Abstract
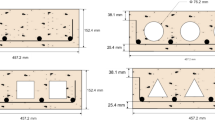
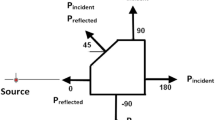
The super speed tube transport (SSTT) system is considered as a strong candidate for next-generation long-distance transport systems because of its anticipated highly efficient performance. Several studies have been conducted on infrastructure systems using concrete to improve the construction and economic feasibility of SSTTs. However, most of these only focused on the applicability of concrete in maintaining its airtightness; the effects of concrete cracks on the airtightness performance have not been investigated. Accordingly, this paper proposes a method using the finite element analysis (FEA) for evaluating the structural damage associated with the airtightness performance of concrete tube structures. An experimental work was conducted to measure this performance by subjecting a concrete tube structure to four stages of displacements at the midspan. Thereafter, to analytically measure the structural damage, the FEA was conducted and the results were compared with the experimental values. It is found that the structural damage expressed in terms of the eroded volume fraction (VF) calculated at each stage is closely correlated with the corresponding airtightness performance obtained from the experiment. These results show that FEA can be efficiently used for conducting experiments in the SSTT design phase to verify the concrete tube’s airtightness performance under many load cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 April 2021
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-6007-1
28 April 2021
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-6007-1
Abbreviations
- A, B, C, and D for Eqs. (8) and (9):
-
Parameters that set the shape of the softening curve
- A f :
-
Area of flow
- B c :
-
Average measured crack length
- C 1 :
-
A constant determined by the initial condition inside the tube
- d :
-
Damage parameter
- d max :
-
Maximum damage level
- E :
-
Elastic modulus
- h :
-
Thickness of structure
- k c :
-
Wall roughness coefficient
- k e :
-
Equivalent air permeability of the system
- k i :
-
Intrinsic permeability of material
- L :
-
Wall thickness
- n :
-
Flow coefficient
- N :
-
Number of cracks
- P 1 :
-
Inflow pressure
- P 2 :
-
Outflow pressure
- P s :
-
Standard atmospheric pressure (101.3 kPa)
- Q :
-
Total flow rate
- R :
-
Gas constant
- r 0b :
-
Initial threshold for brittle damage
- r 0d :
-
Initial threshold for ductile damage
- t :
-
Time immediately after the pump is stopped upon reaching the target internal pressure
- T :
-
Absolute temperature
- t pr :
-
Time required to reach the target internal air pressure
- V :
-
Volume inside the tube structure
- VF :
-
Volume fraction
- W avg :
-
Average crack width (in ft)
- ε max :
-
Maximum principal strain
- ε i j :
-
Total strain
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- σ d :
-
Stress tensor with damage
- σ vp :
-
Viscoplastic stress tensor
References
Devkota P, Park J (2019) Analytical model for air flow into cracked concrete structures for super-speed tube transport systems. Infrastructures 4(4):1–13, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures4040076
Devkota P, Park J, Choi E (2018) Effect of cracks on air-tightness of vacuum tube bridge structures. Proceedings of ninth international conference on bridge maintenance, safety and management (IABMAS), July 9–13, Melbourne, Australia
Ellingwood BR (2001) Earthquake risk assessment of building structures. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 74(3):251–262, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0951-8320(01)00105-3
Frosch RJ (1999) Another look at cracking and crack control in reinforced concrete. ACI Structural Journal 96(3):437–442, DOI: https://doi.org/10.14359/679
Frosch RJ (2001) Flexural crack control in reinforced concrete, design and construction practices to mitigate cracking SP 204. American Concrete Institute, Farmington Hills, MI, USA
Hallquist JO (2006) LS-DYNA, Theory manual. Livermore Software Technology Corporation, Livermore, CA, USA
Jang HW, Hahm D, Jung J-W, Hong J-W (2018) Effective numerical approach to assess low-cycle fatigue behavior of pipe elbows. Nuclear Engineering and Technology 50(5):758–766, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2018.01.020
KCI (2012) Concrete structure standard. Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Sejong, Korea
Luccioni BM, Aráoz GF, Labanda NA (2013) Defining erosion limit for concrete. International Journal of Protective Structures 4(3):315–340, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1260/2041-4196.4.3.315
Nam SW (2010) Parametric study on the capacity of vacuum pump for tube structure. Journal of the Korean Society for Railway 13(5):516–520
Park C-H, Cheon D-S, Park J (2015) Analytical model of fluid flow through closed structures for vacuum tube systems. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2015(210727):1–6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/210727
Park, J, Kim L-H, Nam S-W, Yeo I (2013) Performance evaluation of airtightness in concrete tube structures for super-speed train systems. Magazine of Concrete Research 65(9):535–545, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.12.00161
Park C-H, Synn J-H, Park J (2016) Probabilistic performance assessment of airtightness in concrete tube structures. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 20(5):1443–1451, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0735-z
Rizkalla SH, Lau BL, Simmonds SH (1984) Air leakage characteristics in reinforced concrete. Journal of Structural Engineering 110(5): 1149–1162, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1984)110:5(1149)
Soppe TE, Hutchinson TC (2012) Assessment of gas leakage rates through damaged reinforced-concrete walls. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 24(5):560–567, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000409
Yvonne DM (2007) User’s manual for LS-DYNA concrete material model 159. No. FHWA-HRT-05-062, U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Washington DC, USA
Yvonne DM, Akram A-O, Roger B (2007) Evaluation of LS-DYNA concrete material model 159. U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Washington DC, USA
Ziari A, Kianoush MR (2009) Investigation of flexural cracking and leakage in RC liquid containing structures. Engineering Structures 31(5):1056–1067, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.12.019
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Wonkwang University in 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devkota, P., Jang, H.W., Hong, JW. et al. Finite Element Analysis-Based Damage Metric for Airtightness Performance Evaluation of Concrete Tube Structures. KSCE J Civ Eng 25, 1385–1398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1007-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-1007-8