Abstract
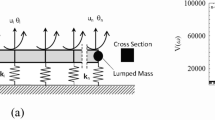
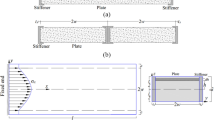
If lateral stiffness distribution of continuum structure is unreasonable, its displacement distribution will be non-uniform under lateral load. The non-uniform displacement distribution will weaken the safety of the structure. The continuum structure is equivalent to the cantilever. The optimal lateral stiffness distribution of the structure is obtained by adjusting the section size distribution. The wind load and earthquake action are simplified into three equivalent static loads: uniform load, inverted triangle load and inertia force related load. The shearing displacement and bending displacement distributions along the structural height are derived. The optimization objective is that the second derivative of the total displacement distribution is zero, that is, the displacement distribution is uniform. The section size of the cantilever is optimized and the optimal scheme is obtained. The optimization results are verified by numerical analysis and finite element analysis. The results show that the uniform displacement criterion can be realized by the cantilever with section size distribution of power function. The optimal parameters of the section under different loads are different. A practical design example is presented to prove the applicability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A(y):
-
Area of section at height y
- c :
-
Generalized parameter to be optimized
- D B(y):
-
Displacement caused by bending moment at height y
- D S(y):
-
Displacement caused by shear force at height y
- E :
-
Elastic modulus of the structure
- e :
-
Base of the natural exponential function
- f(c, y):
-
Total displacement of structure at height y
- G :
-
Shear modulus of the structure
- H :
-
Total height of the structure
- h :
-
Radius of structural bottom section
- \({\bar h}\) :
-
Radius of structural top section
- I(y):
-
Moment of inertia at any height y
- M(y):
-
Bending moment of the structural section
- \(\bar m(y)\) :
-
Mass distribution at height y
- n :
-
Shape control parameter in power function
- q :
-
Intensity of uniform load
- q max :
-
Maximum intensity of inverted triangle load
- Q(y):
-
Shear force of the structural section
- \(\bar q(y)\) :
-
Intensity of inertia force related load
- r :
-
Radius of structural section
- R C(y):
-
Optimal radius distribution under combined load
- R E(y):
-
Optimal radius distribution under inertia force related load
- R I(y):
-
Optimal radius distribution under inverted triangle load
- R U(y):
-
Optimal radius distribution under uniform load
- y :
-
Height of the structure which corresponds to the y axis of the coordinate system
- α :
-
Shape control parameter in natural exponential function
- β :
-
Bottom radius control parameter in power function
- λ :
-
Mass-dependent constant to control the load amplitude
- μ :
-
Coefficient to consider the non-uniform distribution of shear strain in the cross-section
- ρ :
-
Effective cross-section density
- φ U :
-
Weight coefficient of RU(y)
- φ I :
-
Weight coefficient of RI(y)
- φ E :
-
Weight coefficient of RE(y)
References
Chen C, Zou X (2004) Elastic and inelastic drift performance optimization for reinforced concrete building under earthquake loads. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 33(15):929–950, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.385
Chun J, Paulino G, Song J (2019) Reliability-based topology optimization by ground structure method employing a discrete filtering technique. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 60(3):1035–1058, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02255-1
Conlan-Smith C, James K (2019) A stress-based topology optimization method for heterogeneous structures. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 60(1):167–183, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02207-9
Dilgen C, Dilgen S, Aage N, Jensen JS (2019) Topology optimization of acoustic mechanical interaction problems: A comparative review. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 60(2):779–801, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02236-4
Elghazouli A, Kumar M, Stafford P (2014) Prediction and optimization of seismic drift demands incorporating ground motion frequency content. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering 12(1):255–276, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-013-9568-7
Gholizadeh S (2015) Performance-based optimum seismic design of steel structures by a modified firefly algorithm and a new neural network. Advances in Engineering Software 81(51):50–65, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2014.11.003
Kirsch U (1993) Structural optimization: Fundamentals and application. Springer, Berlin, Germany, 237–280
Kobori T, Minai R, Inoue Y, Hisatoku T (1969) On the optimum aseismic design data of tall building structures based on the elasto-plastic earthquake responses. Journal of Earthquake Engineering 10(18):1623–1631
Li Y, Han M, Guo Q (2020) Modified whale optimization algorithm based on tent chaotic mapping and its application in structural optimization. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(12):3703–3713, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-0504-5
Li Y, Lian S (2018) Improved fruit fly optimization algorithm incorporating tabu search for optimizing the selection of elements in trusses. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 22(12):4940–4954, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-2000-0
Liu Z, Guo T, Correia J, Wang L (2020) Reliability-based maintenance strategy for gusset plate connections in steel bridges based on life-cost optimization. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities 34(5):04020088, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001493
Mergos P (2017) Optimum seismic design of reinforced concrete frames according to Eurocode 8 and fib Model Code 2010. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 46(15):1181–1201, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.2851
Mergos P (2018) Efficient optimum seismic design of reinforced concrete frames with nonlinear structural analysis procedures. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 58(6)2565–2581, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2036-x
Miguel LFF, Miguel LFF, Lopez R (2018) Methodology for the simultaneous optimization of location and parameters of friction dampers in the frequency domain. Engineering Optimization 50(12):2108–2122, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2018.1428318
Munk D, Auld D, Steven G, Vio GA (2019) On the benefits of applying topology optimization to structural design of aircraft components. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 60(3):1245–1266, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02250-6
Palizzolo L, Tabbuso P (2019) Reliability-based design optimization of trusses under dynamic shakedown constraints. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 60(3):1097–1108, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02259-x
Park K, Medina R (2007) Conceptual seismic design of regular frames based on the concept of uniform damage. Journal of Structural Engineering 133(7):945–955, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2007)133:7(945)
Talatahari S (2013) Optimum performance-based seismic design of frames using metaheuristic optimization algorithms. Metaheuristic Applications in Structures and Infrastructures 45(2):419–437, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398364-0.00017-6
Xu J, Spencer BF, Lu X (2017) Performance-based optimization of nonlinear structures subject to stochastic dynamic loading. Engineering Structures 134:334–345, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.12.051
Zou X, Chen C, Li G (2007a) Multiobjective optimization for performance-based design of reinforced concrete frames. Journal of Structural Engineering 133(10):1462–1474, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2007)133:10(1462)
Zou X, Teng J, Lorenzis D, Xia S (2007b) Optimal performance-based design of FRP jackets for seismic retrofit of reinforced concrete frames. Composites Part B 38(6):584–597, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2006.07.016
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Project Number 51878017, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Wu, S. & Liao, L. Section Size Optimization of Continuum Structure with Bending and Shearing Deformation for Uniform Displacement Criterion. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 2234–2245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0573-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0573-8