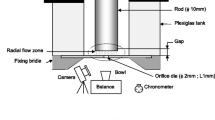
Abstract
Determination of melt rheological behavior within micro-structured geometry is very important for the accurate simulation modeling of micro-molding. Yet studies on the rheological behavior of polymer melts, flowing through micro channels, are complicated due to a large number of factors affecting the melt viscosity. One factor, viscous dissipation, is investigated in the current work through a novel experimental technique to determine the viscous dissipation of a polymer melt flowing through several micro channels with identical aspect ratio. Relative tests are conducted with the melt of high density polyethylene (HDPE) at different temperatures being extruded through the capillary dies with diameters 1000μm, 500μm and 350μm, respectively. It was found that the temperature rise due to viscous dissipation decreases significantly with the reduction of the characteristic size of micro channel at the same shear rate. In addition, based on the suggested model of radial temperature distribution, the influence of viscous heating on the melt viscosity is investigated. The results indicate that viscous dissipation does not play a significant role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. G. Yao and B. Kim, Injection Molding High Aspect Ratio Microfeatures, J Injection Molding Technol, 6(1) (2002) 11–17.
C. Harris, M. Despa and K. Kelly, Design and Fabrication of a Cross Flow Micro Heat Exchanger, J Microelectromech. Syst, 9(4) (2000) 502–508.
D. J. Laser and J. G. Santiago, A review of micro pumps TOPICAL REVIEW, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 14 (2004) 35–64.
W.-C. Chung, C.-K. Chao and C.-T. Ho, Fabrication of highresolution periodical structures on polymer waveguides using a replication process, J OPTICS EXPRESS, 15(14) (2007) 8649–8659.
R. W. Friedl, Injection Molding of Sub-μm Grating Optical Elements, J Injection Molding Technol, 4(2) (2000) 78–83.
Y. K. Shen and W. Y. J. Wu, An analysis of the threedimensional micro-injection molding, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 29(2) (2002) 423–431.
D. S. Kim, K. C. Lee and T. H. Kwon, Micro-channel filling flow considering surface tension effect, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 12 (2002) 236–246.
V. Piotter, K. Mueller and K. Plewa, Performance and simulation of thermoplastic micro injection molding, Microsystem Technologies, 8(6) (2002) 387–390.
D. G. Yao and B. Kim, Simulation of the filling process in micro channels for polymeric materials, Micromech. Microeng, 12 (2002) 604–610.
L. Y. Yu, C. G. Koh and L. J. Lee, Experimental investigation and numerical simulation of injection molding with micro-features, Polymer Engineering and Science, 42(5) (2002) 871–888.
R. D. CHIEN, W. R. JONG and S. C. CHEN, Study on Rheological Behavior of Polymer Melt Flowing through Micro-channels Considering the Wall-slip Effect, Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 15 (2005) 1389–1396.
S. C. CHEN, R. I. TSAI and R. D. CHIEN, Preliminary study of polymer melt rheological behavior flowing through micro-channels, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 32 (2005) 501–510.
C. S. CHEN, S. C. CHEN and L. W. LIAW, Rheological behavior of POM polymer melt flowing through microchannels, European Polymer Journal, 44(6) (2008) 1891–1898.
Yu Tongmin, Wei Yuxin, Xu Bin and Zhuang Jian, Research on Viscous Dissipation of Melt in Filling Flow of Micro Injection Molding, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Frontiers of Design and Manufacturing, Tianjin, China (2008) 156–163.
G. Hay and M. E. MacKay, Pressure and Temperature effects in slit rheometry, J. Rheol, 43(5) (1999) 1099–1116.
S. E. Kadijk and B. H. A. A. Van Den Brule, On the pressure dependency of the viscosity of molten polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci., 34(20) (1994) 1535–1546.
Bu Wen-Feng, Liu Zhi-Gang and ZHAO Yao-Hua, Experimental study and numerical simulation of viscous dissipation effect for flow in microtube, Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 40(1) (2008) 160–163.
Guan Nin, Liu Zhi-gang and Liang Shi-Qiang, Study of viscous dissipation effect for liquid flow in microtube, Progress in Natural Science, 18(11) (2008) 1297–1303.
Xu Peixian, Polymer rheology and application, First Ed. Beijing Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2003.
Bin xu, Minjie Wang, Tongmin Yu, Danyang Zhao: Experimental research on the viscosity of polymer melts filling through micro channels, Symposium on advanced molding technology and materials processing, Beijing, China, (2008) 17–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by Associate Editor Jun Sang Park
Bin Xu received his Masters’ degree in Mechanical Engineering from Liaoning University of Technology, People’s Republic of China, in 2006. He is currently a Ph.D candidate of the School of Mechanical Engineering at Dalian University of Technology, People’s Republic of China. His principal interests are in the areas of micro injection molding, including micro fluid, micro mold design, mainly through experimental and numerical means.
Minjie Wang received the Ph.D degree in Mechanical Engineering from Dalian University of Technology, People’s Republic of China, in 1989. He is currently a professor of School of Mechanical Engineering at Dalian University of Technology. His research interests are in mold technology, polymer molding and high speed machining.
Tongmin Yu is currently a professor of the School of Mechanical Engineering at Dalian University of Technology. His research interests are in mold design and fabrication technology, mold CAD/CAE, precision polymer injection molding and polymer micro injection molding
Danyang Zhao received his Masters’ and Ph.D degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Dalian University of Technology in 2003 and 2007, respectively. He is currently an associate professor at Dalian University of Technology in China. His research interests include the non-Newtonian fluid dynamics of polymer injection/extrusion processes from micro to macro scale, especially the rheological characterization and wall slip of melt flowing process, and mold/die design.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Wang, M., Yu, T. et al. Viscous dissipation influencing viscosity of polymer melt in micro channels. J Mech Sci Technol 24, 1417–1423 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0420-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-010-0420-6