Q. Zu, A lattice Boltzmann method for incompressible two-phase flow on partial wetting surface with large density ratio, J. Comput. Phys., 227 (2007) 763–775.
M. Yoshino and Y. Mizutani, Lattice Boltzmann simulation of liquid-gas flows through solid bodies in a square duct, Math. Comput. Simul., 72 (2006) 264–269.
A. J. Briant, P. Papatzacos and J. M. Yeomans, Lattice Boltzmann simulations of contact line motion in a liquid-gas system, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A, 360 (2002) 485–495.
A. J. Briant, A. J. Wagner and J. M. Yeomans, Lattice Boltzmann simulations of contact line motion: I. Liquid-gas system, Phys. Rev. E, 69 (2004) 031602.
J. W. Cahn, Critical point wetting, J. Chem. Phys., 66 (1977) 3667–3672.
Y. Kataoka and T. Inamuro, Numerical simulations of the behavior of a drop in a square pipe flow using the two-phase lattice Boltzmann method, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A, 369 (2011) 2528–2536.
Y. Tanaka, Y. Washio, M. Yoshino and T. Hirata, Numerical simulation of dynamic behavior of droplet on solid surface by the two-phase lattice Boltzmann method, Comput. Fluids, 40 (2011) 68–78.
P. L. Bhatnagar, E. P. Gross and M. Krook, A model for collision processes in gases. I. Small amplitude processes in changed and neutral one-component systems, Phys. Rev., 94 (1954) 511–525.
L. Wu, M. Tsutahara, L. S. Kim and M. Y. Ha, Threedimensional lattice Boltzmann simulations of droplet formation in a cross-junction microchannel, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 34 (2008) 852–864.
Q. Zou and X. He, On pressure and velocity flow boundary conditions and bounceback for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model, Phys. Fluids, 9 (1997) 1591–1610.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Yang Na
M. Y. Ha received his B.S. degree from Pusan National University, Korea in 1981, his M.S. degree, in 1983, from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Korea, and his Ph.D. degree from Pennsylvania State University, USA in 1990. Dr. Ha is currently a Professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering at Pusan National University in Buasn, Korea. He serves as an Editor of the Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology. His research interests are focused on thermal management, computational fluid dynamics, and micro/nanofluids.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, S.W., Ha, M.Y., Kim, Ss. et al. A numerical study on the behavior of the water meniscus formed between a flat surface and a flat or circular tip. J Mech Sci Technol 28, 1285–1295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0118-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0118-2