Abstract
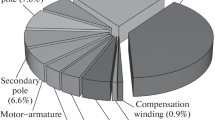
Some critical components of motors and generators have sliding electrical contacts. Electrical brushes are usually used in these contact points to conduct current between the stationary part and the moving part of the motor. In this paper, studies on brush wear against copper commutators are briefly reviewed. The main influential factors in brush wear are associated with both mechanical wear and electrical wear. Brush wear is affected by various factors, including temperature, material properties, sliding speed, contact force, and interfacial as well as environmental conditions. The mechanical wear of brushes is proportional to brush spring pressure and sliding speed, and the electrical wear of brushes is associated with current and contact voltage drop. For characterization, a brush wear test machine is designed, and influential factors, such as electrical contact resistance, temperature, wear mass loss, and so on, are measured. The wear tests are processed using a small brush-type automotive DC motor. The study primarily aims to investigate the effects of the wear behavior of copper-graphite brushes on small brush-typed DC motors. The variable conditions of electrical current are obtained by changing the brush spring pressure and the sliding speed. The results are electrical contact resistance, voltage drop, brush surface temperature rise, and so on. Brush wear is greatly changed by electrical current, which indicates that high current itself not only produces more Joule heating but also causes an increase in voltage drop that will result in additional Joule heating.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Zhongliang, C. Zhenhua, X. Jintong and D. Guoyun, Effect of PV factor on the wear of carbon brushes for micromotors, Wear, 265 (2008) 949–953.
I. Yasar, A. Canakci and F. Arslan, The effect of the brush spring pressure on the wear behaviour of copper-graphite brushes with electrical current, Tribology International, 40 (2007) 1381–1386.
Y. Feng, M. Zhang and Y. Xu, Effect of the electric current on the friction and wear properties of the CNT-Ag-G composites, Carbon 43 (2005) 2685–2692.
H. Zhao, G. C. Barber and J. Liu, Friction and wear in high speed sliding with and without electrical current, Wear 249 (2001) 409–414.
M. D. Bryant, J. P. Wang and J. W. Lin, Thermal mounding in high speed dry sliders: experiment, theory and comparision, Wear (181–183) (1994) 668–677.
Z. L. Hu, Z. H. Chen and J. T. Xia, Study on surface film in the wear of electrographite brushes against copper commutators for variable current and humidity, Wear (264) (2008) 11–17.
W. G. Shin and S. H. Lee, An analysis of the main factors on the wear of brushes for automotive small brush-type DC motor, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 24 (2010) 37–41.
W. G. Shin and S. H. Lee, Determination of accelerated condition for brush wear of small brush-type DC motor in using Design of Experiment (DOE) based on the Taguchi method, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 25(2) (2011) 317–322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Guest Editor Dong-Ho Bae
Wae-Gyeong Shin is a senior researcher in the Intelligent Vehicle Technology R&D Division of the Korea Automotive Technology Institute (KATECH) in Chonan, Korea. She received her master’s degree in Polymer Composite Material Engineering in Gyeongsang National University in 1996. She obtained her Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering in Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea in 2010. Her current research interests include materials property analysis, electronic automotive parts, electric vehicles, and reliability engineering.
Young-Sik Song is a principle researcher in the Green Car Powertrain R&D Division of the Korea Automotive Technology Institute (KATECH) in Chonan, Korea. He received his master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering in Sungkyunkwan University in 1990. He obtained his Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering in Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea in 1997. His current research interests include powertrain parts, automotive electronic parts, and reliability engineering.
Young-Kyo Seo is a senior researcher in the Material and Components R&D Division of the Korea Automotive Technology Institute (KATECH) in Chonan, Korea. He is currently a candidate for Ph.D. at the School of Mechanical Engineering in Chungnam University in Daejeon, Korea. He is engaged in remanufacturing and reliability engineering of automotive chassis and drive shaft parts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, WG., Song, YS. & Seo, YK. Correlation analysis of brush temperature in brush-type DC motor for predicting motor life. J Mech Sci Technol 26, 2151–2154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0534-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0534-0