Abstract
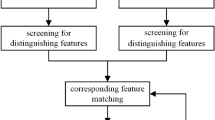
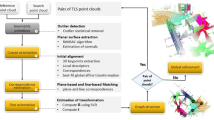
Mobile laser scanning can quickly and dynamically obtain a wide range of urban scene point clouds. However, due to factors such as occlusion and field of view limitation, it needs to be supplemented by terrestrial laser scanning. The acquisition methods and data quality of mobile point clouds and terrestrial point clouds are quite different, the target of urban scene point clouds is complex and diverse, and the corresponding feature is difficult to extract, so the point cloud fusion is difficult. To this end, a point cloud registration method of mobile and terrestrial scanning based on the target features of artificial ground objects is proposed. Firstly, the data features of mobile laser scanning point clouds and terrestrial laser scanning point clouds are analyzed, and the point clouds are diluted with equal density. Then, the artificial ground objects are extracted as the registration primitives to reduce the scene complexity, and the features of urban scenes and the features of point cloud eigenvalues and principal curvature attributes are analyzed. Combined with the octree voxel index, the multi-scale key point extraction method is constructed to extract the multi-scale key points of registration primitives. Finally, the key point constraint is used to improve the deficiencies of 4PCS (4-Points Congruent Sets) algorithm and ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm to complete the registration of mobile and terrestrial point clouds in different road scenes. Experiments show that the point cloud registration accuracy can reach 2.6 cm, which provides a feasible method for high precision fusion of multi-platform laser point clouds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao L, Cheng Z, Dang G (2010) Study on normal estimation for 3D point clouds. Computer Engineering and Applications 46(23):1–7
Besl PJ, Mckay ND (1992) A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 14(2):239–256, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/34.121791
Dold C, Brenner C (2006) Registration of terrestrial laser scanning data using planar patches and image data. International Archives of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 36:25–27, DOI: https://doi.org/10.15488/3750
Gressin A, Cannelle B, Mallet C, Papelard JP (2012) Trajectory based registration of 3D LiDAR point clouds acquired with a mobile mapping system. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Melbourne, Australia 117–122, DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-I-3-117-2012
Guo YL, Sohel FA, Bennamoun M, Wan JW, Lu M (2013) RoPS: A local feature descriptor for 3D rigid objects based on rotational projection statistics. International Conference on Communications. IEEE 1–16, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSPA.2013.6487310
Higinio GJ, Joaquin MS, Lucia D (2016) Automatic registration of mobile LiDAR Data using high-reflectivity traffic signs. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 142(8), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001143
Hui C, Bhanu B (2007) 3D free-form object recognition in range images using local surface patches. Pattern Recognition Letters 28(10):1252–1262, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2007.02.009
Liang YB, Zhan QM, Che EZ, Chen MW, Zhang DL (2013) Automatic registration of terrestrial laser scanning data using precisely located artificial planar targets. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters 11(1):69–73, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2013.2246134
Liu RF, Wang P, Yan ZJ, Lu XS (2020) Hierarchical classification of pole-like objects in mobile laser scanning point clouds. The Photogrammetric Record 35(169):81–107, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/phor.12307
Lu XS, Liu RF, Tian MY, Liu B (2014) Application of improved mathematical morphology for vehicle-mounted laser point cloud ground filtering. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 39(5):514–519, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20130020
Ren HW, Liu RF, Wang F, Yang JB (2022) Automatic extraction method of urban road curb boundary from vehicle-borne laser point clouds. KSCE J Civ Eng, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-1540-0
Stamos I, Leordeanu M (2003) Automated feature-based range registration of urban scenes of large scale. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Madison, WI, USA 2003:555–561, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2003.1211516
Takai S, Date H, Kanai S, Niina Y, Ikeda T (2013) Accurate registration of MMS point clouds of urban areas using trajectory. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2(5):277–282, DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-II-5-W2-277-2013
Theiler PW, Wegner JD, Schindler K (2013) Markerless point cloud registration with keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 1(2):283–288
Wang F, Liu RF, Ren, HW, Chai YN (2020) Multi-stage vehicle-mounted laser point cloud registration using road target features. Journal of Surveying and Mapping Science and Technology 37(05):496–502
Weber T, Hansch R, Hellwich O (2015) Automatic registration of unordered point clouds acquired by Kinect sensors using an overlap heuristic. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 102:96–109, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.12.014
Xu GX, Pang YJ, Bai ZX, Wang YL, Lu ZW (2021) A fast point clouds registration algorithm for laser scanners. Applied Sciences 11(8):3426, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083426
Xu YS, Boerner R, Yao W, Hoegner L, Stilla U (2017) Automated coarse registration of point clouds in 3D urban scenes using voxel based plane constraint. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 4:185–191, DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-IV-2-W4-185-2017
Xuan W, Hua X, Zou J, Xiao X, Zhao B (2019) Point cloud normal vector estimation method for adaptive optimal neighborhood size selection. Science of Surveying and Mapping 44(10):101–108+116
Yan L, Tan JX, Liu H, Xie H, Chen CJ (2018) Automatic non-rigid registration of multi-strip point clouds from mobile laser scanning systems. International Journal of Remote Sensing 39(5–6):1713–1728, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1410248
Yang BS, Dong Z, Liang FX, Liu Y (2016) Automatic registration of large-scale urban scene point clouds based on semantic feature points. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 113(3):43–58, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.12.005
Yang BS, Liang FX, Huang, RG (2017) Progress, challenges and perspectives of 3D LiDAR point cloud processing. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica 46(10):1509–1516
Zhan X, Cai Y, Li H, Li Y, He P (2020) A point cloud registration algorithm based on normal vector and particle swarm optimization. Measurement and Control 53(3):265–275, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0020294019858217
Zhang WM, Qi JB, Wan P, Wang HT, Yan GJ (2016) An easy-to-use airborne LiDAR data filtering method based on cloth simulation. Remote Sensing 8(6):501, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060501
Zhang X, Li H, Cheng Z (2008) Curvature estimation of 3D point cloud surfaces through the fitting of normal section curvatures. Proceedings of AsiaGraph, Tokyo, Japan, 72–79
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National key research and development program (2018YFB1600302); National Natural Science Foundation of China (42001414); and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China(ZR2019BD033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cong, B., Li, Q., Liu, R. et al. Research on a Point Cloud Registration Method of Mobile Laser Scanning and Terrestrial Laser Scanning. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 5275–5290 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0366-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-022-0366-0