Abstract
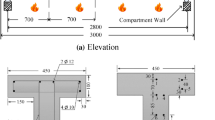
To explore the influence of the loading conditions and fire exposure time on the residual mechanical properties of concrete T-beams, 10 concrete T-shaped beams were designed and manufactured. Three levels of loading were applied to the concrete T-beams during fire tests, namely, unloaded, loaded without concrete cracking and normal service conditions. The fire test durations were 60 min, 90 min, and 120 min. After the fire tests, static loading tests were carried out on the fire-damaged T-beams to determine the residual flexural capacity. The test results showed that with an increase in load ratio and fire time, the maximum temperature experienced by the concrete and steel bar increased. For example, for the specimens that underwent 120 minutes of fire exposure, the temperature of the specimen with a load ratio of 0.44 was larger than that with load ratios of 0.12 and 0, and the difference was 60°C and 80°C, respectively. During the fire tests, the mid-span deflection also increased significantly with an increase in load ratio and fire duration. In addition, the flexural load-bearing capacity after fire exposure decreased with an increase in load ratio and fire time. Compared with the bearing capacity, the degradation of the flexural rigidity was more obvious. For example, when the fire exposure time was 120 minutes, the bending capacity of the beam with a load ratio of 0.44 was approximately 4.5% lower and 5.1% lower than that with a load ratio of 0.12 and 0, respectively, and the reduction in flexural rigidity became 6.8% and 15%, respectively. Considering the effect of cracking, ANSYS was used to analyze the temperature field, deflection, and bearing capacity of the T-beams. It was determined that the calculation model that considers the effects of cracks was more accurate than the calculation model that disregards the appearance of cracks. This study can provide a basis for the assessment of fire damage and the repair of concrete structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akca AH, Zihnioglu NO (2013) High performance concrete under elevated temperatures. Construction and Building Materials 44:317–328, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.005
Akca AH, Özyurt N (2018) Effects of re-curing on microstructure of concrete after high temperature exposure. Construction and Building Materials 168(4):431–441, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.122
Akca AH, Özyurt N (2020) Post-fire mechanical behavior and recovery of structural reinforced concrete beams. Construction and Building Materials 253, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119188
Ba GZ, Miao JJ, Zhang WP (2016) Influence of cracking on heat propagation in reinforced concrete structures. Journal of Structural Engineering 142(7), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001483
China Academy of Building Research (2012) Standard methods for testing of concrete structures. China Architecture of Building Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Ebrahimi SH (2021) Residual stress effects on crack-tip stress singularity in XFEM fracture analysis. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids 86:104191, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2020.104191
ENV 1993-1-2 (1993) Eurocode 3, Design of steel structures, Part 1.2: Structural fire design. ENV 1993-1-2, European Committee for Standardization
Faron A, Rombach GA (2020) Simulation of crack growth in reinforced concrete beams using extended finite element method. Engineering Failure Analysis 116, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104698
Fu CG, Lou Y (2007) Experimental research and engineering application of prestressed steel reinforced concrete structure. Science Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Gabriela L, Albuquerque AB, Silva JPC (2018) Behavior of thermally restrained RC beams in case of fire. Engineering Structures 174: 407–417, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.07.075
Gao WY, Dai JG, Teng JG, Chen GM (2013) Finite element modeling of reinforced concrete beams exposed to fire. Engineering Structures 52(9):488–501, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.03.017
Gong W, Ueda T (2017) Properties of self-compacting concrete containing copper slag aggregate after heating up to 400°C. Structural Concrete 19(6):1873–1880, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/suco.201700234
Guo ZH, Shi XG (2011) Experiment and calculation of reinforced concrete at elevated temperatures. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China
ISO 834 (1999) Fire resistance test: Elements of building construction. ISO 834, Geneva, Switzerland
Kodur VKR, Agrawal A (2016) Critical factors governing the residual response of reinforced concrete beams exposed to fire. Fire Technology 52(4):967–993, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-015-0527-5
Kodur VKR, Dwaikat RB, Fike RS (2010) An approach for evaluating the residual strength of fire-exposed RC beams. Magazine of Concrete Research 62(7):479–488, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.2010.62.7.479
Liu CW, Liu CF, Xu WL, Zhang XB, Lan Y (2018) A fractal-interpolation model for diagnosing spalling risk in concrete at elevated temperatures. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 22(12): 5154–5163, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-0697-z
Lu LM, Yong YC, Robby TL (2015) Influencing factors for fire performance of simply supported RC beams with implicit and explicit transient creep strain material models. Fire Safety 73:29–36, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2015.02.009
Miao JJ, Chen N, Hou XY (2013) Experimental study and numerical analysis on fire damage of reinforced concrete beams under the coupling of damage and high temperature. Journal of Building Structures 34(3):1–11, DOI: https://doi.org/10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2013.03.001 (in Chinese)
Reddy DV, Sobhan K, Liu L,Young JDJ (2015) Size effect on fire resistance of structural concrete. Engineering Structures 99:468–478, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.05.015
Song Y, Fu CG, Liang ST, Li D, Dang LJ, Sun CF, Kong WY (2020) Residual shear capacity of reinforced concrete beams after fire exposure. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(11):3330–3341, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1758-7
Thongchom C, Lenwari A, Aboutaha RS (2019) Effect of sustained service loading on post-fire flexural response of reinforced concrete T-beams. ACI Structural Journal 116(3):243–254, DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/51714477
Xu YY, Wu B, Jiang M, Huang X (2012) Experimental study on residual flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beams after exposure to fire. Advanced Materials Research 457–458:183–187, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.457-458.183
Yu B, Kodur VKR (2014) Fire behavior of concrete T-beams strengthened with near-surface mounted FRP reinforcement. Engineering Structures 80:350–361, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.09.003
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51608289, 51708319); Postdoctoral Innovation Project in Shan dong Province (2019057); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018M632640); Qingdao Postdoctoral Applied Research Project (Grant No. 2018103) and First-Class Discipline Project Funded by the Education Department of Shandong Province. The financial support is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Lu, X., Ba, G. et al. Influence of Loading Conditions on the Residual Flexural Capacity of Reinforced Concrete T-beams after Fire Exposure. KSCE J Civ Eng 25, 4710–4723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1924-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1924-6