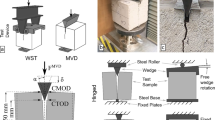
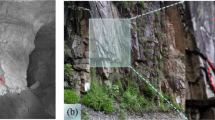
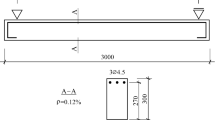
Abstract
In this paper, three-point bending tests were carried out o investigate the post-peak cyclic loading behavior of dam concrete under two loading rates. The fracture parameters, residual load capacity, cyclic modulus, dissipated energy, and deformation recovery were presented and analyzed. The analysis was made to understand the evolution of fracture process zone (FPZ) under post-peak cyclic loading for dam concrete by utilizing digital image correlation (DIC) technique. The results showed while the dam concrete under a higher loading rate showed an increase in maximum load, it is not necessarily the same for post-peak bearing capacity. The specimens with higher post-peak bearing capacity had higher residual stiffness, higher dissipation energy, and higher Crack Mouth Opening Displacement (CMOD) reversibility under cyclic loading. The FPZ development was investigated quantitatively, and the extension and retraction of its tip were observed. Moreover, it was found that the FPZ in specimens with higher residual stiffness developed more slowly, and FPZ had a more significant retraction rate during unloading for the specimens with higher residual bearing capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Crack length
- a 0 :
-
Initial crack length
- a c :
-
Critical crack length
- CMOD 0 :
-
CMOD at the reloading beginning
- CMOD c :
-
CMOD at the maximum load
- CMOD max :
-
CMOD at the peak load
- CMOD residual :
-
CMOD at the end of unloading
- E 0 :
-
Tangent modulus at the beginning
- E l :
-
Secant modulus of the loading process
- E l,50 :
-
Tangent modulus at 50% loading stage
- E unl :
-
Secant modulus of the unloading process
- E unl,50 :
-
Tangent modulus at 50% unloading stage
- exx :
-
Horizontal strain
- h :
-
The height of the beam
- K ini :
-
Initial fracture toughness
- K un :
-
Critical fracture toughness
- P u :
-
The maximum load
- S :
-
The span of the beam
- T :
-
Strain threshold
- t :
-
The thickness of the beam
- W i :
-
The dissipated energy of the i-th loading cycle
- α :
-
Crack height ratio
- β :
-
Span-height ratio
References
Ardito R, Maier G, Massalongo G (2008) Diagnostic analysis of concrete dams based on seasonal hydrostatic loading. Engineering Structures 30(11):3176–3185, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.04.008
ASTM C33 (2003) Standard specifications for concrete aggregates. ASTM C33, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Bažant ZP, Gettu R (1992) Rate effects and load relaxation in static fracture of concrete. ACI Materials Journal 89(5):456–468
Bhattacharjee SS, Leger P (1993) Seismic cracking and energy dissipation in concrete gravity dams. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 22(11):991–1007, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.4290221106
Bhowmik S, Ray S (2019) An experimental approach for characterization of fracture process zone in concrete. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 211:401–419, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.02.026
Cedolin L, Dei Poli S, Iori I (1983) Experimental determination of the fracture process zone in concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 13(4):557–567, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(83)90015-7
Choi S, Shah SP (1997) Measurement of deformations on concrete subjected to compression using image correlation. Experimental Mechanics 37(3):307–313, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02317423
De Sortis A, Paoliani P (2007) Statistical analysis and structural identification in concrete dam monitoring. Engineering Structures 29(1):110–120, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2006.04.022
Deng Z, Li Q, Fu H (2008) Comparison between mechanical properties of dam and sieved concretes. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 20(4):321–326, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2008)20:4(321)
Elices M, Rocco CG (2008) Effect of aggregate size on the fracture and mechanical properties of a simple concrete. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 75(13):3839–3851, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2008.02.011
Fedele R, Maier G, Miller B (2005) Identification of elastic stiffness and local stresses in concrete dams by in situ tests and neural networks. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering 1(3):165–180, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15732470500030513
Ghrib F, Tinawi R (1995) An application of damage mechanics for seismic analysis of concrete gravity dams. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 24(2):157–173, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.4290240203
Ghuzlan KA, Carpenter SH (2006) Fatigue damage analysis in asphalt concrete mixtures using the dissipated energy approach. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 33(7):890–901, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/106-032
Guinea GV, Pastor JY, Planas J, Elices M (1998) Stress intensity factor, compliance and CMOD for a general three-point-bend beam. International Journal of Fracture 89(2):103–116, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007498132504
Guo Y, Chen X, Li X, Li S, Guo S (2019) Experimental study on fracture behavior of three-graded concrete under cyclic loading after initial static loading. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 103:102272, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102272
Hu X, Duan K (2004) Influence of fracture process zone height on fracture energy of concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 34(8):1321–1330, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.12.027
Hu XZ, Wittmann FH (1992) Fracture energy and fracture process zone. Materials and Structures 25(6):319–326, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472590
Leger P, Venturelli J, Bhattacharjee SS (1993) Seasonal temperature and stress distributions in concrete gravity dams, Part 1: Modeling. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 20(6):999–1017, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/193-131
Li ST, Chen X, Feng L, Zhang X, Fan X, Lu J (2019a) Experimental study on concrete fracture process zone using digital image correlation technique. Journal of Testing and Evaluation 49(2), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1520/JTE20180863
Li X, Chen X, Jivkov AP, Zhang J (2019b) 3D mesoscale modeling and fracture property study of rubberized self-compacting concrete based on uniaxial tension test. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 104:102363, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102363
Li Q, Deng Z, Fu H (2004) Effect of aggregate type on mechanical behavior of dam concrete. ACI Materials Journal 101(6):483–492
Li ST, Fan XQ, Chen XD, Liu SS, Guo YZ (2020) Development of fracture process zone in full-graded dam concrete under three-point bending by DIC and acoustic emission. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 230:106972, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.106972
Mata J (2011) Interpretation of concrete dam behaviour with artificial neural network and multiple linear regression models. Engineering Structures 33(3):903–910, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.12.011
Miao S, Pan PZ, Yu P, Zhao S, Shao C (2020) Fracture analysis of Beishan granite after high-temperature treatment using digital image correlation. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 225:106847, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106847
Mihashi H, Nomura N, Niiseki S (1991) Influence of aggregate size on fracture process zone of concrete detected with three dimensional acoustic emission technique. Cement and Concrete Research 31:737–744, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(91)90168-H
Nomura N, Mihashi H, Izumi M (1991) Correlation of fracture process zone and tension softening behavior in concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 21(4):545–550, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(91)90104-P
Poissant J, Barthelat F (2010) A novel “subset splitting” procedure for digital image correlation on discontinuous displacement fields. Experimental Mechanics 50(3):353–364, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9220-2
Reinhardt HW, Cornelissen HAW (1984) Post-peak cyclic behaviour of concrete in uniaxial tensile and alternating tensile and compressive loading. Cement and Concrete Research 14(2):263–270, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(84)90113-3
Ren Q, Xu L, Wan Y (2007) Research advance in safety analysis methods for high concrete dam. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences 50(1):62–78, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-007-6008-4
Safavizadeh SA, Kim YR (2017) DIC technique to investigate crack propagation in grid-reinforced asphalt specimens. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 29(6):04017011
Saouma VE, Broz JJ, Brühwiler E, Boggs HL (1991) Effect of aggregate and specimen size on fracture properties of dam concrete. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 3(3):204–218, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(1991)3:3(204)
Shah SP (1990) Determination of fracture parameters (\(\rm{K}_{\rm{lc}}^{\rm{s}}\) and CTODc) of plain concrete using three-point bend tests. Materials and Structures 23(6):457–460, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472029
Skarżyński Ł, Tejchman J (2013) Experimental investigations of fracture process using DIC in plain and reinforced concrete beams under bending. Strain 49(6):521–543
Song J, Gu C, Su H, Gu H, Huang X (2016) Observed displacement data-based identification method of structural damage in concrete dam. Engineering Failure Analysis 66:202–211, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.04.013
Sutton MA, Turner JL, Bruck HA, Chao TA (1991) Full-field representation of discretely sampled surface deformation for displacement and strain analysis. Experimental Mechanics 31:168–177, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02327571
Swartz SE, Go CG (1984) Validity of compliance calibration to cracked concrete beams in bending. Experimental Mechanics 24(2):129–134, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02324995
Tatin M, Briffaut M, Dufour F, Simon A, Fabre JP (2015) Thermal displacements of concrete dams: Accounting for water temperature in statistical models. Engineering Structures 91:26–39, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15732470500030513
Tong W (1997) Detection of plastic deformation patterns in a binary aluminum alloy. Experimental Mechanics 37(4):452–459, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02317313
Wang CC, Deng JM, Ateshian GA, Hung CT (2002) An automated approach for direct measurement of two-dimensional strain distributions within articular cartilage under unconfined compression. Journal of Bimechanical Engineering 124(5):557–567, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1503795
Wecharatana M, Shah SP (1983) Predictions of non-linear fracture process zone in concrete. Journal of Engineering Mechanics 109(5):1231–1246, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1983)109:5(1231)
World Commission on Dams (2000) Dams and development: A new framework for decision-making. Earthscan, London, UK, 75–293
Wu K, Chen B, Yao W (2001) Study of the influence of aggregate size distribution on mechanical properties of concrete by acoustic emission technique. Cement and Concrete Research 31:919–923, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00504-X
Wu Z, Rong H, Zheng J, Xu F, Dong W (2011) An experimental investigation on the FPZ properties in concrete using digital image correlation technique. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 78(17):2978–2990, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2011.08.016
Xu S, Reinhardt HW (1999) Determination of double-K criterion for crack propagation in quasi-brittle materials, Part II: Analytical evaluating and practical measuring methods for three-point bending notched beams. International Journal of Fracture 98(2):151–177, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018740728458
Zhang XX, Ruiz G, Yu RC, Tarifa M (2009) Fracture behaviour of high-strength concrete at a wide range of loading rates. International Journal of Impact Engineering 36(10–11):1204–1209, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.04.007
Acknowledgments
The research is based upon the work supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Excellent Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20190075); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51979090); Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by China Association for Science and Technology (Grant No. 2017QNRC00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Li, S. & Cheng, X. Experimental Study of Evolution of Fracture Process Zone in Dam Concrete under Cyclic Loading Using Digital Image Correlation. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 727–740 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1835-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1835-6