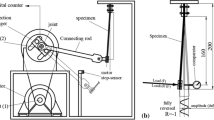
Abstract
The effect of thickness on the mechanical properties of Al 6K21-T4 sheet specimens under uniaxial tension was investigated. In order to reduce the thickness of the specimens without changing the microstructure and grain size, chemical etching was carried out, resulting in Al sheets ranging from 0.40 mm to 1.58 mm in thickness. Additionally, the effect of surface roughness was determined by finite element (FE) calculations performed using FE code MARC 2007. Tensile specimens of varying surface roughness were modeled and simulated. An analysis of the combined effects of the thickness and surface roughness revealed that the yield and tensile strengths decreased when the number of grains over the thickness was decreased. The ductility also decreased when reducing the thickness. An FE simulation showed that both the surface roughness and thickness affected the flow-curve shape. Moreover, the effect of the surface roughness tended to increase when decreasing the sheet thickness of specimens having the same roughness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Vollertsen, Z. Hu, H. Schulze Niehoff and C. Theiler, State of the art in micro forming and investigations into micro deep drawing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 151 (2004) 70–79.
P. J. M. Janssen, Th. H. de Keijser and M. G. D. Geers, An experimental assessment of grain size effects in the uniaxial straining of thin Al sheet with a few grains across the thickness, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 419 (2006) 238–249.
T. A. Kals and R. Eckstein, Miniaturization in sheet metal working, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 103 (2000) 95–101.
L. V. Raulea, A. M. Goijaerts, L. E. Govaert and F. P. T. Baaijens, Size effects in the processing of thin metal sheets, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 115 (2001) 44–48.
T. Fulop, W. A. M. Brekelmans and M. G. D. Geers, Size effects from grain statistics in ultra-thin metal sheets, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 174 (2006) 233–238.
M. Henning and H. Vehoff, Statistical size effects based on grain size and texture in thin sheets, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 452–453 (2007) 602–613.
L. Peng, F. Liu, J. Ni and X. Lai, Size effects in thin sheet metal forming and its elastic-plastic constitutive model, Mater. Design, 28 (2007) 1731–1736.
R. Kals, F. Vollertsen and M. Geiger, Scaling effects in sheet metal forming, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Sheet Metal, II, Enschede (1996) 65–75.
R. T. A. Kals, R. Eckstein and M. Geiger, Miniaturization in metal working, Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sheet Metal, Twente (1998) 15–24.
Y. F. Wang, Z. F. Yue and J. Wang, Numerical study of effect of surface roughness on superelastic behaviour of shape memory alloy, Materials Sci. Eng. A, 458 (2007) 312–318.
H. A. Al-Qureshi, A. N. Klein and M. C. Fredel, Grain size and surface roughness effect on the instability strains in sheet metal stretching, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 170 (2005) 204–210.
K. Yamagushi and P. B. Mellor, Thickness and grain size dependence of limit strains in sheet metal stretching, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 18 (1976) 85–90.
A. Parmar and P. B. Mellor, J. Chakrabarty, A new model for the prediction of instability and limit strains in thin sheet metals, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 19 (1977) 389–398.
S. I. Oh, C. C. Chen and S. Kobayashi, Ductile fracture in axisymmetric extrusion and drawing, J. Eng. Ind. Trans. ASME, 101 (1979) 36–44.
Y. W. Lee, Fracture prediction in metal sheets, Ph.D Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, (2005) 98–102.
S. Okazawa, T. Usami, H. Noguchi and F. Fujii, Theredimensional necking bifurcation in tensile steel specimens, J. Eng. Mechanics, 128(4) (2002) 479–485.
J. S. Jeon, S. Hyun and Y. S. Kim, Micromechanics on spherical contact with roughness, Key Eng. Mater., 339 (2007) 141–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by Associate Editor Seong Beom Lee
Young Suk Kim is currently a professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kyungpook National University in Daegu, Korea. He received his B.S. degree from Hanyang University in 1979 and M.S. degree from Seoul National University in 1981. He received his Ph.D degree from Kobe University, Japan, in 1986. Dr. Kim’s research interests include sustainable material processing, nano/micro mechanics, FEM and biomechanics.
Chang Hee Suh is currently a senior researcher at the Daegu Machinery Institute of Components & Materials. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Kyungpook National University, Korea, in 1998 and 2001. His research interests include computational mechanics, material processing, and fracture mechanics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suh, C.H., Jung, YC. & Kim, Y.S. Effects of thickness and surface roughness on mechanical properties of aluminum sheets. J Mech Sci Technol 24, 2091–2098 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0707-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0707-7