Abstract
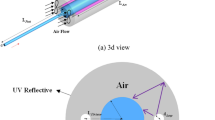
This paper investigates the three dimensional flow field and organism concentration in a UV disinfection channel. The modified P-1 model is newly adopted to solve the UV intensity field. This modified P-1 model for radiative transfer can yield an accurate light intensity for even complicated geometries. The effect of UV light intensity on the disinfection of microorganisms has been considered in the species equation. Differently from existing literatures, this study has used the Euler method for the calculation of both the flow field and the concentration of organisms. The CFD modeling results are compared with existing experimental data [1] for a UV channel, which shows outstanding agreement. The effects of inlet velocity, absorption coefficients of lamps quartz and water on the disinfection efficiency are investigated. With a smaller inlet velocity and smaller absorption coefficients, higher disinfection efficiency has been obtained. The current CFD model has the capability to predict the performance of UV disinfection channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Chiu, D. A. Lyn, P. Savoye and E. R. Blatchley, Integrated UV Disinfection Model Based on Particle Tracking, J. Environ. Eng-ASEC. 125(1) (1999) 7–16.
H. M. Murphy, S. J. Payne and G. A. Gagnon, Sequential UV-and chlorine-based disinfection to mitigate Escherichia coli in drinking water biofilms, Water. Res. 42 (2008) 2083–2092.
P. Paraskeva and N. J. D. Graham, Treatment of a secondary municipal effluent by ozone, UV and micro-filtration: microbial reduction and effect on effluent quality, Desalination 186 (2005) 47–56.
L. Rizzo, Inactivation and injury of total coliform bacteria after primary disinfection of drinking water by TiO2 photocatalysis, J. Hazard. Mater. 165 (2009) 48–51.
D. A. Sozzi and F. Taghipour, Computational and experimental study of annular photo-reactor hydrodynamics, Int. J. Heat. Fluid. Fl. 27 (2006) 1043–1053.
D. A. Lyn, K. Chiu and E. R. Blatchley, Numerical Modeling of Flow and Disinfection in UV Disinfection Channels, J. Environ. Eng. 125(1) (1999) 17–26.
W. B. Rauen, B. Lin, R. A. Falconer and E. C. Teixeira, CFD and experimental model studies for water disinfection tanks with low Reynolds number flows, Chem. Eng. J. 137 (2008) 550–560.
G. Spadoni, E. Bandini and F. Santarelli, Scattering Effects in Photosensitized Reactions, Chem. Eng. Sci. 33 (1978) 517–524.
T. Yokota, K. Yashima, T. Takigawa and K. Takahashi, A New Random-Walk Model for Assessment of Light Energy Absorption by a Photosynthetic Microorganism, J. Chem. Eng. JPN. 24 (1991) 558–562.
R. L. Romero, O. M. Alfano and A. E. Cassano, Cylindrical Photocatalytic Reactors. Radiation Absorption and Scattering Effects Produced by Suspended Fine Particles in an Annular Space, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 36(8) (1997) 3094–3109.
G. Sgalari, G. Camera-Roda and F. Santarelli, Discrete Ordinate Method in the Analysis of Radiative Transfer in Photocatalytically Reacting Media, Int. commun. Heat. Mass. 25(5) (1998) 651–660.
V. K. Pareek and A. A. Adesina, Light intensity distribution in a photocatalytic reactor using finite volume, AIChE. 50(6) (2004) 1273–1288.
E. R. Blatchley, Numerical modelling of UV intensity: Application to collimated-beam reactors and continuous-flow systems, Water. Res. 31(9) (1997) 2205–2218.
D. Liu, W. Chin, K. linden and J. Ducoste, Numerical simulation of UV disinfection reactors: Evaluation of alternative turbulence models, Appl. Math. Model. 31 (2007) 1753–1769.
J. J. Ducoste, D. Liu and K. Linden, Alternative Approaches to Modeling Fluence Distribution and Microbial Inactivation in Ultraviolet Reactors: Lagrangian versus Eulerian, J. Environ. Eng. 131(10) (2005) 1393–1403.
K. Abe, T. Kondoh and Y. Nagano, A new turbulence model for predicting fluid flow and heat transfer in separating and reattaching flows-II. Thermal field calculations, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 38(8) (1994) 1467–1481.
FLUENT 6.3 User’s Guide.
B. Yu, B. Q. Deng and C. N. Kim, Performance evaluation P-1 model in a photocatalytic reactor, Chem. Eng. Sci. 63 (2008) 5552–5558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by Associate Editor Haecheon Choi
Chang Nyung Kim is a full professor of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering, Kyung Hee University in the Republic of Korea. His research focuses on computational fluid dynamics, micro-fluidic flow, heat transfer, biomechanics, and environmental fluid mechanics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Deng, B. & Kim, C.N. A numerical prediction on the reduction of microorganisms with UV disinfection. J Mech Sci Technol 24, 1465–1473 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0502-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0502-5