Abstract
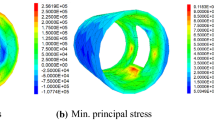
Voids between primary support and secondary lining of existing tunnels pose a serious threat to safety and have become a key challenge for tunnel engineering. Due to the poor bonding performance between concrete slurry backfill and lining concrete, the integrity of supporting structures cannot be guaranteed. In recent years, vault grouting with formwork has proved to be effective in solving this problem. However, few studies have focused on the selection of grouting materials and associated grouting process parameters. In this paper, a slight-expanding concrete slurry is selected as the grouting material. The early strength growth trend of the slight-expanding slurry is explored via laboratory tests. The compatibility of the slight-expanding slurry and the lining concrete is analyzed by comparing the slump, expanding diameter, water retention and compressive strength. Bonding-body specimens were fabricated using a mold developed for this work. Furthermore, we compare the compressive strength and failure mode in order to investigate the bonding properties between the sight-expanding slurry and lining concrete at different grouting intervals and pressures. A reasonable set of operational parameters is subsequently proposed. Finally, field tests undertaken in an expressway tunnel in south China are performed in order to determine the impact of grouting with formwork on tunnel lining, while the grouting effect at the vault is evaluated using a ground penetrating radar. The slight-expanding slurry exhibited a high early strength and rapid hardening. Adding slight-expanding slurry to lining concrete at a volume ratio of 1:0.2 increased the slump, diameter and compressive strength by 13.4%, 15.6%, and 25.0%, respectively. When a grouting interval is less than 6 h, the pressure of grouting with formwork should be no less than 0.2 MPa, while for a grouting interval of 8 h, the grouting pressure should be no less than 0.4 MPa. The grouting pressure of 0.4 MPa exerts a limited effect on the existing secondary lining concrete, and the stress increment produced by grouting accounts for 6–17% of the total increment. The results presented can provide a reference for future tunnel construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ZL, Ma WB, Guo XX, Zou WH, Wang Y (2017) Complete set of technologies for immediately grouting into crown void with formwork after secondary lining concrete pour for new railway tunnels. Railway Engineering 57(11):48–52 (in Chinese)
GB/T 50080-2016 (2016) Standard for test method of performance on ordinary fresh concrete. GB/T 50080-2016, China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing, China, 5–10
GB/T 50081-2019 (2019) Standard for test methods of concrete physical and mechanical properties. GB/T 50081-2019, China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing, China, 5–15
GB/T 50448-2008 (2008) Code for application technique of cementitious grout. GB/T 50448-2008, China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing, China, 4–5
Guan BS (2004) Key points of tunnel maintenance management. People’s Communications Press, Beijing, China, 22–24
Guo ML, Huang SP (2016) The research of detection and treatment of tunnel lining cavity. MATEC Web of Conferences 44:02079, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20164402079
Hsiao FY, Wang CL, Chern JC (2009) Numerical simulation of rock deformation for support design in tunnel intersection area. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 24(1):14–21, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2008.01.003
Huang F, Zhu HH, Xu QW, Cai YC, Zhuang XY (2013) The effect of weak interlayer on the failure pattern of rock mass around tunnel — Scaled model tests and numerical analysis. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 35:207–218, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.06.014
JTG/T D70-2010 (2010) Guidelines for design of highway tunnel. JTG/T D70-2010, People’s Communications Press, Beijing, China, 35–45
Kazemian S, Prasad A, Huat BB, Mohammed TA, Aziz FNA (2010) Effect of cement, sodium silicate, kaolinite and water on the viscosity of the grout. Scientific Research and Essays 5(22):3434–3442
Lai JX, Qiu JL, Fan HB, Chen JX, Hu ZN, Zhang Q, Wang JB (2017) Structural safety assessment of existing multiarch tunnel: A case study. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2017: 1697041, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1697041
Lee DH, Lee HK, Kim YG (2002) A study on mechanical behavior and cracking characteristics of tunnel lining by model experiment. Geosystem Engineering 5(4):104–112, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/12269328.2002.10541195
Leung C, Meguid MA (2011) An experimental study of the effect of local contact loss on the earth pressure distribution on existing tunnel linings. Tunnelling Underground Space Technology 26(1):139–145, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2010.08.003
Lin CJ, Wang XT, Li Y, Zhang FK, Xu ZH, Du YC (2020) Forward modelling and GPR imaging in leakage detection and grouting evaluation in tunnel lining. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(1):278–294, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1530-z
Lv B (2017) Experiment study on compatibility and binding force performance of new filling materials intunnel vault with grouting. Railway Construction Technology 2:18–21 (in Chinese)
McIntyre S, Kaltzakorta I, Liggat JJ, Pethrick RA, Rhoney I (2005) Influence of the epoxy structure on the physical properties of epoxy resin nanocomposites. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research 44(23):8573–8579, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ie048835w
Meguid MA, Dang HK (2009) The effect of erosion voids on existing tunnel linings. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 24(3):278–286, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2008.09.002
Sembenelli PG, Sembenelli G (1999) Deep jet-grouted cut-offs in riverine alluvia for ertan cofferdams. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 125(2):142–153, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1999)125:2(142)
Talesnick M, Baker R (1999) Investigation of the failure of a concrete-lined steel pipe. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 17(2): 99–121, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008913408452
Wang JF, Huang HW, Xie XY, Bobet A (2014) Void-induced liner deformation and stress redistribution. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 40:263–276, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2013.10.008
Yang B, Ren SQ (2017) New technology of preventing tunnel secondary lining void. Highway Tunnel 3:53–58 (in Chinese)
Yashiro K, Kojima Y, Shimizu M (2007) Historical earthquake damage to tunnels in Japan and case studies of railway tunnels in the 2004 Niigataken-Chuetsu earthquake. Quarterly Report of RTRI 48(3):136–141, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2219/rtriqr.48.136
Ye F, Qin N, Liang X, Ouyang A, Qin Z, Su EJ (2021) Analyses of the defects in highway tunnels in China. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 107:103658, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103658
Ye Q, Zhang ZN, Kong DY, Chen RS (2007) Influence of nano-SiO addition on properties of hardened cement paste as compared with silica fume. Construction and Building Materials 21(3):539–545, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.09.001
Zhang SL (2012) Research on health diagnosis and technical condition evaluation of tunnel lining structure. PhD Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Zhang H (2017) Application of casting layer by layer and window by window and grouting through mold to tunnel lining. Tunnel Construction 37(12):1607–1612 (in Chinese)
Zhang YX, Shi YF, Zhao YD, Yang JS (2017) Damage in concrete lining of an operational tunnel. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities 31(4):06017002, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001032
Zhao DP, Tan XR, Jia LL (2014) Study on investigation and analysis of existing railway tunnel diseases. Applied Mechanics and Materials 580:1218–1222, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.580-583.1218
Zhou Y, Wang GH, Yuan YF (2020) Basic properties and engineering application of bentonite-cement-water glass grouting. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(9):2742–2750, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1928-7
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51378053). The gauges used in the field tests were provided by Dandong Qiangong Instrument Co., LTD. The simulation device for the grouting with formwork proposed herein is subject to a patent application (#ZL 2018 2 1690398.6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Tan, Z., Zhao, J. et al. Experimental Study on Instant Grouting with Formwork for Tunnels. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 394–405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1998-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1998-1