Abstract
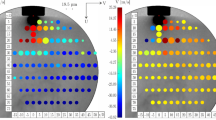
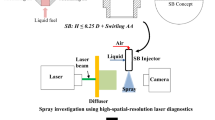
Spray characteristics of an injector employed in the 5 Newton-class of liquid-propellant thruster are addressed with an evolutionary feature of droplets. Information for the droplets is obtained through Dual-mode phase Doppler anemometry (DPDA) measurement in terms of the velocity, diameter, number density, and turbulent intensity. In addition, instantaneous images for the macroscopic view of spray are supplemented by flow visualization technique using laser sheet. It is demonstrated by the investigation of spray images that the injector under consideration meets an angular injection requirement at all of the injection pressures specified. Spray shedding is also featured with a schematization of the frozen images. Dynamic behavior of spray droplets and their atomization evolution along the geometric axis of injector-nozzle orifice with varying injection pressures are scrutinized by depicting the cumulative droplet populations mapped onto a velocity-diameter domain. The evolutionary behavior is further authenticated on the basis of the distribution for number density and turbulent intensity of droplets. It is inferred that the higher injection pressure generates the smaller droplets undergoing the greater deceleration along the spray stream due to the augmented Reynolds number and Weber number. Even though spray characterization of the current type of injectors is to be inevitable to their performance estimation at the design stage, it has never been reported to date. It is expected that the present results will be able to contribute to the appreciation of injector performance and to the design engineering of brand-new thrusters as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Kim, J. Park, S. Kim, J. Choi and K. W. Jang, Test and performance evaluation of small liquid-monopropellant rocket engines, 42 nd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, (2006) AIAA-2006-4388.
K. Miller, J. Sisco, N. Nugent and W. Anderson, Combustion instability with a single-element swirl injector, Journal of Propulsion and Power, 23(5) (2007) 1102–1112.
R. J. Kenny, M. D. Moser, J. Hulka and G. Jones, Cold flow testing for liquid propellant rocket injector scaling and throttling, 42 nd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, (2006) AIAA-2006-4705.
X. Li and J. Shen, Experimental study of sprays from annular liquid jet breakup, Journal of Propulsion and Power, 15(1) (1999) 103–110.
J. Y. Koo, The effects of injector nozzle geometry and operating pressure conditions on the transient fuel spray behavior, KSME International Journal, 17(3) (2003) 617–625.
R. Payri, S. Molina, F. J. Salvador and J. Gimeno, A study of the relation between nozzle geometry, internal flow and sprays characteristics in Diesel fuel injection systems, KSME International Journal, 18(7) (2004) 1222–1235.
R. D. Reitz and F. V. Bracco, Mechanism of atomization of a liquid jet, Physics of Fluids, 25(10) (1982) 1730–1742.
C. F. Edwards and K. D. Marx, Analysis of the ideal phase-Doppler system: limitations imposed by the single-particle constraint, Atomization & Sprays, 2(3) (1992) 319–366.
M. Saffman, The use of polarized light for optical particle sizing, Proc. of 3 rd International Symposium on Applications of Laser Anemometry to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, (1986) 387–398.
G. Gréhan, G. Gouesbet, A. Naqwi and F. Durst, Evaluation of a phase Doppler system using generalized Lorenz-Mie theory, Proc. of International Conference on Multiphase Flows, Tsukuba, Japan, (1991) 291–294.
S. V. Sankar, A. Inenaga and W. D. Bachalo, Trajectory dependent scattering in phase Doppler interferometry: minimizing and eliminating sizing errors, Proc. of 6 th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, (1992) Paper 12.2.
J. Domnick, V. Dorfner, F. Durst and M. Yamashita, Performance evaluation of different phase-Doppler systems, Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 11(1) (1994) 91–100.
C. Tropea, T. H. Xu, F. Onofri, G. Gréhan and P. Haugen, Dual-mode phase Doppler anemometry, Proc. of 7 th International Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, (1994) Paper 18.3.
J. S. Kim, J. S. Kim, H. Jung, J. Park, S. Kim and K. W. Jang, A study on the spray characteristics of a liquid-propellant thruster injector by PIV/PDA optical measurements, 5 th Joint ASME/JSME Fluids Engineering Conference, (2007) FEDSM2007-37105.
E. W. Schmidt, Hydrazine and Its Derivatives: Preparation, Properties, Applications, 2nd Ed. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, USA, (2001).
C. Tropea, T. H. Xu, F. Onofri, G. Gréhan, P. Haugen and M. Stieglmeier, Dual-mode phase-Doppler anemometer, Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 13(2) (1996) 165–170.
A. H. Lefebvre, Atomization and Sprays, Hemisphere Publishing Corp., New York, (1989).
L. C. Ganippa, G. Bark, S. Andersson and J. Chomiak, Cavitation: a contributory factor in the transition from symmetric to asymmetric jets in cross-flow nozzles, Experiments in Fluids, 36(4) (2004) 627–634.
H. Hiroyasu, Spray break-up mechanism from the hole-type nozzle and its applications, Atomization and Sprays, 10(3–5) (2000) 511–527.
T. Tamaki, M. Shimizu, K. Nishida and H. Hiroyasu, Effects of cavitation and internal flow on atomization of a liquid jet, Atomization and Sprays, 8(2) (1998) 179–197.
M. Kato, H. Kano, K. Date, T. Oya and K. Niizuma, Flow analysis in nozzle hole in consideration of cavitation, (1997) SAE Paper 970052.
J. Lee, S. Kang and B. Rho, Intermittent atomization characteristics of multi-hole and single-hole Diesel nozzle, KSME International Journal, 16(12) (2002) 1693–1701.
Z. Faragó and N. Chigier, Morphological classification of disintegration of round liquid jets in a coaxial air stream, Atomization and Sprays, 2(2) (1992) 137–153.
J. H. Im, M. K. Kim and Y. Yoon, Self-pulsation characteristics of a swirl injector, 10 th International Congress on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Kyoto, Japan, (2006) ICLASS06-092.
B. J. Azzopardi, Measurement of drop sizes, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 22(9) (1979) 1245–1279.
H. Jung, J. S. Kim, S. Kim and J. Park, Effects of fuel-injection pressure on the spray breakup characteristics in small LRE injector, Journal of the Korean Society of Propulsion Engineers, 11(3) (2007) 50–57.
C. Baumgarten, J. Stegemann and G. P. Merker, A new model for cavitation induced primary break-up of Diesel sprays, Proc. of 18 th ILASS Europe Conference, Zaragoza, Spain, (2002) 15–20.
G. Stiesch, Modeling Engine Spray and Combustion Processes, Springer-Verlag NY Inc., New York, (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by Associate Editor Jun Sang Park
Jin Seok Kim obtained his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Mechanical Engineering in 2005 and 2007, respectively, from Sunchon National University, Korea. He is currently a Ph.D. candidate.
Jeong Soo Kim took his master’s and Ph.D. degrees in Aerospace Engineering in 1987 and 1992, respectively from KAIST, Korea. Since then, he worked for Agency for Defense Development and Korea Aerospace Research Institute as a principal researcher up to 2004. Also he researched at TRW (USA) as an assistant program manager from 1996 to 1998. He is currently a faculty member in the School of Mechanical Engineering of Pukyong National University, Korea. His research fields extend into the development of space propulsion engines with their components design, T&E of liquid rocket engines, and the numerical simulation of combustion phenomena.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Kim, J.S. A characterization of the spray evolution by dual-mode phase doppler anemometry in an injector of liquid-propellant thruster. J Mech Sci Technol 23, 1637–1649 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0209-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0209-7