Abstract
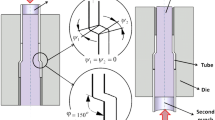
Tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) is a new and novel severe plastic deformation (SPD) technique suitable for fabrication of bulk nanograined tubular materials. There are several parameters in the TCAP process. The present paper investigates the effects of curvature angles, deformation ratio (maximum radius during TCAP/initial radius) and deformation direction on the plastic deformation behavior, strain homogeneity and required loads in TCAP processing. The results showed that higher curvature angles (ψ 1 and ψ 3) leads to better strain homogeneity while have not having any significant effect on the process loads. Also, at the second curvature angle of 90°, the best condition is achieved with good strain homogeneity and lower load requirements rather than lower angles. Investigation of deformation direction showed that inlet deformation direction causes tube thinning at the end of the process, and thus, using the inlet case is not recommended.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev and I. V. Alexandrov, Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation, Progress in Materials Science, 45 (2000) 103–189.
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon, Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement, Progress in Materials Science, 51 (2006) 881–981.
H. K. Kim, M. Choi, C. S. Chung and D. H. Shin, Fatigue crack growth behavior in ultrafine grained low carbon steel, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 16 (2002) 1246–1252.
H. K. Kim, Low-temperature creep behavior of ultrafinegrained 5083 Al alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 24 (2010) 2075–2081.
A. P. Zhilyaev and T. G. Langdon, Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: Fundamentals and applications, Progress in Materials Science, 53 (2008) 893–979.
Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, N. Tsuji and T. Sakai, Novel ultrahigh straining process for bulk materials development of the accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process, Acta Materialia, 47 (1999) 579–583.
M. Reihanian, R. Ebrahim, M. M. Moshksar, D. Terada and N. Tsuji, Microstructure quantification and correlation with flow stress of ultrafine grained commercially pure Al fabricated by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP), Materials Characterization, 59 (2008) 1312–1323.
Y. Beygelzimer, V. Varyukhin, S. Synkov and D. Orlov, Useful properties of twist extrusion, Materials Science and Engineering A, 503 (2009) 14–17.
A. Shirdel, A. Khajeh and M. M. Moshksar, Experimental and finite element investigation of semi-constrained groove pressing process, Materials & Design, 31 (2010) 946–950.
G. Faraji and P. Asadi, Characterization of AZ91/alumina nanocomposite produced by FSP, Materials Science and Engineering A, 528 (2011) 2431–2440.
P. Asadi, G. Faraji and M. K. Besharati, Producing of AZ91/SiC composite by friction stir processing (FSP), The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 51 (2010) 247–260.
G. Faraji, M. M. Mashhadi and H. S. Kim, Microstructure inhomogeneity in ultra-fine grained bulk AZ91 produced by accumulative back extrusion (ABE), Materials Science and Engineering A, 528 (2011) 4312–4317.
G. Faraji, O. Dastani and S. A. A. Akbari Mousavi, Effect of process parameters on microstructure and micro-hardness of AZ91/Al2O3 surface composite produced by FSP, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 20 (2011) 1583–1590.
K. Wu, K. Deng, K. Nie, Y. Wu, X. Wang, X. Hu and M. Zheng, Microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/AZ91 composite deformed through a combination of forging and extrusion process, Materials and Design, 31 (2010) 3929–3932.
B. Tolaminejad and K. Dehghani, Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of nanostructured AA1070 aluminum after equal channel angular extrusion, Materials & Design, 34 (2012) 285–292.
G. Faraji and H. Jafarzadeh, Accumulative torsion back (ATB) processing as a new plastic deformation technique, Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 27 (2012) 507–511.
X. Han and L. Hua, Comparison between cold rotary forging and conventional forging, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 23 (2009) 2668–2678.
S. M. Byon, C. H. Moon and Y. Lee, Strain gradient plasticity based finite element analysis of ultra-fine wire drawing process, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 23 (2009) 3374–3384.
G. Faraji, M. M. Mashhadi and H. S. Kim, Tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) as a novel severe plastic deformation method for cylindrical tubes, Materials Letters, 65 (2011) 3009–3012.
G. Faraji, M. M. Mashhadi and H. S. Kim, Deformation behavior in tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) using triangular and semicircular channels, Materials Transactions, 53 (2012) 8–12.
A. V. Nagasekhar, S. C. Yoon, Y. Tick-Hon and H. S. Kim, An experimental verification of the finite element modelling of equal channel angular pressing, Computational Materials Science, 46 (2009) 347–351.
G. Faraji, M. M. Mashhadi, S-H. Joo and H. S. Kim, The role of channel angle on plastic deformation behavior in tu-bular channel angular pressing (TCAP), Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, (2012) In press.
G. Faraji, H. Jafarzadeh, H. J. Jeong, M. M. Mashhadi and H. S. Kim, Numerical and experimental investigation of the deformation behavior during the accumulative back extrusion of an AZ91 magnesium alloy, Materials & Design, 35 (2012) 251–258.
H. S. Kim, Finite element analysis of deformation behaviour of metals during equal channel multi-angular pressing, Materials Science and Engineering A, 328 (2002) 317–323.
H. S. Kim, M. H. Seo and S. I. Hong, On the die corner gap formation in equal channel angular pressing, Materials Science and Engineering A, 291 (2000) 86–90.
G. I. Raab, Plastic flow at equal channel angular processing in parallel channels, Materials Science and Engineering A, 410 (2005) 230–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Jin weon Kim
Ghader Faraji is a Ph.D candidate in the University of Tehran in the field of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering. He was selected as a best researcher Ph.D. candidate of the University of Tehran in 2011. He has published more than 27 ISI journal papers, 3 Iranian journal papers and more than 18 conference papers. He has also 7 Iranian patents. Main research fields are metal forming, severe plastic deformation and producing ultra fine grain materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faraji, G., Mashhadi, M.M., Dizadji, A.F. et al. A numerical and experimental study on tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) process. J Mech Sci Technol 26, 3463–3468 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0874-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0874-9